Unlocking the Power of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Power of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software has revolutionized the way we understand and interact with the world around us. It empowers users to analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data, providing invaluable insights across diverse fields. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of GIS software, delving into its functionalities, benefits, and applications.
Understanding the Foundation: What is GIS Software?
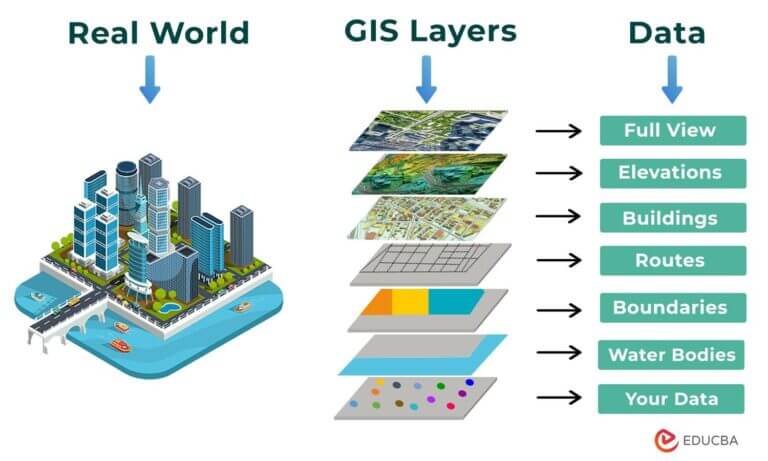
GIS software is a powerful tool that integrates various technologies to capture, store, analyze, manage, and display geographically referenced information. This information, often referred to as geospatial data, is linked to specific locations on Earth. GIS software effectively transforms raw data into actionable insights by leveraging spatial relationships and patterns.
Core Components of GIS Software:
-
Data Acquisition: GIS software facilitates the collection of spatial data from diverse sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, GPS devices, and digital maps. This data can be in various formats, such as raster (pixels) or vector (points, lines, and polygons).
-
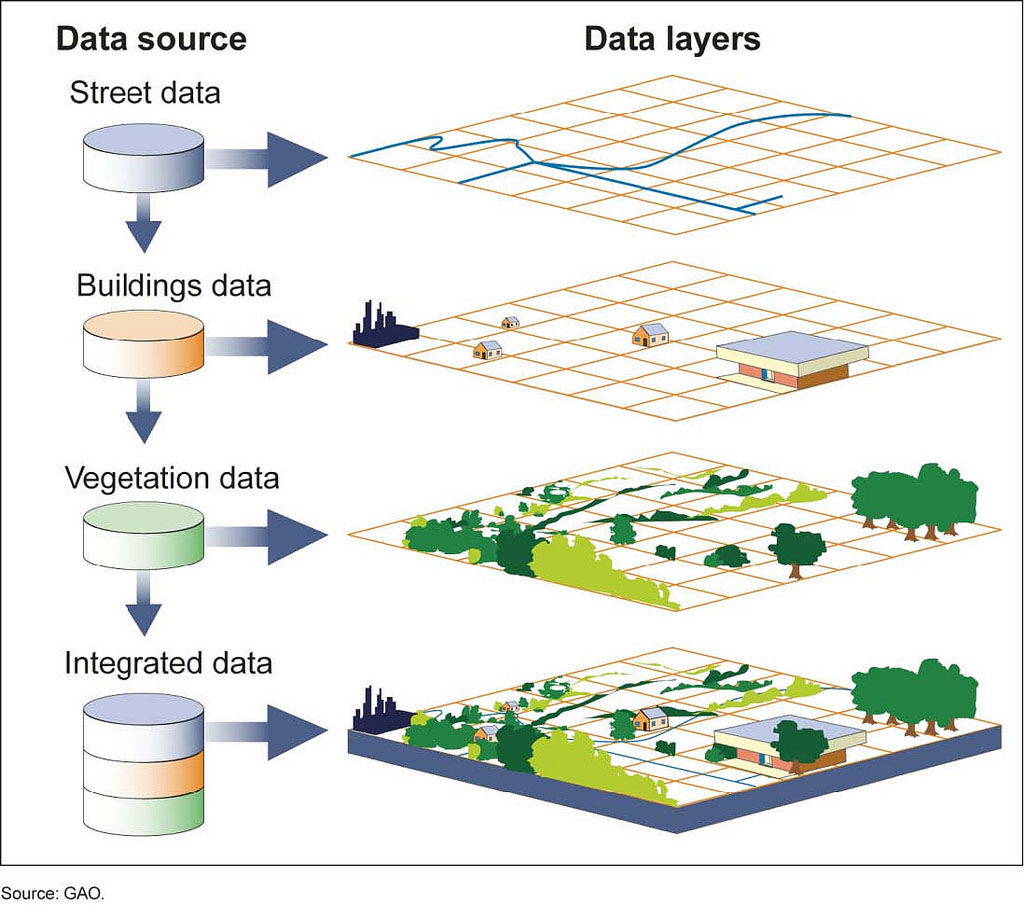
Data Management: Once acquired, GIS software efficiently organizes and manages spatial data, ensuring its accuracy, integrity, and accessibility. This involves defining data structures, establishing relationships between different data layers, and implementing robust storage systems.
-
Data Analysis: GIS software offers a wide array of analytical tools for exploring spatial relationships and patterns within data. This encompasses tasks like proximity analysis, overlay analysis, network analysis, and geostatistical analysis.
