Tunisia on the World Map: A North African Gem
Related Articles: Tunisia on the World Map: A North African Gem
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tunisia on the World Map: A North African Gem. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tunisia on the World Map: A North African Gem
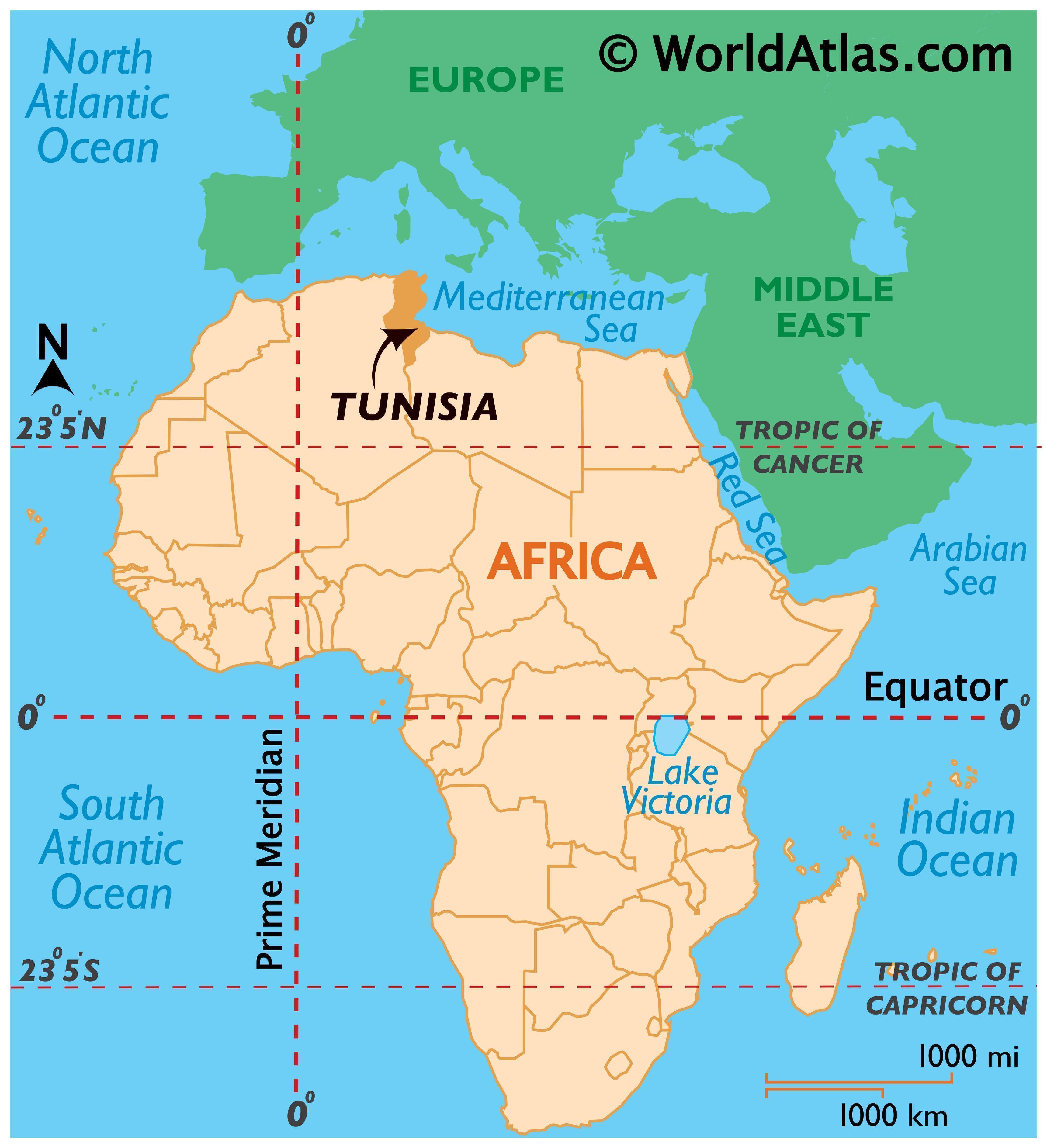
Tunisia, a nation nestled in North Africa, occupies a strategic location on the world map. Its geographical position, encompassing a diverse landscape of coastal plains, fertile valleys, and the vast Sahara Desert, has shaped its history, culture, and economy. Understanding Tunisia’s place within the global context requires examining its unique features and exploring its significance in the wider world.
