Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at the Current Global Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at the Current Global Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at the Current Global Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at the Current Global Map

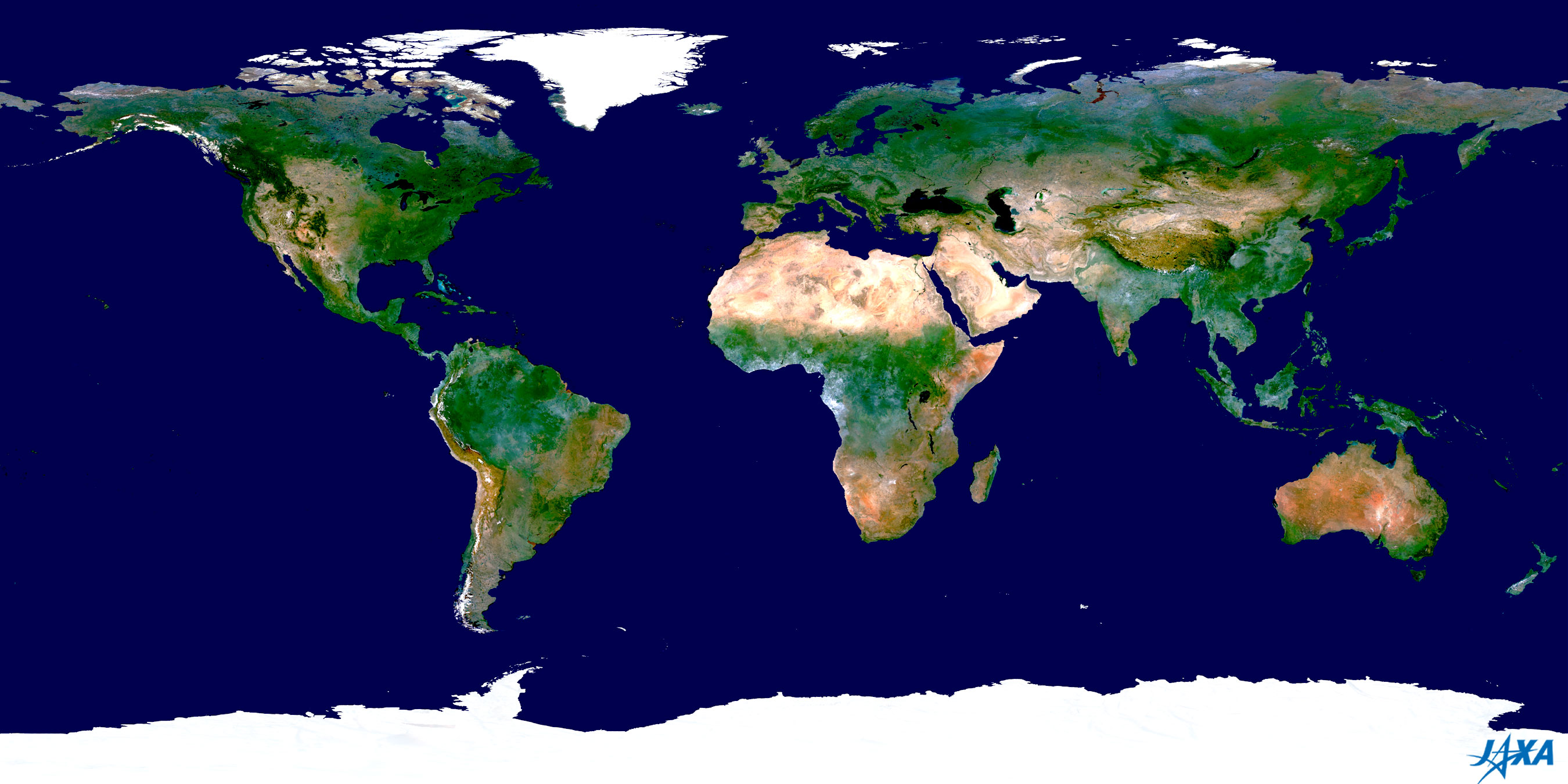
The Earth’s surface, a dynamic and intricate tapestry of landforms, oceans, and human settlements, is constantly evolving. Understanding this ever-changing landscape is crucial for various disciplines, from environmental science to urban planning and disaster preparedness. This article delves into the current global map, examining its components, its significance in diverse fields, and the various ways it aids our comprehension of the planet.