-
Visualization and Mapping: GIS software excels at creating visually compelling maps and presentations that communicate spatial information effectively. This involves selecting appropriate map projections, symbolizing data effectively, and designing interactive maps for user engagement.
Key Benefits of Utilizing GIS Software:
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: GIS software provides a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships, enabling informed decisions based on data-driven insights. This is particularly valuable in fields like urban planning, resource management, and disaster response.
-
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: GIS software streamlines workflows by automating repetitive tasks, such as data processing and map creation. This frees up valuable time for analysts to focus on higher-level tasks and strategic planning.
-
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: GIS software facilitates collaborative work by enabling data sharing and visualization across teams and stakeholders. This fosters transparency, promotes informed decision-making, and improves project outcomes.
-
Unveiling Hidden Patterns and Trends: GIS software’s analytical capabilities reveal spatial patterns and trends that might be obscured by traditional data analysis methods. This allows for a deeper understanding of complex phenomena, leading to more effective solutions.
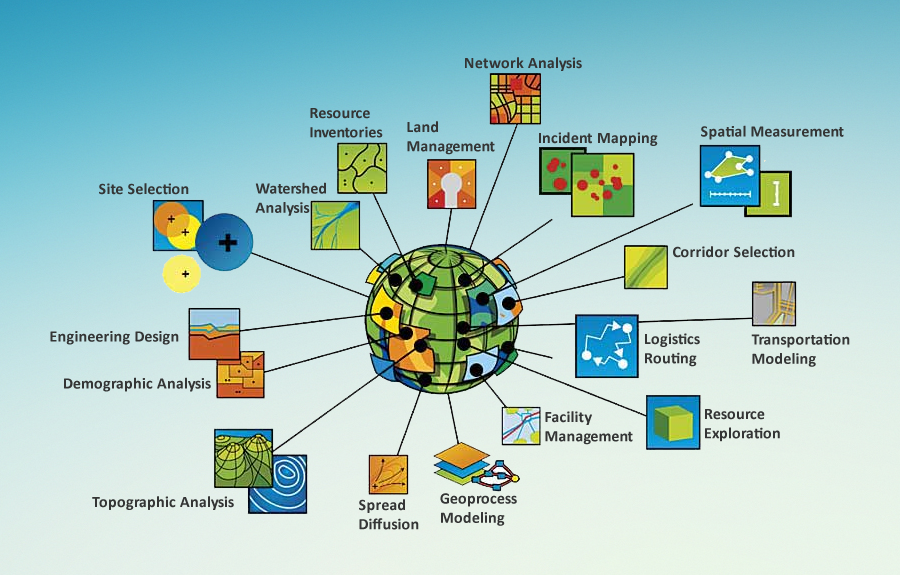
Diverse Applications of GIS Software:
GIS software finds applications across numerous sectors, empowering professionals to solve real-world problems. Here are a few examples:
-
Environmental Management: GIS software assists in monitoring environmental conditions, assessing pollution levels, managing protected areas, and mitigating natural disasters.
