Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Pangea
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Pangea
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Pangea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Pangea

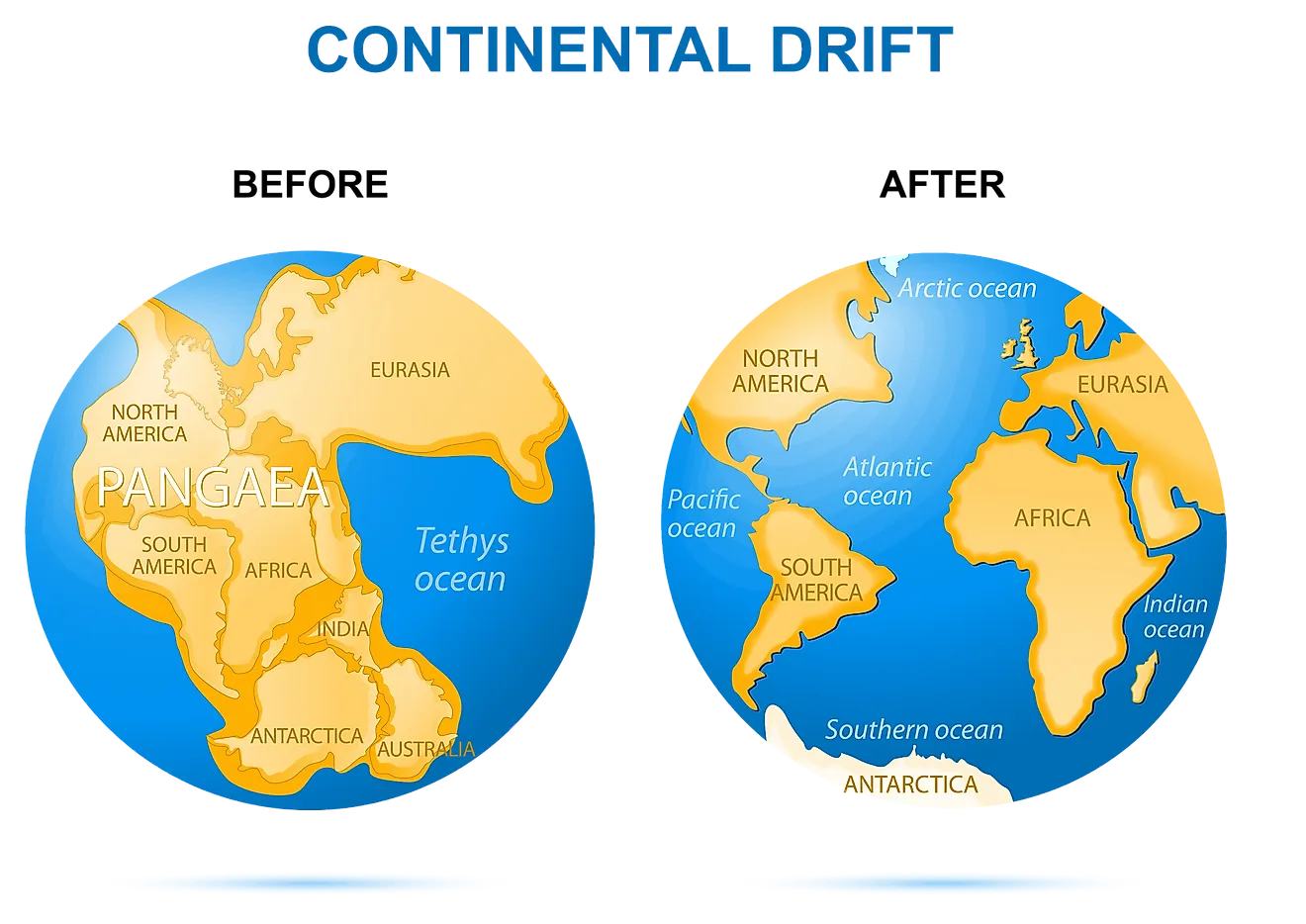
The Earth’s surface is a dynamic landscape, constantly reshaped by the relentless forces of plate tectonics. Millions of years ago, the continents we know today were once joined together in a supercontinent known as Pangea. This colossal landmass, spanning the globe, offers a fascinating glimpse into the Earth’s history and its profound influence on life and geological formations.
Pangea: A Supercontinent’s Genesis
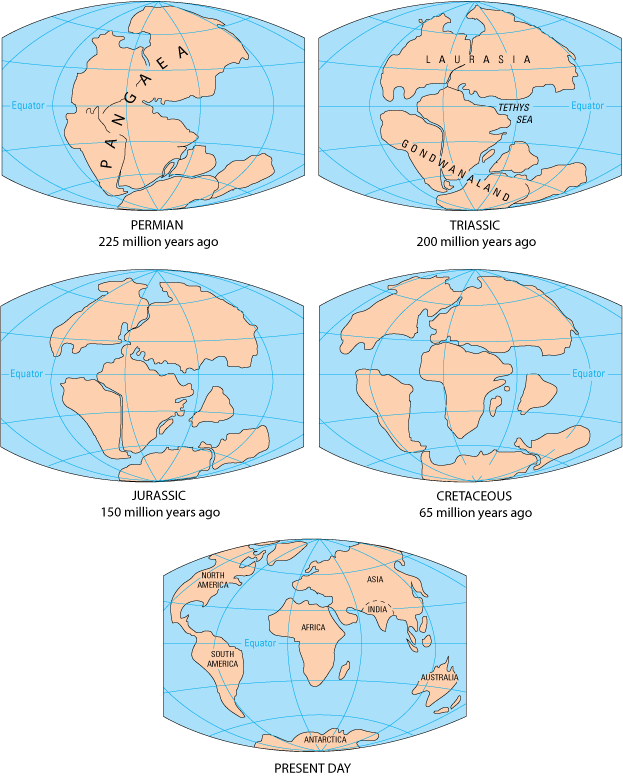
The formation of Pangea is a complex geological process spanning hundreds of millions of years. It began during the Paleozoic Era, approximately 335 million years ago, with the gradual convergence of smaller landmasses. These ancient continents, like Laurasia and Gondwana, drifted together, driven by the movement of tectonic plates.
