Unraveling the Threads of History: A Journey Through the Silk Road in China
Related Articles: Unraveling the Threads of History: A Journey Through the Silk Road in China
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Threads of History: A Journey Through the Silk Road in China. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Threads of History: A Journey Through the Silk Road in China

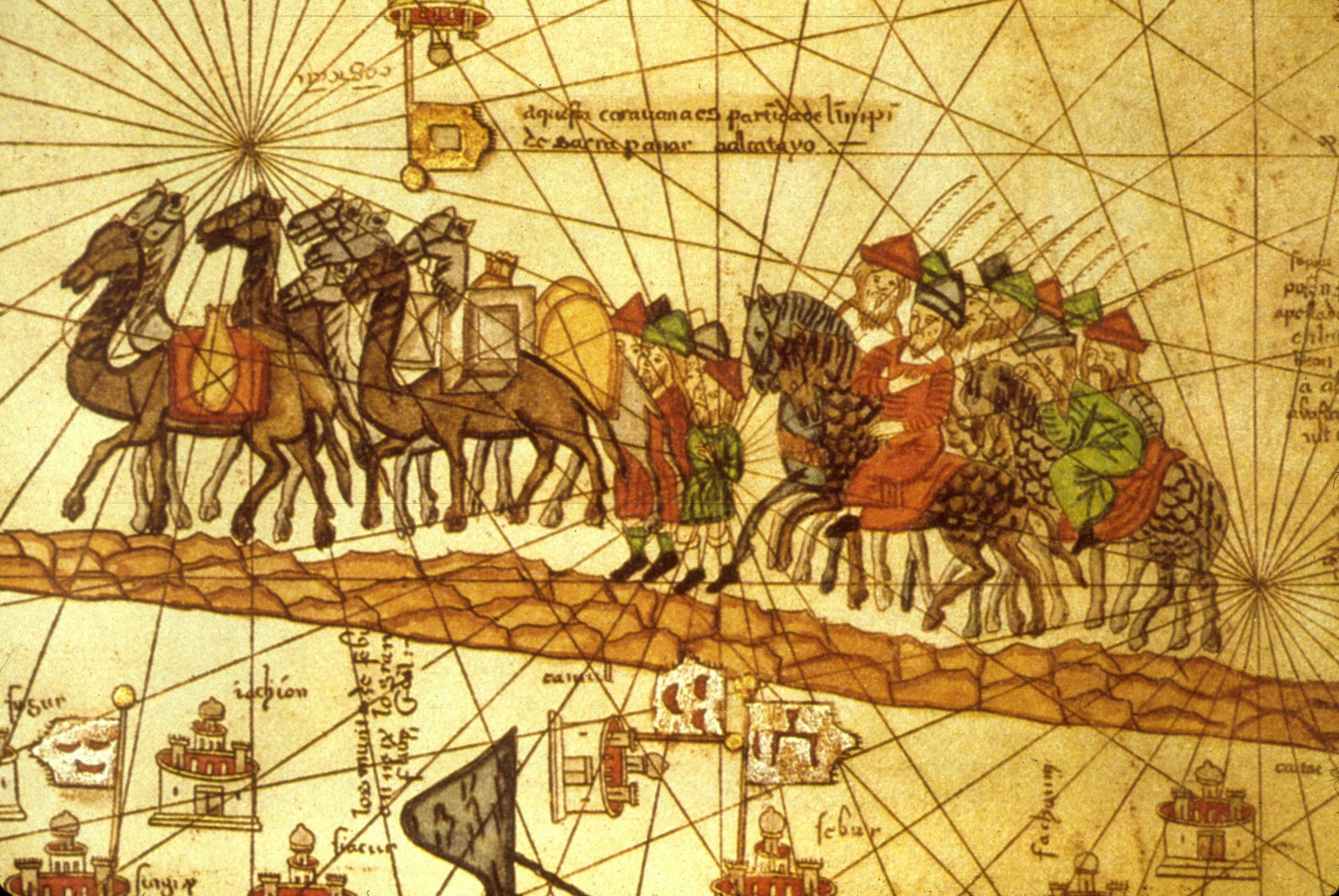
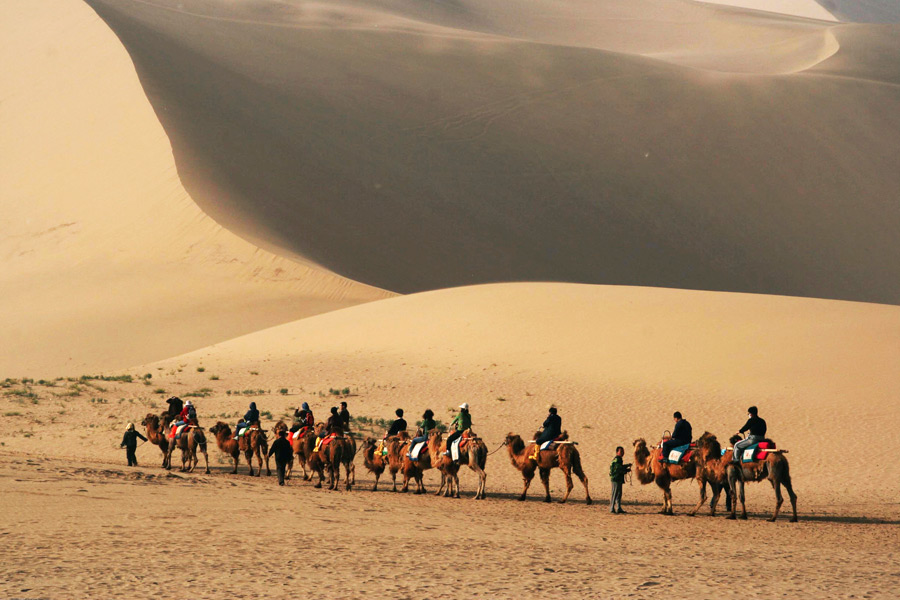
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes that spanned millennia and continents, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of humanity. While the term "Silk Road" often