Unraveling the Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to the Back Muscles Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to the Back Muscles Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to the Back Muscles Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to the Back Muscles Map

The human back, a marvel of intricate anatomy, houses a complex network of muscles responsible for a wide range of movements, from simple posture maintenance to powerful athletic feats. Understanding the back muscles map, a visual representation of these muscles and their functions, is crucial for anyone seeking to optimize their physical health, enhance performance, or recover from injury.
A Deeper Dive into the Back Muscles Map:
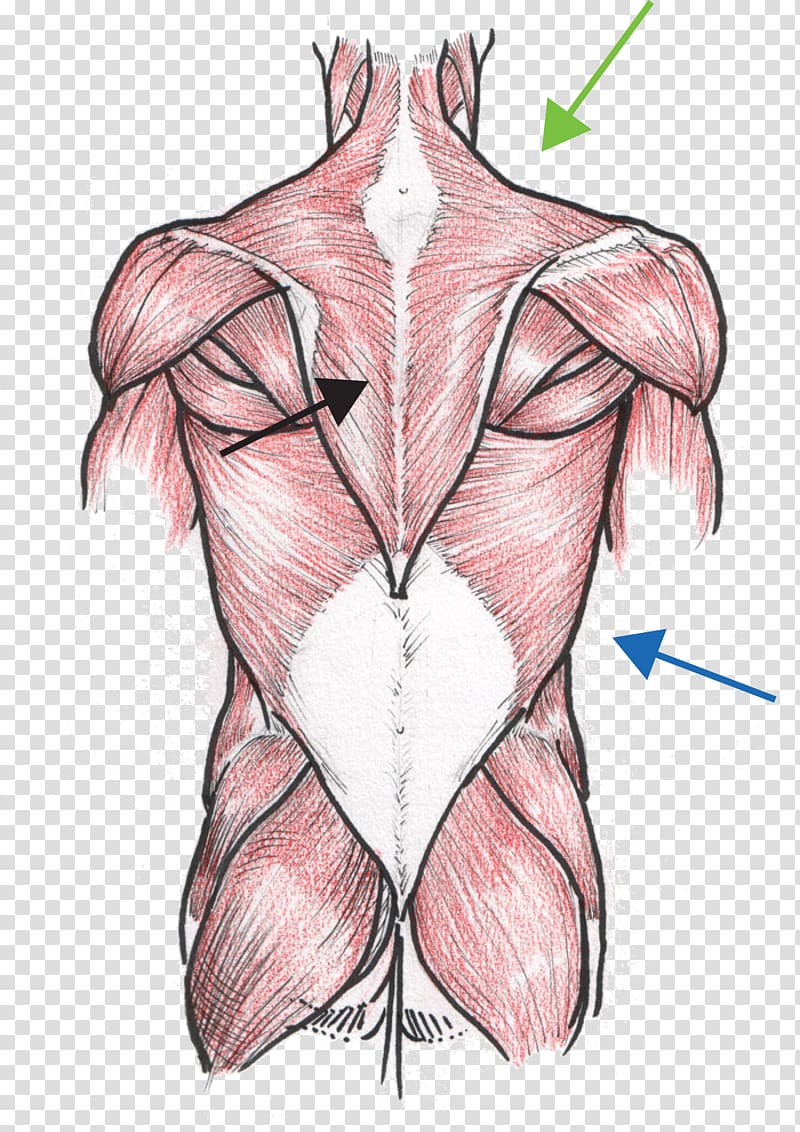
The back muscles map is a visual guide that dissects the intricate tapestry of muscles that make up the human back. It classifies these muscles into distinct groups based on their location, function, and anatomical connections.