A Crossroads of History and Culture:
Tunisia’s location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert has positioned it as a meeting point for various civilizations throughout history. Phoenician settlements, Roman conquests, Arab invasions, and Ottoman rule have all left their mark on the country’s cultural tapestry. This rich heritage is evident in its ancient ruins, vibrant cities, and diverse traditions.
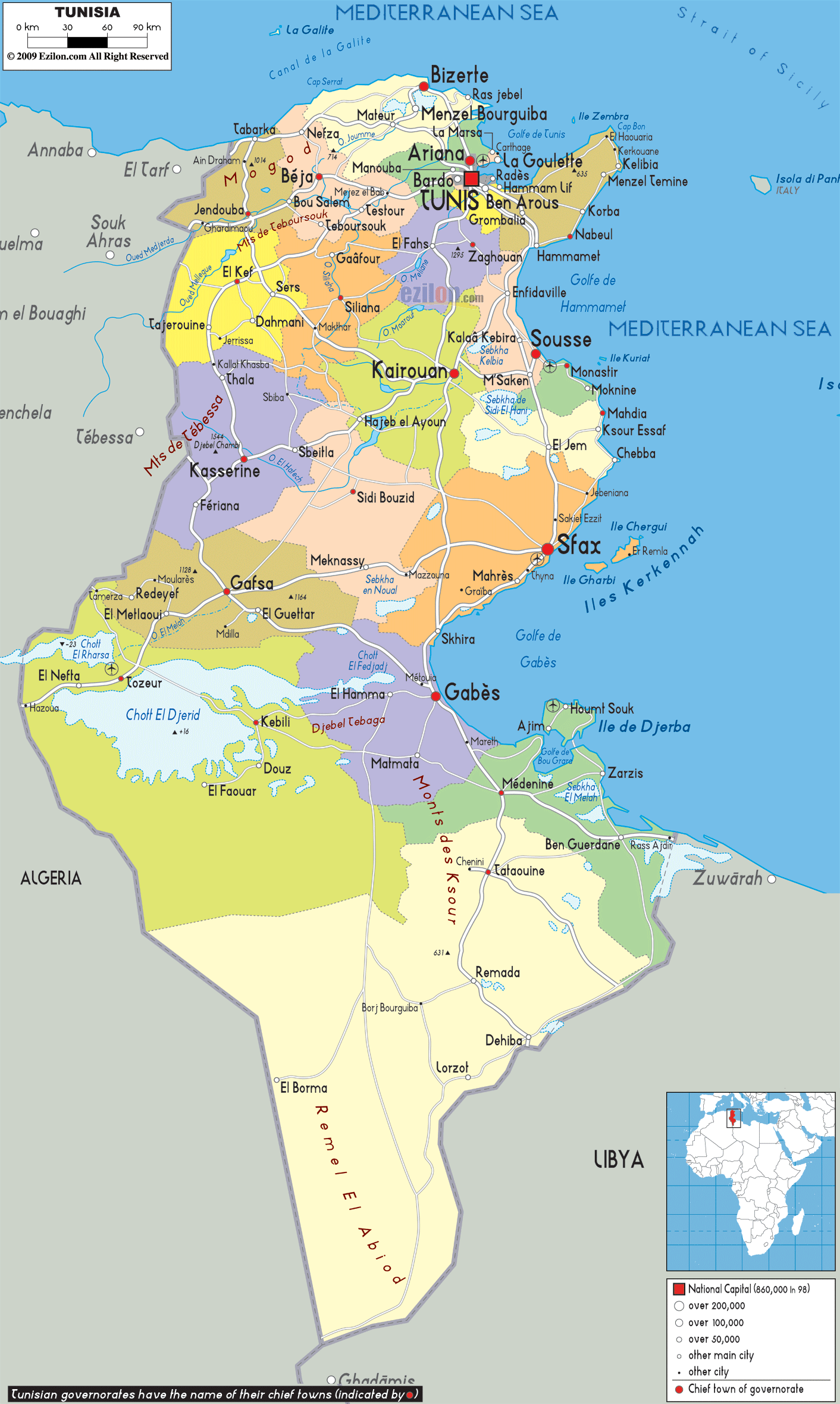
- Carthage: The ancient Phoenician city of Carthage, located near modern-day Tunis, was once a powerful maritime empire, rivaling Rome for control of the Mediterranean. Its ruins, including the Punic Ports and the Tophet, are a testament to its former glory.
