Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics
Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics
- 3.1 The Earth’s Shifting Crust: A Visual Representation
- 3.2 The Importance of Plate Tectonics Maps: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s Dynamics
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions About Plate Tectonics Maps
- 3.4 Tips for Utilizing Plate Tectonics Maps
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Window into Earth’s Evolutionary Journey
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics
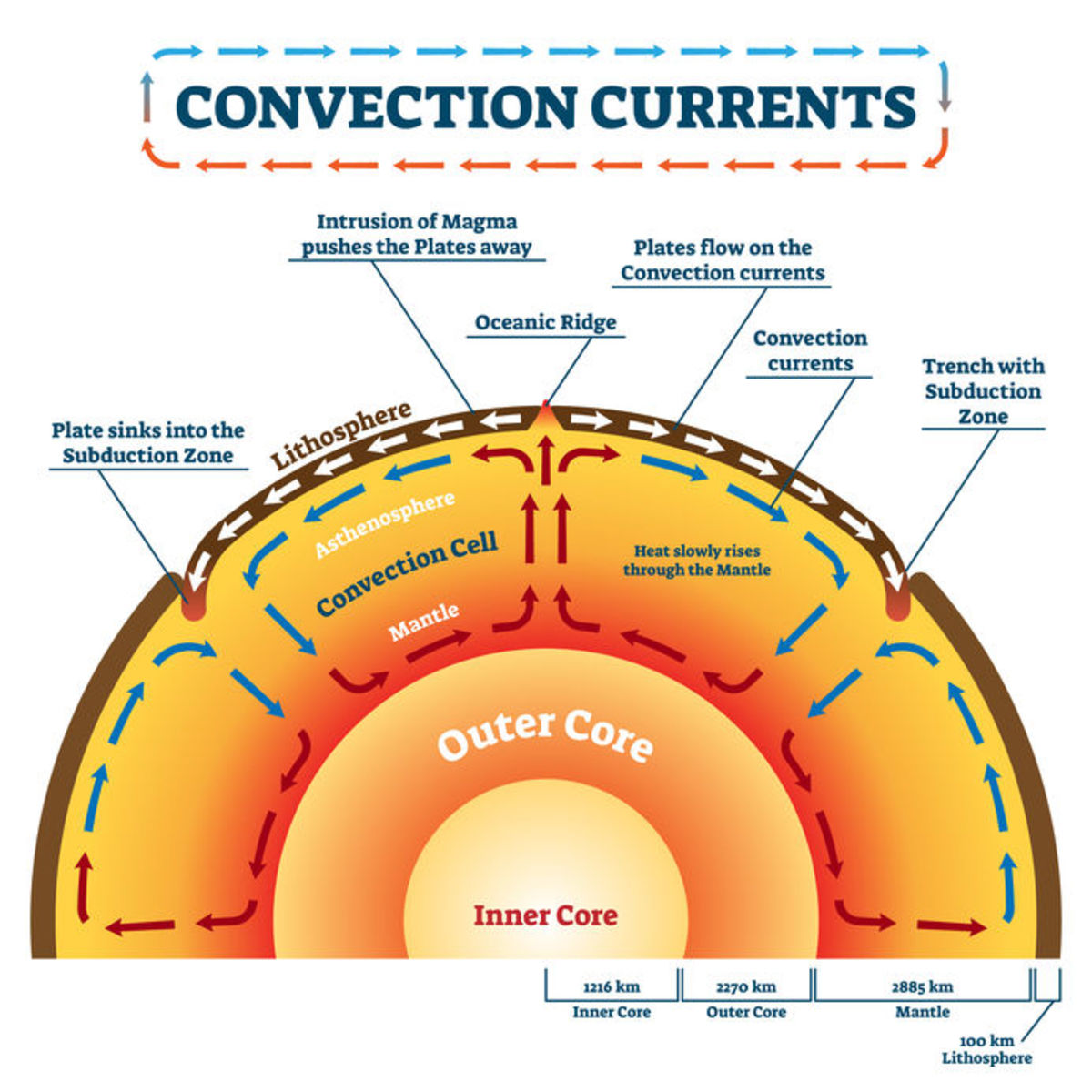
The Earth’s surface is not a static, unchanging entity. It is a dynamic mosaic of massive, moving plates, constantly interacting and reshaping the planet’s landscape. These plates, known as tectonic plates, are the building blocks of our planet’s geology, driving processes that shape mountains, create volcanoes, and trigger earthquakes. Understanding the intricate dance of these plates is fundamental to comprehending the Earth’s past, present, and future.