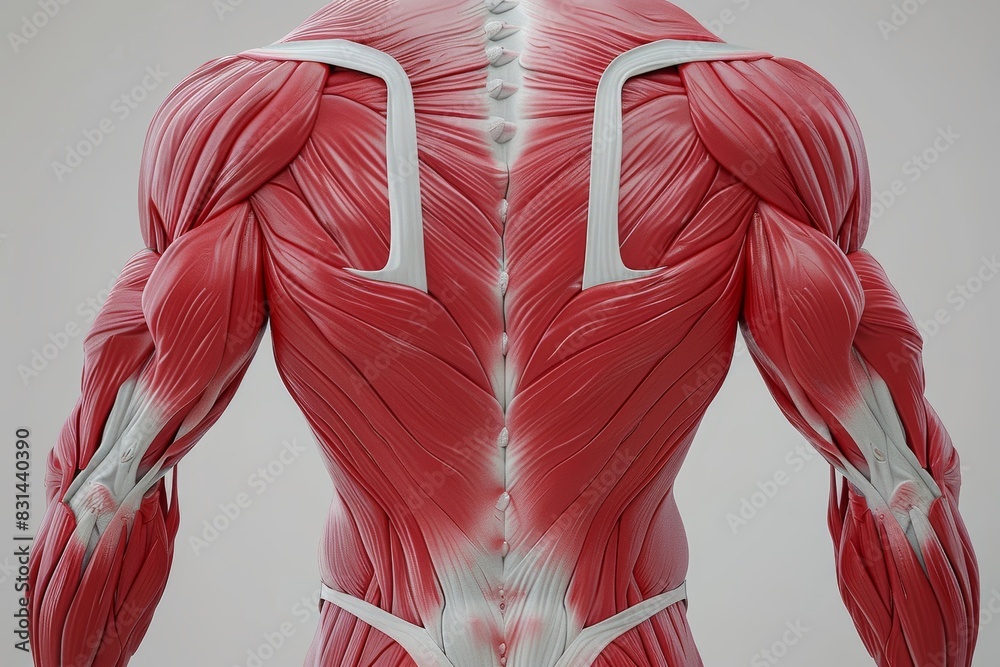
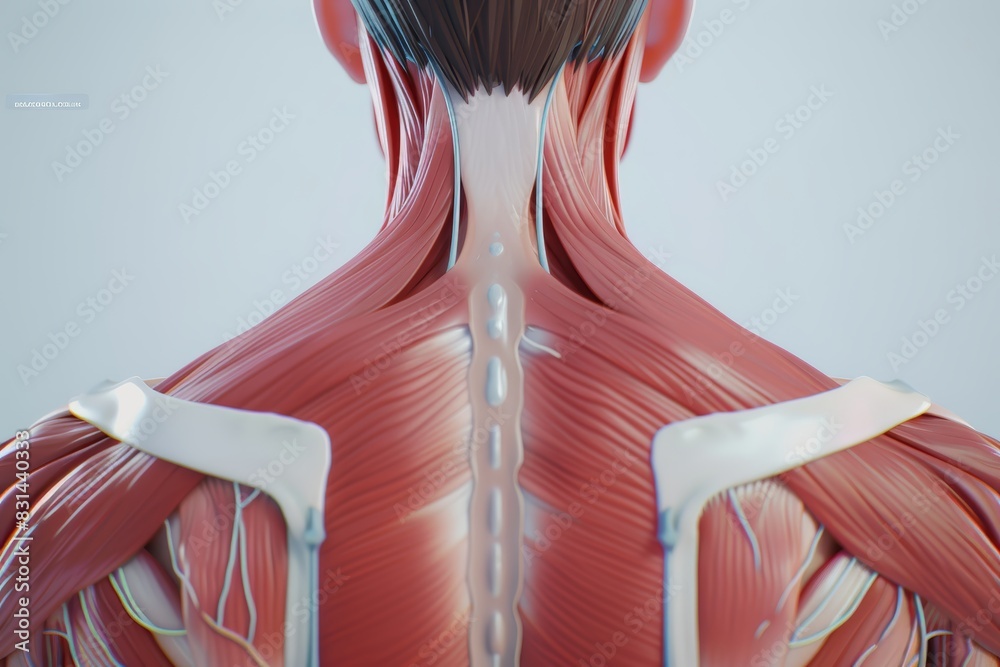
Superficial Back Muscles:
- Trapezius: This large, diamond-shaped muscle spans the upper back and neck. It plays a crucial role in shoulder elevation, retraction, and depression, as well as head rotation.