-
Urban Planning and Development: GIS software enables planners to analyze land use patterns, optimize infrastructure development, and create sustainable urban environments.
-
Transportation and Logistics: GIS software optimizes transportation routes, manages fleet operations, and facilitates efficient delivery networks.
-
Public Safety and Emergency Response: GIS software supports emergency response teams by providing real-time situational awareness, facilitating resource allocation, and coordinating rescue efforts.
-
Agriculture and Forestry: GIS software enables precision agriculture, optimizes resource allocation, and monitors forest health.
-
Health and Disease Management: GIS software helps track disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and implement targeted public health interventions.
-
Business and Marketing: GIS software aids in market analysis, site selection, customer segmentation, and targeted marketing campaigns.
FAQs about GIS Software:
Q: What are the different types of GIS software available?
A: There are various GIS software options available, catering to different needs and budgets. Some popular examples include:
- ArcGIS (Esri): A comprehensive and widely used professional-grade GIS software suite.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software, popular for its flexibility and community support.
- MapInfo Pro: A desktop GIS software known for its user-friendly interface and advanced analytical capabilities.
- Google Earth Pro: A powerful visualization tool that combines satellite imagery with GIS functionalities.
Q: How can I learn to use GIS software?
A: There are several avenues for learning GIS software:
- Online Courses: Numerous online platforms offer comprehensive GIS courses, ranging from introductory to advanced levels.
- University Programs: Many universities offer degrees and certificates in GIS, providing a thorough understanding of the field.
- Workshops and Training Sessions: GIS software vendors often conduct workshops and training sessions to introduce users to their products.
- Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including tutorials, documentation, and user forums, provide valuable learning materials.
Q: What are the essential skills needed for GIS work?
A: A successful GIS professional typically possesses the following skills:
- Strong Spatial Thinking: The ability to visualize and analyze spatial relationships is crucial.
- Data Analysis Skills: Expertise in data manipulation, analysis, and interpretation is essential.
- Mapping and Visualization Skills: The ability to create clear and effective maps and presentations is highly valuable.
- Technical Proficiency: Familiarity with GIS software, programming languages, and data management techniques is essential.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and solve spatial problems using GIS tools is vital.
Tips for Effective GIS Software Usage:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before embarking on any GIS project, clearly define the project goals and objectives.
- Choose the Right Software: Select GIS software that aligns with your specific needs, budget, and project requirements.
- Acquire Quality Data: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your data sources, as this directly impacts the validity of your analysis.
- Understand Data Formats: Familiarize yourself with different data formats used in GIS, such as raster and vector data.
- Utilize Analytical Tools: Explore the various analytical tools offered by your GIS software to extract meaningful insights from your data.
- Create Effective Visualizations: Design visually appealing and informative maps that effectively communicate your findings.
- Stay Updated: The field of GIS is constantly evolving, so stay informed about new technologies, software updates, and best practices.
Conclusion:
GIS software has become an indispensable tool in a wide range of fields, empowering professionals to analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data. Its ability to unlock the power of location-based information has revolutionized decision-making, improved efficiency, and fostered innovation across diverse sectors. By harnessing the capabilities of GIS software, individuals and organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the world around them, make informed decisions, and solve complex challenges. As technology continues to advance, GIS software will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of our interconnected world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Spatial Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!