By the late Permian period, around 250 million years ago, these landmasses had coalesced into a single, massive supercontinent. This colossal landmass, encompassing nearly all of Earth’s continental crust, was named Pangea, meaning "all Earth" in Greek.
A World Reshaped: The Geography of Pangea
Pangea’s geography was significantly different from the world we know today. The supercontinent was surrounded by a single vast ocean called Panthalassa, with a smaller inland sea known as the Tethys Sea. The interior of Pangea was characterized by vast deserts and arid plains, while the coastal regions were likely more humid and temperate.
The Breakup of Pangea: A New World Emerges
The existence of Pangea was not destined to last. Around 200 million years ago, during the Triassic period, the supercontinent began to break apart. This dramatic event, driven by the relentless forces of plate tectonics, gave rise to the modern continents and oceans.
The breakup of Pangea was a gradual process, with the continents drifting apart at a rate of a few centimeters per year. This slow but persistent movement eventually led to the formation of the Atlantic Ocean, separating North America from Europe and Africa. The Indian subcontinent, once part of Gondwana, drifted northward, eventually colliding with Asia, forming the Himalayas.
The Legacy of Pangea: Shaping Life and Landscapes
The existence and breakup of Pangea had profound consequences for life on Earth. The supercontinent’s vast size and diverse environments fostered the evolution of new species. The formation of Pangea also led to significant changes in global climate, with the interior experiencing extreme temperatures and arid conditions.
The breakup of Pangea further influenced the distribution of life on Earth. As the continents drifted apart, species became isolated, leading to the evolution of unique flora and fauna on each landmass. This process of continental drift and isolation is a key driver of biodiversity on Earth.
Understanding Pangea: A Window into the Earth’s History
The study of Pangea offers valuable insights into the Earth’s history and the dynamic processes that shape our planet. By reconstructing the supercontinent’s geography and understanding its breakup, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of:
- Plate tectonics: Studying the breakup of Pangea helps scientists understand the mechanisms behind plate movement and the forces that shape Earth’s surface.
- Geological formations: The formation and breakup of Pangea created vast mountain ranges, deep ocean trenches, and other geological features that continue to influence the Earth’s landscape.
- Climate change: The formation and breakup of Pangea had significant impacts on global climate, altering ocean currents, atmospheric circulation, and the distribution of landmasses.
- Evolution of life: The isolation of continents created distinct environments, promoting the evolution of unique species and shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions about Pangea
1. What evidence supports the existence of Pangea?
The existence of Pangea is supported by a wealth of geological and paleontological evidence. This includes:
- Matching coastlines: The coastlines of continents, particularly those across the Atlantic Ocean, show remarkable similarities, suggesting they were once joined.
- Fossil distribution: Identical fossils of ancient plants and animals have been found on continents now separated by vast oceans, indicating they were once connected.
- Rock formations: Similar rock formations and geological structures can be found on continents now separated, pointing to a shared geological history.
2. How long did Pangea exist?
Pangea existed for approximately 160 million years, from its formation around 335 million years ago to its breakup around 175 million years ago.
3. What caused the breakup of Pangea?
The breakup of Pangea was driven by the forces of plate tectonics. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle created stresses within the supercontinent, causing it to fracture and drift apart.
4. What were the consequences of Pangea’s breakup?
The breakup of Pangea had significant consequences for Earth’s geography, climate, and the evolution of life. It led to the formation of the Atlantic Ocean, changed global ocean currents, and facilitated the isolation and diversification of species.
5. Can we predict future supercontinents?
While the exact future of plate tectonics is uncertain, scientists predict that the continents will continue to move and potentially form new supercontinents in the future. However, these events are likely to occur over millions of years.
Tips for Understanding Pangea
- Visualize the supercontinent: Use maps and illustrations to visualize the arrangement of continents in Pangea.
- Explore paleontological evidence: Learn about the fossils that support the existence of Pangea and how they contribute to our understanding of the supercontinent.
- Understand plate tectonics: Familiarize yourself with the basic principles of plate tectonics to grasp the forces that shaped Pangea and its breakup.
- Connect with other geological events: Explore how the formation and breakup of Pangea relate to other significant geological events, such as the formation of mountain ranges and ocean basins.
Conclusion
Pangea, the ancient supercontinent, offers a captivating glimpse into the Earth’s dynamic history. Its formation and breakup reveal the power of plate tectonics and its profound influence on Earth’s geography, climate, and the evolution of life. By studying Pangea, we gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s ever-changing landscape and the interconnectedness of life on our planet. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of Earth’s past, Pangea serves as a reminder of the transformative power of geological forces and the enduring legacy of a supercontinent that once dominated the globe.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Pangea. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!