evokes images of camels laden with silk traversing vast deserts, the network encompassed far more than just silk and camels. It was a vibrant artery of cultural exchange, fostering the transmission of ideas, religions, technologies, and artistic influences between East and West. This article delves into the Silk Road’s impact on China, exploring its historical significance, geographical scope, and enduring legacy.
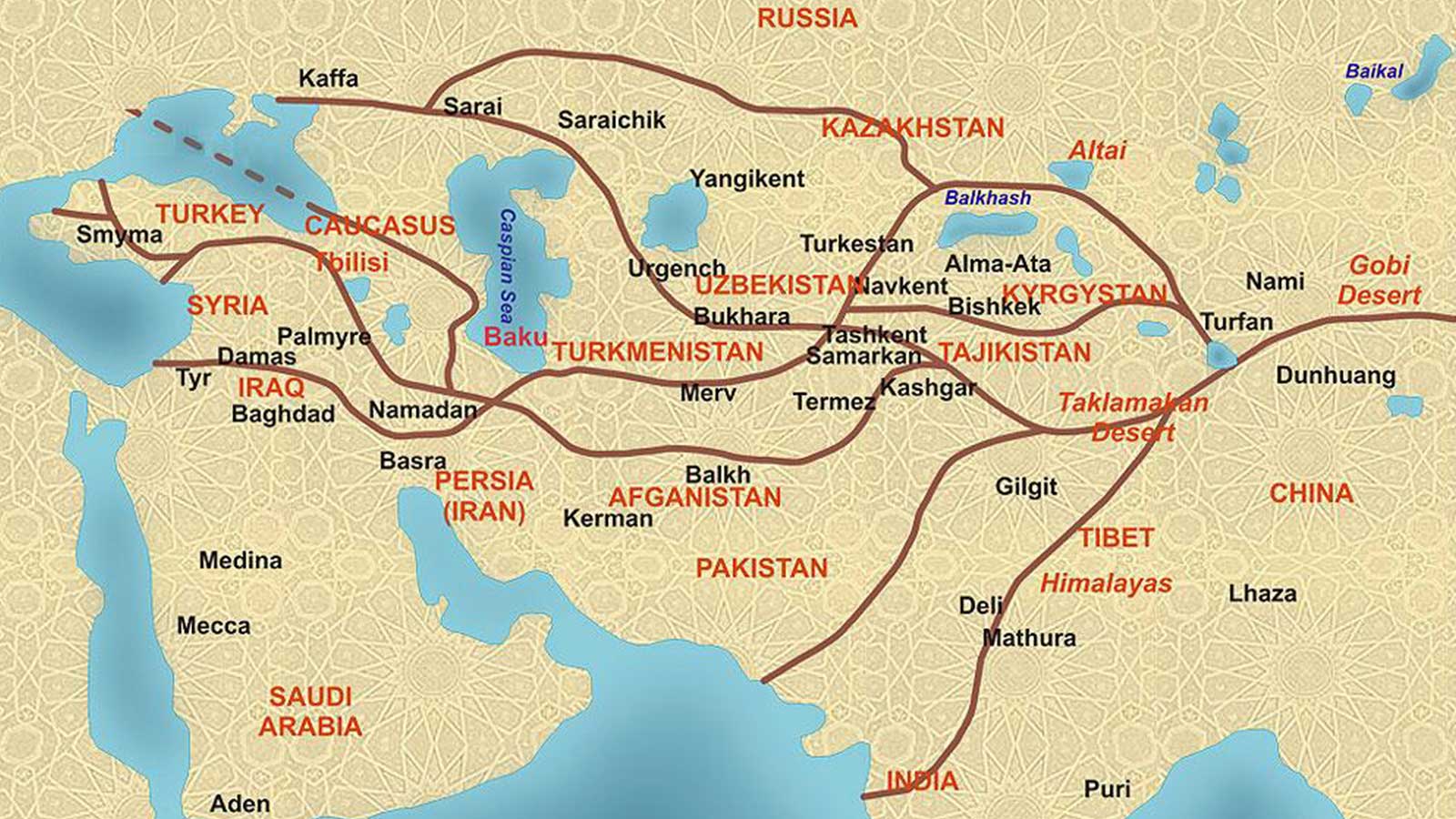
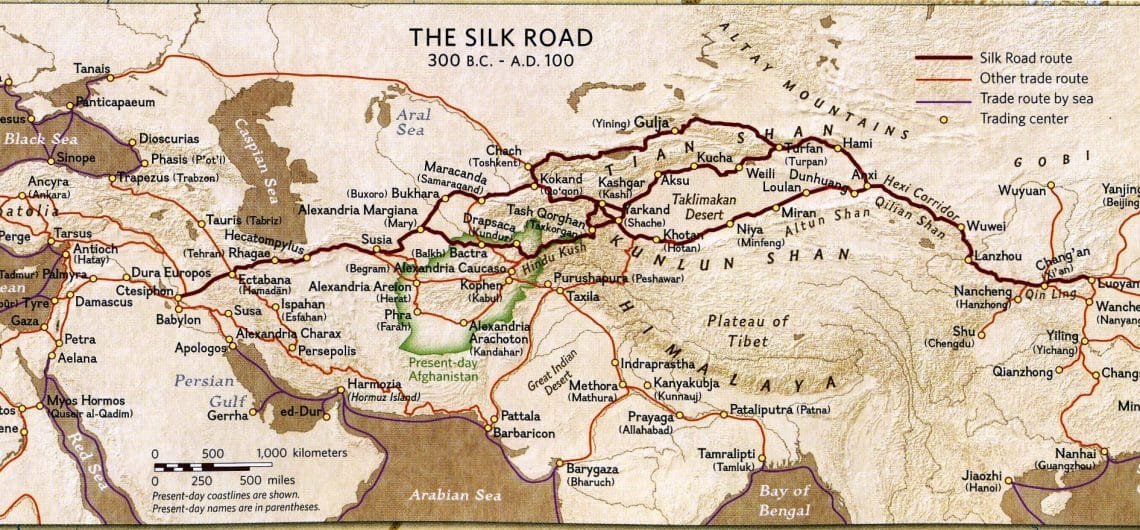
Mapping the Silk Road in China
The Silk Road, as a single, continuous route, is a myth. It was, in reality, a complex web of interconnected paths that evolved over centuries. In China, the Silk Road’s starting point was Xi’an, the ancient capital of the Han Dynasty, located in the heart of the modern Shaanxi province. From there, it branched out in multiple directions, traversing diverse landscapes and cultures.
The Northern Silk Road: This route, also known as the "Land Route," snaked through the Gobi Desert, crossing the towering Tian Shan mountains and the vast plains of Central Asia. It eventually connected to the Mediterranean world via the Middle East and Europe. This route was crucial for the trade of silk, porcelain, tea, and other Chinese goods in exchange for spices, textiles, and precious metals from the West.