- Dougga: This well-preserved Roman city, listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcases the architectural prowess of the Roman Empire. Its amphitheater, forum, and temples offer a glimpse into Roman life in North Africa.
- Kairouan: Founded in the 7th century AD, Kairouan is one of the holiest cities in Islam. Its Great Mosque, with its intricate mosaics and courtyard, is a masterpiece of Islamic architecture.
A Bridge Between Continents:
Tunisia’s strategic location on the Mediterranean Sea has made it a vital link between Africa, Europe, and the Middle East. Its coastline, stretching for over 1,300 kilometers, has served as a passageway for trade, migration, and cultural exchange for centuries. This geographical advantage has also contributed to the country’s economic development, particularly in the tourism sector.
- Tourism: Tunisia’s stunning beaches, ancient ruins, and vibrant culture attract millions of tourists annually, making it a major contributor to the country’s economy.
- Trade: Tunisia’s strategic location has positioned it as a hub for trade between Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. The country is a major exporter of agricultural products, textiles, and phosphates.
- Connectivity: Tunisia’s modern infrastructure, including its international airports and seaports, facilitates trade and travel, connecting the country to the global network.
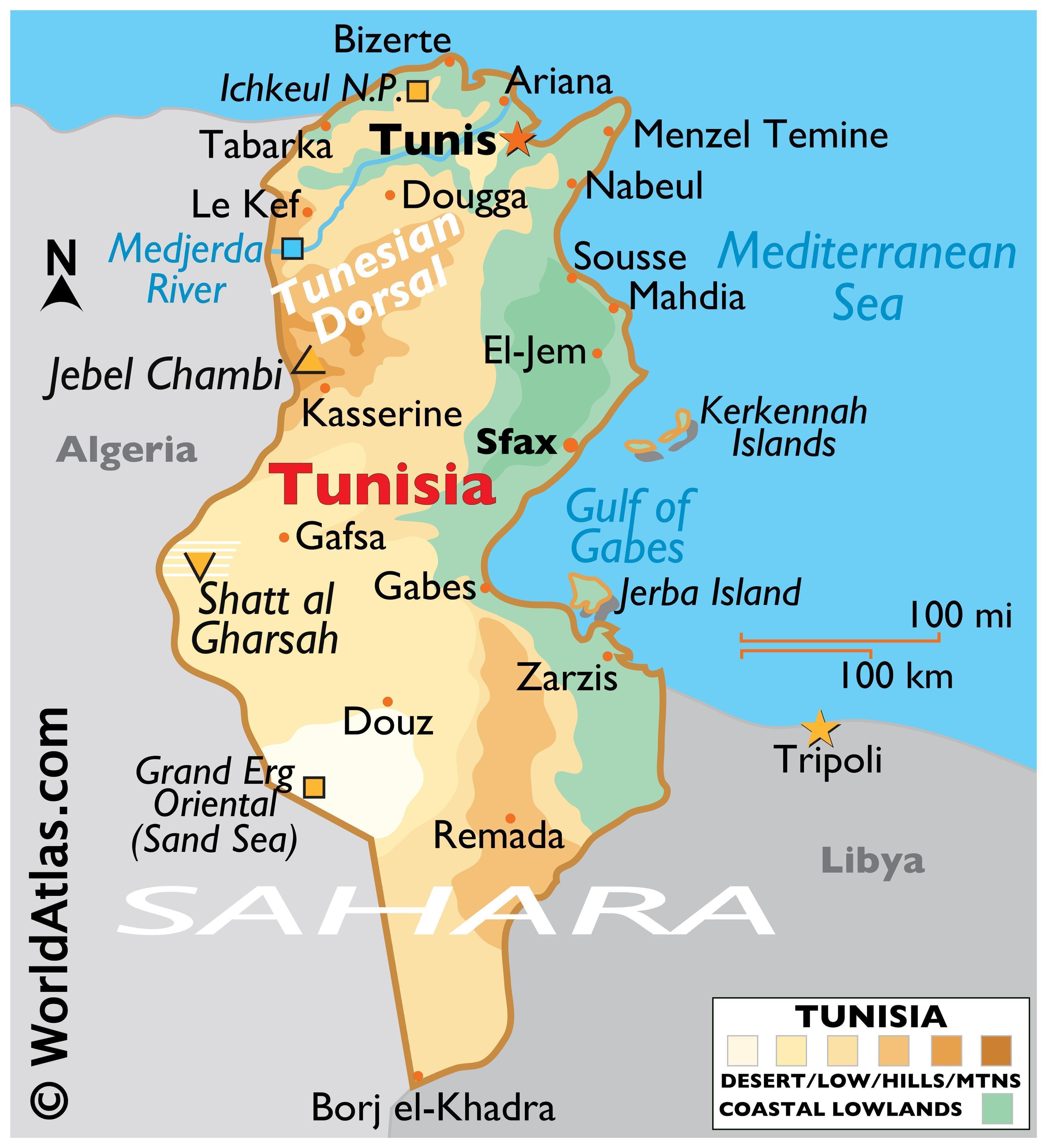
A Diverse Landscape:
Tunisia’s geography is as diverse as its history. The country’s northern region boasts fertile plains and rolling hills, while the south is dominated by the vast Sahara Desert. This geographical variation has resulted in a range of ecosystems, from coastal wetlands to arid deserts.
- The Northern Coastal Plains: This region is characterized by fertile soil and a Mediterranean climate, making it ideal for agriculture. Olive groves, vineyards, and citrus orchards dot the landscape.
- The Atlas Mountains: The Atlas Mountains, running through the north-central region, provide scenic views and offer opportunities for hiking and trekking.
- The Sahara Desert: The vast Sahara Desert occupies much of southern Tunisia, offering unique opportunities for adventure tourism and exploring the desert’s unique ecosystem.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Tunisia faces a number of challenges, including economic instability, political transitions, and environmental concerns. However, the country also boasts significant opportunities for growth and development.
- Economic Diversification: Tunisia’s economy is heavily reliant on tourism and agriculture. Diversifying the economy by promoting manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy sectors is crucial for long-term growth.