The Building Blocks of the Global Map:
The current global map, a composite representation of the Earth’s surface, is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources. This data encompasses various aspects, including:
- Topographical Features: Elevations, depressions, mountains, valleys, and other landforms are meticulously mapped using satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground surveys. This data provides a detailed understanding of the Earth’s physical structure.
- Hydrological Features: Rivers, lakes, oceans, and other water bodies are meticulously mapped, highlighting their geographical distribution, flow patterns, and depth. This information is vital for understanding water resources, navigation, and climate patterns.
- Political Boundaries: National borders, state lines, and administrative divisions are delineated on the map, providing a clear visual representation of political organization. This information is essential for understanding geopolitical dynamics, economic relationships, and international cooperation.
- Urban and Rural Areas: Cities, towns, and rural settlements are marked on the map, showcasing the spatial distribution of human populations. This data is crucial for urban planning, infrastructure development, and resource allocation.
- Vegetation and Land Cover: Forests, grasslands, deserts, and other vegetation types are mapped, providing insights into biodiversity, ecosystem health, and land use patterns. This information is vital for environmental conservation, resource management, and climate modeling.
The Importance of the Global Map:
The current global map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s surface, providing insights into its intricate systems and facilitating informed decision-making in various fields. Some key applications include:
- Navigation and Transportation: The map is indispensable for navigation, guiding ships, airplanes, and vehicles across land and water. It facilitates efficient transportation networks, connecting people and resources across vast distances.
- Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of natural resources, such as minerals, water, and forests, is crucial for sustainable resource management. The map provides a visual framework for planning resource extraction, conservation, and allocation.
- Environmental Monitoring: The map serves as a vital tool for monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, desertification, and sea-level rise. This data is essential for developing strategies to mitigate environmental damage and promote sustainable practices.
- Disaster Preparedness and Response: The map plays a critical role in disaster preparedness and response, providing information on vulnerable areas, potential hazards, and evacuation routes. This data helps minimize damage and ensure efficient rescue operations.
- Urban Planning and Development: The map aids urban planners in understanding the spatial distribution of populations, infrastructure, and resources. This information is crucial for developing sustainable cities, optimizing transportation networks, and managing urban growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Global Map:
-
What is the difference between a physical map and a political map?
- A physical map focuses on the Earth’s natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and oceans. In contrast, a political map emphasizes human-made boundaries, such as countries, states, and cities.
-
How is the global map updated?
- The global map is constantly updated with new data from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, ground surveys, and government agencies.
-
What are some of the challenges in creating an accurate global map?
- Challenges include the vastness of the Earth’s surface, the constantly changing landscape, and the need to integrate data from multiple sources.
-
How is the global map used in everyday life?
- The global map is used in countless ways, from navigating to a new destination to understanding weather patterns and planning travel routes.
Tips for Using the Global Map Effectively:
- Choose the right map for your needs: Different maps are designed for different purposes. Consider the specific information you need and select the map that best meets your requirements.
- Understand the map’s scale: The scale of a map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Choose a map with a scale that is appropriate for your needs.
- Use map symbols and legends: Map symbols and legends provide information about the features represented on the map. Take the time to familiarize yourself with these symbols and their meanings.
- Consider using online mapping tools: Online mapping tools offer a wide range of interactive features, including zooming, panning, and layering different data sets.
Conclusion:
The current global map, a dynamic and multifaceted representation of the Earth’s surface, is a powerful tool for understanding our planet and guiding our actions. It provides a framework for navigating, managing resources, monitoring the environment, and responding to disasters. As technology advances and data collection methods improve, the global map will continue to evolve, offering increasingly comprehensive and insightful representations of the Earth’s ever-changing landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Look at the Current Global Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!