- Latissimus Dorsi: The largest muscle in the back, the latissimus dorsi originates from the lower vertebrae, pelvis, and ribs, extending to the humerus. It functions in shoulder extension, adduction, and internal rotation, contributing to powerful pulling movements.
- Rhomboid Major and Minor: Located beneath the trapezius, these muscles connect the scapula to the vertebrae. They are responsible for scapular retraction and downward rotation, promoting proper shoulder posture.
- Levator Scapulae: This muscle originates from the cervical vertebrae and inserts on the scapula. It elevates the scapula, assists in neck flexion, and contributes to head rotation.
Deep Back Muscles:
- Erector Spinae: This powerful muscle group runs along the entire length of the spine, spanning from the sacrum to the skull. It plays a vital role in maintaining upright posture, extending the spine, and providing trunk stability.
- Splenius Capitis and Cervicis: These muscles connect the cervical vertebrae to the skull and the thoracic vertebrae. They assist in head extension, rotation, and lateral flexion.
- Multifidus: This deep muscle group is located between the spinous processes of vertebrae. It provides segmental control and stability for the spine, contributing to posture and movement.
- Rotatores: These short muscles connect adjacent vertebrae, enabling fine-tuned rotation and stabilization of the spine.
Back Muscles and Their Functions:
Posture and Stability: Many back muscles work in concert to maintain proper posture and spinal stability. The erector spinae, multifidus, and rotatores provide structural support and control the spine’s movements, preventing excessive strain and injury.
Movement: The latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and other muscles facilitate a wide range of movements, including pulling, pushing, lifting, and rotating. They contribute to activities like swimming, rowing, and weightlifting.
Breathing: The back muscles, particularly the intercostal muscles between the ribs, play a vital role in respiration. They assist in expanding and contracting the chest cavity, enabling air intake and exhalation.
Injury and Rehabilitation:
Understanding the back muscles map is crucial for effectively treating and rehabilitating back injuries. Identifying the specific muscle(s) involved allows for targeted interventions, including stretching, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy.
Benefits of Knowing the Back Muscles Map:
- Improved Posture: By understanding the muscles responsible for posture, individuals can proactively engage them to maintain a healthy, balanced posture, reducing the risk of back pain and other musculoskeletal issues.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Knowledge of the back muscles map empowers athletes to optimize their training programs by targeting specific muscles for strength and flexibility, improving performance and reducing the risk of injury.
- Pain Management: By understanding the anatomy of the back, individuals can better identify the source of pain and take appropriate steps for relief, including stretching, strengthening exercises, and seeking professional medical advice.
- Increased Awareness: Familiarity with the back muscles map fosters a deeper understanding of the body’s intricate workings, promoting a more mindful approach to physical activity and overall health.
FAQs about the Back Muscles Map:
Q: What are the most common back muscle injuries?
A: Some common back muscle injuries include strains, sprains, and muscle spasms. These can be caused by overuse, sudden movements, poor posture, or underlying conditions.
Q: How can I prevent back pain?
A: Maintaining good posture, engaging in regular exercise, stretching, and avoiding overuse can help prevent back pain.
Q: What are some good exercises for strengthening the back muscles?
A: Some effective exercises include rows, pull-ups, deadlifts, planks, and back extensions. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified professional before starting any new exercise program.
Q: When should I see a doctor for back pain?
A: Seek medical attention if your back pain is severe, persistent, accompanied by numbness or weakness, or worsens with time.
Tips for Using the Back Muscles Map:
- Visualize the Muscles: Regularly study the back muscles map to familiarize yourself with the location and function of each muscle.
- Engage in Targeted Exercises: Incorporate exercises that specifically target different back muscles, promoting balanced strength and flexibility.
- Practice Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture throughout the day, consciously engaging the back muscles to maintain a healthy alignment.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a physical therapist or other qualified professional for personalized exercise recommendations and guidance on proper form.
Conclusion:
The back muscles map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the intricate anatomy of the back and its crucial role in maintaining posture, movement, and overall health. By delving into this visual representation, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay of muscles, enabling them to make informed decisions about their physical well-being, enhance athletic performance, and manage back pain effectively. It is a roadmap for optimizing back health and function, promoting a more active and fulfilling life.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to the Back Muscles Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!