- Political Stability: Tunisia has experienced political turmoil in recent years. Establishing a stable and democratic government is essential for attracting foreign investment and fostering economic growth.
- Environmental Sustainability: Tunisia’s environment faces threats from climate change, desertification, and pollution. Sustainable development practices and environmental conservation measures are vital for protecting the country’s natural resources.
FAQs on Tunisia’s World Map Position:
- What is Tunisia’s geographical location? Tunisia is located in North Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east, Algeria to the west, and Libya to the southeast.
- What are Tunisia’s main geographical features? Tunisia’s landscape encompasses coastal plains, fertile valleys, the Atlas Mountains, and the vast Sahara Desert.
- Why is Tunisia’s location significant? Tunisia’s strategic location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert has made it a vital link between Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, facilitating trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
- What are the main challenges and opportunities facing Tunisia? Tunisia faces economic instability, political transitions, and environmental concerns. However, it also boasts significant opportunities for growth and development in various sectors.
Tips for Understanding Tunisia’s World Map Position:
- Use online maps and atlases: Explore interactive maps and atlases to visualize Tunisia’s location in relation to other countries and continents.
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can provide insights into Tunisia’s role in global trade routes and historical events.
- Research geographical features: Learn about Tunisia’s diverse landscape, including its coastal plains, mountains, and deserts.
- Explore cultural connections: Investigate Tunisia’s cultural influences from various civilizations, highlighting its role as a bridge between continents.
Conclusion:
Tunisia’s position on the world map is a reflection of its rich history, diverse culture, and strategic location. Its geographical features have shaped its identity and its role in the global network. Understanding Tunisia’s place within the world context is crucial for appreciating its unique contributions to history, culture, and global affairs. As Tunisia navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its strategic location will continue to play a vital role in its future development and its place on the world stage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tunisia on the World Map: A North African Gem. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!