Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views
- 3.1 Understanding Earth Map Views
- 3.2 Common Earth Map Views and Their Characteristics
- 3.3 Applications of Earth Map Views
- 3.4 Importance and Benefits
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Using Earth Map Views Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views
The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and complex sphere, teeming with life and diverse landscapes. To comprehend its intricate geography, we rely on maps, which provide a visual representation of our world. Earth map views, in particular, play a crucial role in understanding the planet’s spatial relationships, facilitating navigation, and enabling informed decision-making.
Understanding Earth Map Views
Earth map views are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, projected onto a flat surface. This projection process involves transforming the Earth’s spherical shape into a two-dimensional plane, inevitably introducing distortions. Different map projections emphasize specific aspects of the Earth, leading to variations in shape, size, and relative positioning of geographic features.
Common Earth Map Views and Their Characteristics
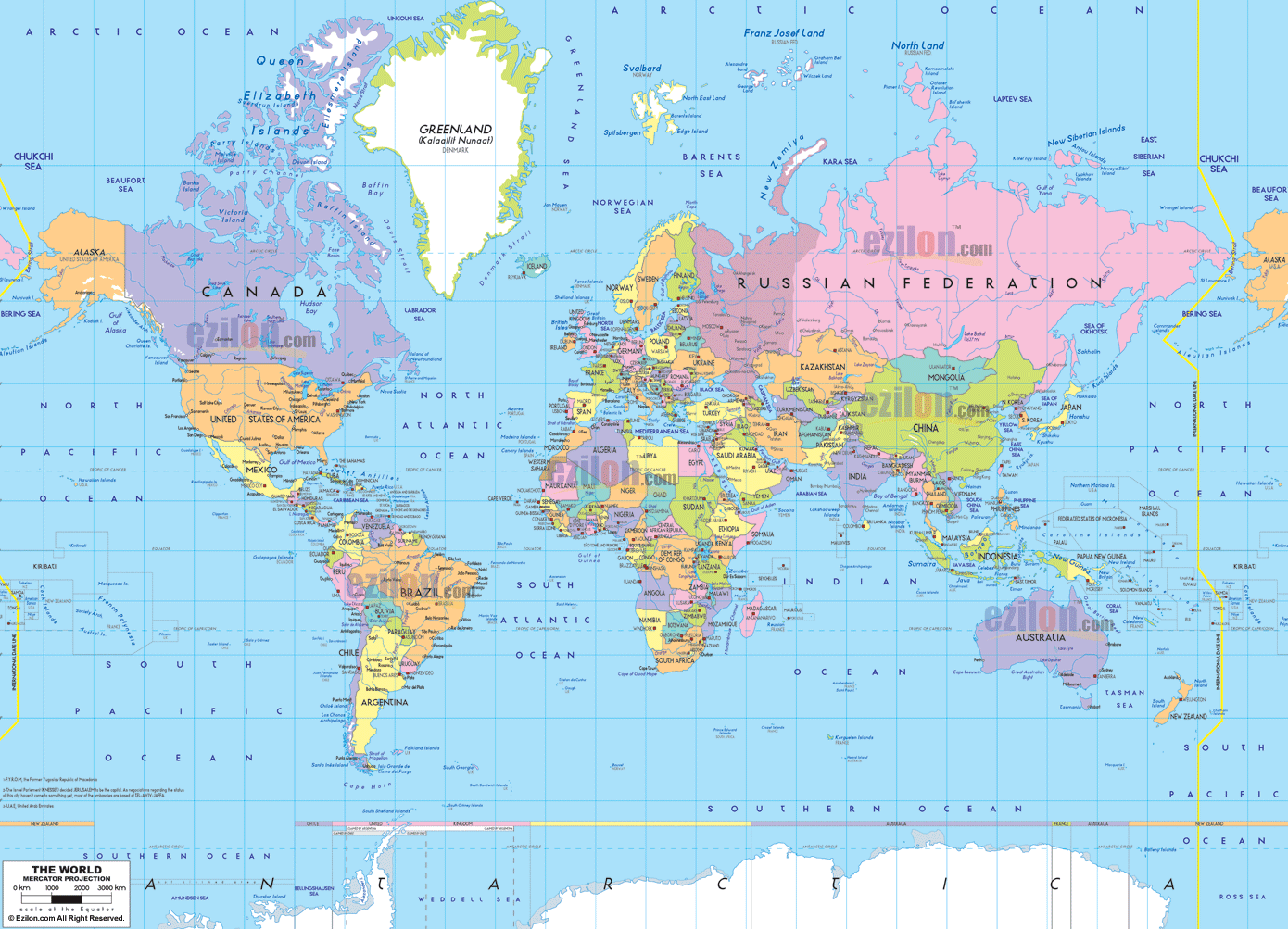
1. Mercator Projection:
- Distortion: Extreme distortion at the poles, with landmasses near the equator appearing larger than they are.