The Southern Silk Road: This route, often referred to as the "Sea Route," utilized the waterways of the South China Sea, connecting China to Southeast Asia, India, and beyond. It facilitated the trade of silk, spices, and other commodities, fostering maritime exchange and cultural interaction.
Historical Significance
The Silk Road played a pivotal role in shaping Chinese history and culture. It facilitated economic growth, fostered cultural exchange, and influenced the development of Chinese art, literature, and technology.
-
Economic Prosperity: The Silk Road facilitated the flourishing of trade, bringing immense wealth to China. The demand for Chinese silk, porcelain, and other goods spurred economic growth and urbanization, leading to the development of thriving cities like Xi’an, Dunhuang, and Guangzhou.
-
Cultural Diffusion: The Silk Road served as a conduit for the exchange of ideas, religions, and artistic influences. Buddhism, originating in India, spread to China along the Silk Road, profoundly impacting Chinese philosophy, art, and architecture. The transmission of technologies, such as papermaking, gunpowder, and printing, also contributed to cultural development.
-
Political Influence: The Silk Road fostered diplomatic relations between China and other civilizations. The Han Dynasty established diplomatic missions along the route, promoting peace and trade. It also facilitated the spread of Chinese political and administrative systems to neighboring regions.
The Enduring Legacy
The Silk Road’s influence extends far beyond its historical significance. Its legacy continues to resonate in modern China and the world.
-
Cultural Heritage: The Silk Road has left an indelible mark on Chinese culture, evident in its art, architecture, literature, and cuisine. The Silk Road cities, with their ancient temples, bustling markets, and cultural landmarks, serve as reminders of the vibrant past.
-
Modern Trade Routes: The concept of the Silk Road has inspired modern economic initiatives, such as the "One Belt One Road" (OBOR) initiative, which aims to revitalize trade and infrastructure development along ancient Silk Road routes.
-
Tourism and Cultural Exchange: The Silk Road has become a popular destination for tourists, offering a unique glimpse into China’s rich history and cultural heritage. It also promotes intercultural understanding and exchange, fostering collaboration and cooperation between nations.
FAQs About the Silk Road in China
1. What were the main goods traded along the Silk Road?
Silk, porcelain, tea, spices, textiles, precious metals, and other luxury goods were traded along the Silk Road.
2. What were the main challenges faced by travelers on the Silk Road?
Travelers faced challenges such as bandits, harsh weather conditions, difficult terrain, and disease outbreaks.
3. How did the Silk Road influence Chinese art and architecture?
The Silk Road introduced new artistic styles and techniques, leading to the development of unique architectural styles, such as the Mogao Caves in Dunhuang, which feature elaborate Buddhist murals and sculptures.
4. What was the role of the Silk Road in the spread of Buddhism to China?
Buddhism, originating in India, spread to China along the Silk Road, where it was embraced by many and became one of the major religions in the country.
5. What is the significance of the Silk Road in modern China?
The Silk Road continues to be a source of inspiration for modern China, fostering cultural exchange, promoting tourism, and driving economic development through initiatives like the OBOR.
Tips for Exploring the Silk Road in China
-
Research and Plan: Thoroughly research the Silk Road route, including its historical significance, cultural attractions, and practical considerations.
-
Embrace the Journey: The Silk Road is not just about reaching a destination but about the journey itself. Embrace the diverse landscapes, cultures, and experiences along the way.
-
Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions. Dress modestly, avoid loud behavior, and learn basic greetings in the local language.
-
Seek Local Guidance: Engage with local guides and tour operators to gain deeper insights into the history and culture of the region.
-
Capture the Memories: Document your journey through photography, journaling, or other forms of creative expression.
Conclusion
The Silk Road in China stands as a testament to the power of human connection and the enduring legacy of cultural exchange. It is a tapestry woven with threads of trade, diplomacy, and cultural diffusion, leaving an indelible mark on the history and culture of China and the world. The Silk Road continues to inspire, reminding us of the interconnectedness of humanity and the importance of fostering understanding and collaboration across borders. As we explore its ancient routes and marvel at its enduring legacy, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of history that binds us all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Threads of History: A Journey Through the Silk Road in China. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!