The Earth’s Shifting Crust: A Visual Representation
A plate tectonics map provides a visual representation of these colossal plates and their interactions. This map, often referred to as a tectonic map, is a powerful tool for scientists and researchers, offering insights into the Earth’s internal structure and the forces that drive its evolution.
Key Elements of a Plate Tectonics Map:
- Plate Boundaries: The map clearly defines the boundaries between these tectonic plates, highlighting areas of intense geological activity.
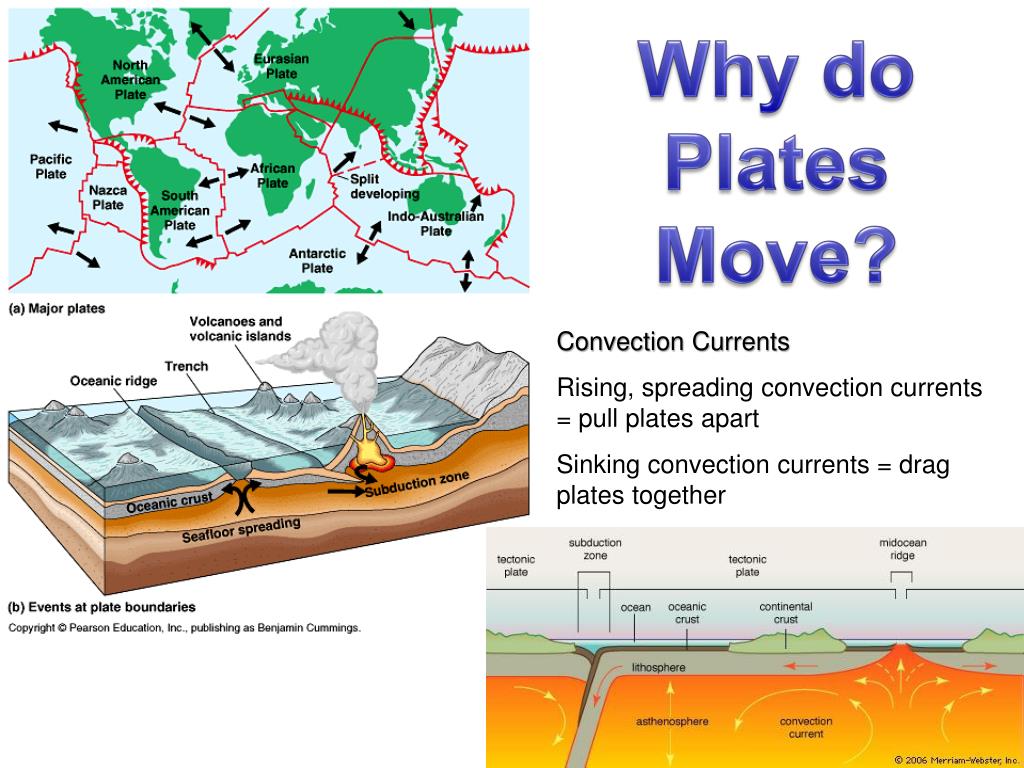
- Plate Motion: Arrows indicate the direction and relative speed of plate movement, revealing the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust.
- Geological Features: The map often incorporates information about major geological features such as mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquake zones, directly linked to plate interactions.
- Plate Types: Different types of plates are distinguished, including oceanic plates, continental plates, and mixed plates, each with unique characteristics and behaviors.