- Strengths: Preserves angles and shapes of small areas, making it ideal for navigation.
- Weaknesses: Distorts areas near the poles, making them appear much larger than they are in reality.
2. Robinson Projection:
- Distortion: Moderate distortion, with a balance between area and shape.
- Strengths: Offers a visually appealing and balanced representation of the Earth.
- Weaknesses: Doesn’t preserve angles or shapes accurately.
3. Winkel Tripel Projection:
- Distortion: Minimizes distortion in area, shape, and distance.
- Strengths: Provides a good compromise between various map properties.
- Weaknesses: Doesn’t excel in any one area, making it less suitable for specific applications.
4. Goode Homolosine Projection:
- Distortion: Utilizes an interrupted projection, dividing the Earth into continents for less distortion.
- Strengths: Preserves area accurately, making it ideal for representing global population distribution or resource allocation.
- Weaknesses: Distorts shapes and distances, making it less suitable for navigation.
5. Orthographic Projection:
- Distortion: Shows a hemisphere of the Earth as it would appear from space.
- Strengths: Provides a realistic view of the Earth, especially for satellite imagery.
- Weaknesses: Doesn’t show the entire Earth at once, and distances are distorted towards the edges.
6. Azimuthal Equidistant Projection:
- Distortion: Preserves distances from a central point.
- Strengths: Useful for mapping distances from a specific location.
- Weaknesses: Distorts shapes and areas away from the central point.
Applications of Earth Map Views
Earth map views are indispensable tools across various fields, including:
- Navigation: Mercator projections, with their preservation of angles, are widely used for navigation and cartography.
- Geography and Cartography: Different map projections allow cartographers to represent specific geographic features or phenomena accurately.
- Climate Science: Earth map views facilitate visualization of climate patterns, temperature anomalies, and global warming trends.
- Environmental Science: They help analyze environmental data, such as deforestation, pollution levels, and biodiversity distribution.
- Resource Management: Earth map views aid in managing resources, such as water, land, and minerals.
- Urban Planning: They assist in urban development, infrastructure planning, and resource allocation.
- Education: Earth map views provide a visual representation of the Earth, facilitating understanding of geography, history, and global relationships.
Importance and Benefits
Earth map views are essential for understanding the Earth’s complex geography and facilitating informed decision-making. They offer several key benefits:
- Visual Representation: They provide a visual representation of the Earth, making it easier to grasp its spatial relationships and geographic features.
- Data Visualization: Earth map views allow visualization of various data sets, enabling analysis and interpretation of patterns and trends.
- Decision Support: They provide critical information for informed decision-making in various fields, including navigation, resource management, and environmental protection.
- Education and Awareness: Earth map views promote understanding of the Earth’s interconnectedness and the importance of sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why are there different types of Earth map views?
A: Different map projections emphasize specific aspects of the Earth, such as area, shape, or distance. This leads to variations in distortion, making each projection suitable for different applications.
Q: Which Earth map view is the most accurate?
A: No single map projection is completely accurate. Each projection involves distortions, and the choice of projection depends on the specific application.
Q: How do I choose the right Earth map view for my needs?
A: Consider the purpose of the map, the geographic region being represented, and the specific aspects you want to emphasize.
Q: What are the limitations of Earth map views?
A: All map projections involve distortions, and they cannot accurately represent the Earth’s spherical shape on a flat surface.
Tips for Using Earth Map Views Effectively
- Understand the projection: Familiarize yourself with the type of projection used and its inherent distortions.
- Consider the purpose: Choose the projection that best suits your specific needs and the data you are representing.
- Use multiple perspectives: Compare different map views to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data.
- Analyze the distortions: Be aware of the distortions introduced by the projection and interpret the data accordingly.
- Consult reliable sources: Use maps from reputable sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Conclusion
Earth map views are fundamental tools for understanding our planet and its complexities. By accurately representing the Earth’s surface, they facilitate navigation, enable data visualization, and support informed decision-making across various disciplines. As technology continues to advance, Earth map views will continue to evolve, offering new perspectives and insights into our planet’s intricate geography.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth: A Comprehensive Look at Earth Map Views. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!