Dissecting the Map:
A closer examination of a plate tectonics map reveals a fascinating world of geological processes:
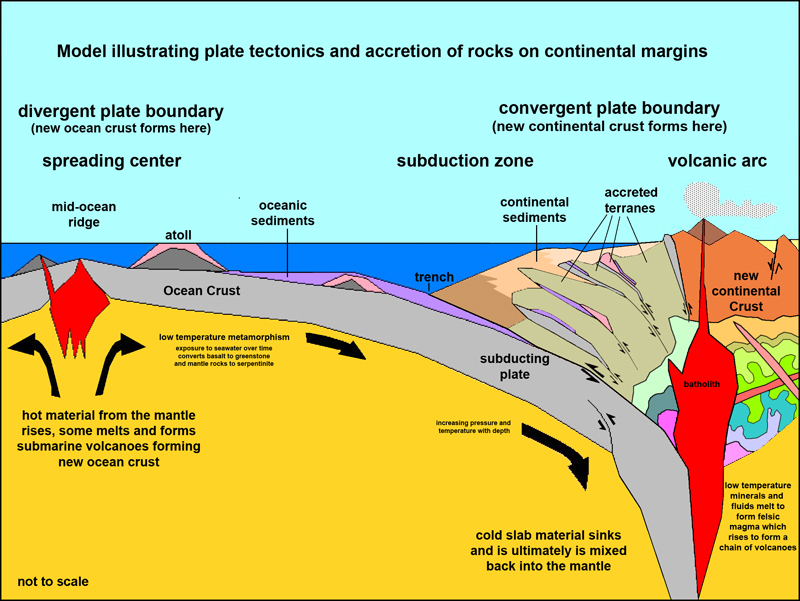
- Divergent Boundaries: These boundaries mark areas where plates move apart, allowing magma from the Earth’s mantle to rise and create new crust. This process, known as seafloor spreading, is responsible for the formation of mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys.
- Convergent Boundaries: Here, plates collide, resulting in a dramatic interplay of forces. The denser plate subducts beneath the lighter plate, leading to the formation of volcanic arcs, deep ocean trenches, and mountain ranges.
- Transform Boundaries: At these boundaries, plates slide horizontally past each other, creating friction and generating earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault in California is a prime example of a transform boundary.
The Importance of Plate Tectonics Maps: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s Dynamics
Plate tectonics maps serve as invaluable tools for various scientific disciplines:
- Geophysics: Understanding the movement and interaction of tectonic plates provides crucial insights into the Earth’s internal structure, composition, and dynamics.
- Geology: Plate tectonics maps are essential for studying the formation of geological features, predicting earthquake occurrences, and understanding the distribution of natural resources.
- Volcanology: The map highlights areas prone to volcanic eruptions, aiding in hazard assessment and risk mitigation.
- Seismology: By identifying active fault lines, the map helps scientists predict earthquake activity and develop strategies for earthquake preparedness.
- Earth Sciences Education: Plate tectonics maps are instrumental in teaching and visualizing the complex processes that shape our planet, fostering a deeper understanding of Earth’s dynamic nature.
Frequently Asked Questions About Plate Tectonics Maps
Q: How are plate tectonics maps created?
A: Plate tectonics maps are created using various techniques, including:
- Satellite imagery: Satellites provide data on surface features, allowing scientists to map plate boundaries and measure plate motion.
- GPS data: Global Positioning System (GPS) data provides precise measurements of plate movement, aiding in the construction of accurate maps.
- Seismic data: Analyzing seismic waves generated by earthquakes helps scientists determine the location and depth of plate boundaries.
- Magnetic data: Variations in the Earth’s magnetic field provide clues about the age and movement of oceanic plates.
Q: How often are plate tectonics maps updated?
A: Plate tectonics maps are continuously updated as new data becomes available, reflecting the ongoing dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. Technological advancements in data acquisition and analysis lead to more precise and detailed maps.
Q: What are the limitations of plate tectonics maps?
A: While plate tectonics maps offer valuable insights, they have limitations:
- Simplification: Maps often simplify complex geological processes, potentially overlooking nuanced interactions between plates.
- Scale: Plate tectonics maps are often presented at a global scale, limiting the detail of regional geological features.
- Data limitations: The accuracy of maps depends on the availability and quality of data, which can be limited in certain regions.
Tips for Utilizing Plate Tectonics Maps
- Understanding Plate Types: Familiarize yourself with the different types of plates (oceanic, continental, and mixed) and their characteristics.
- Identifying Boundaries: Recognize the different types of plate boundaries (divergent, convergent, and transform) and their associated geological features.
- Interpreting Plate Motion: Pay attention to the arrows indicating plate movement and their relative speeds.
- Relating Features to Plate Interactions: Connect the location of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquake zones to the types of plate boundaries.
Conclusion: A Window into Earth’s Evolutionary Journey
Plate tectonics maps are essential tools for understanding the Earth’s dynamic history and predicting future geological events. By visualizing the movement and interaction of tectonic plates, these maps provide a gateway to unlocking the secrets of our planet’s evolution, allowing us to appreciate the intricate forces that have shaped the world we inhabit. As our understanding of plate tectonics continues to evolve, so too will the accuracy and detail of these maps, offering a deeper and more comprehensive view of Earth’s dynamic landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Earth’s Dynamic Landscape: A Journey Through Plate Tectonics. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!