The Shifting Borders of Power: Exploring the Ancient Macedonian Map
Related Articles: The Shifting Borders of Power: Exploring the Ancient Macedonian Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Borders of Power: Exploring the Ancient Macedonian Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Borders of Power: Exploring the Ancient Macedonian Map
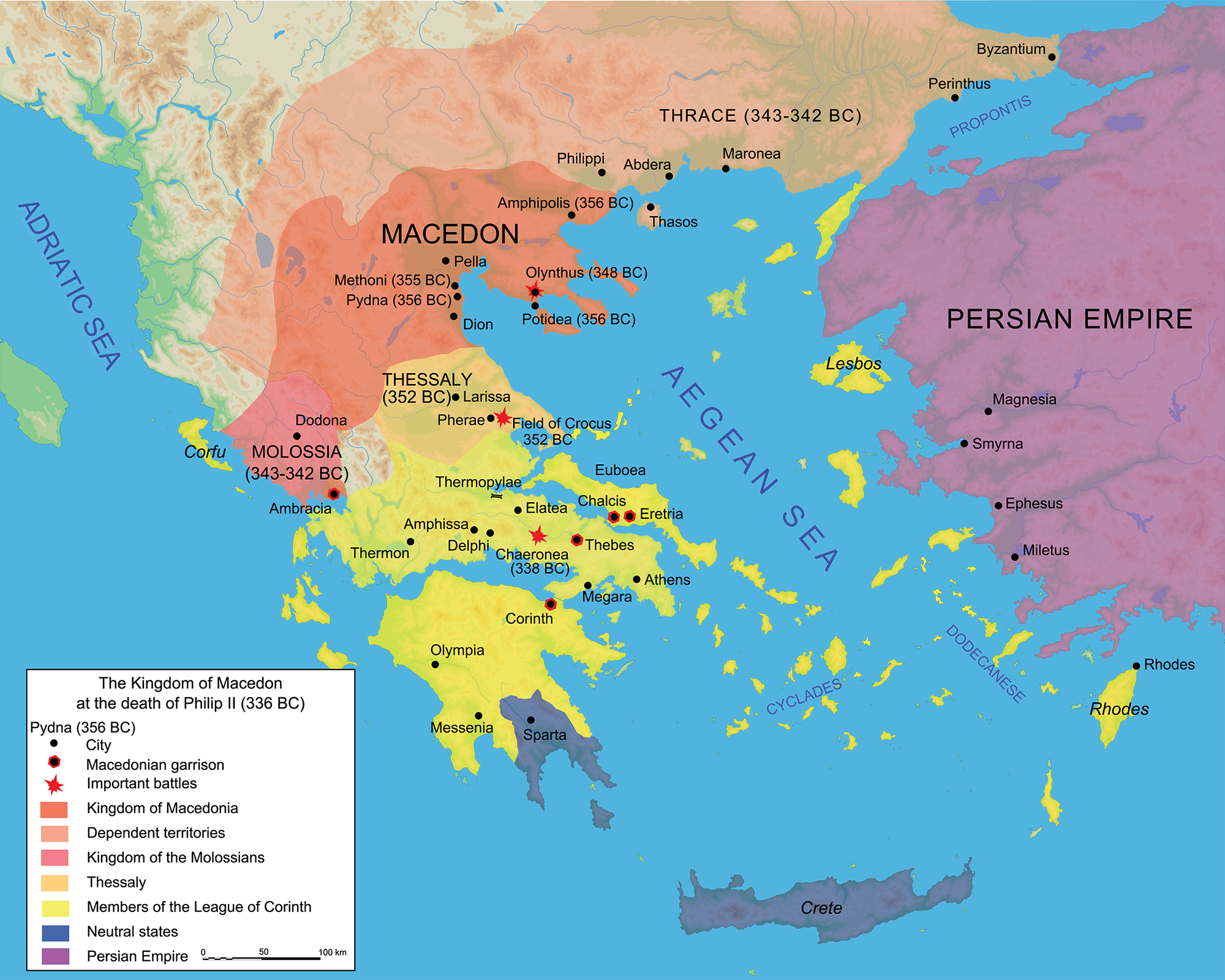
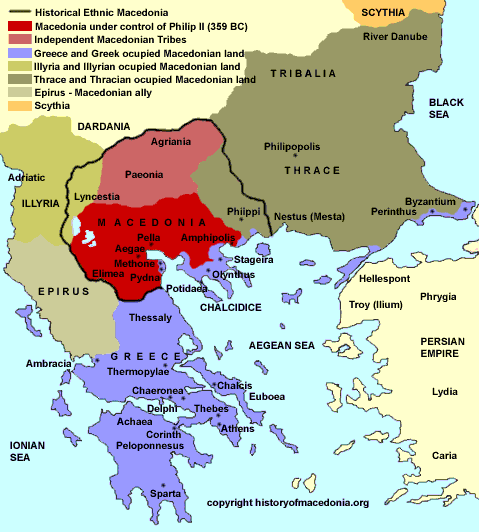
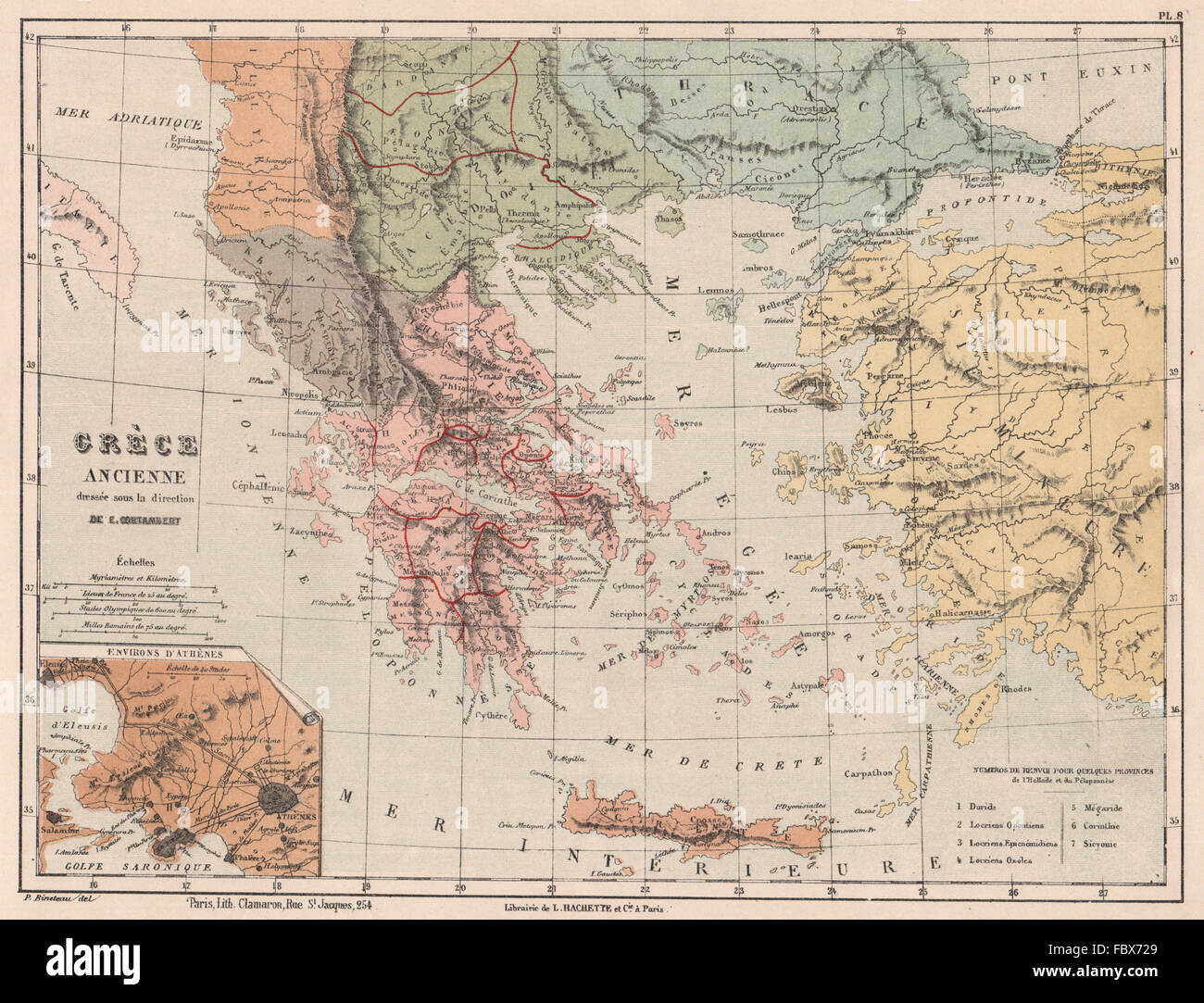
The ancient world was a tapestry of shifting borders and evolving empires, and Macedonia, a region nestled in the northern Balkans, played a pivotal role in this dynamic landscape. Understanding the ancient Macedonian map is crucial for comprehending the political, cultural, and military developments that shaped the ancient Mediterranean world.
A Land of Transition:
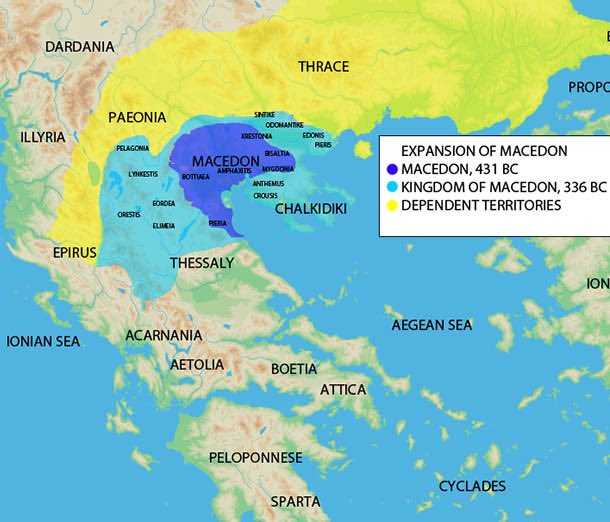
Ancient Macedonia was not a singular, static entity. Its boundaries fluctuated dramatically over centuries, reflecting the ebb and flow of power and the rise and fall of various empires. The region’s geography, a mosaic of fertile valleys, rugged mountains, and strategic passes, contributed to this fluidity. The presence of the Axios and Strymon rivers facilitated trade and communication, while the Pindus mountain range provided natural barriers and strategic strongholds.
From the Early Kingdoms to Philip II:
The earliest recorded inhabitants of the region were the Paeonians, a Thracian people. By the 7th century BCE, the Macedonians, a Greek-speaking people, had established their own kingdoms. These early kingdoms, often fragmented and vying for power, laid the foundation for the later rise of a unified Macedonian state.
The 4th century BCE witnessed the emergence of King Philip II, a visionary leader who unified the various Macedonian kingdoms and forged a formidable military force. Under his reign, Macedonia expanded its influence, conquering much of the Greek mainland and laying the groundwork for the vast empire his son, Alexander the Great, would build.
The Macedonian Empire: A Brief Golden Age:
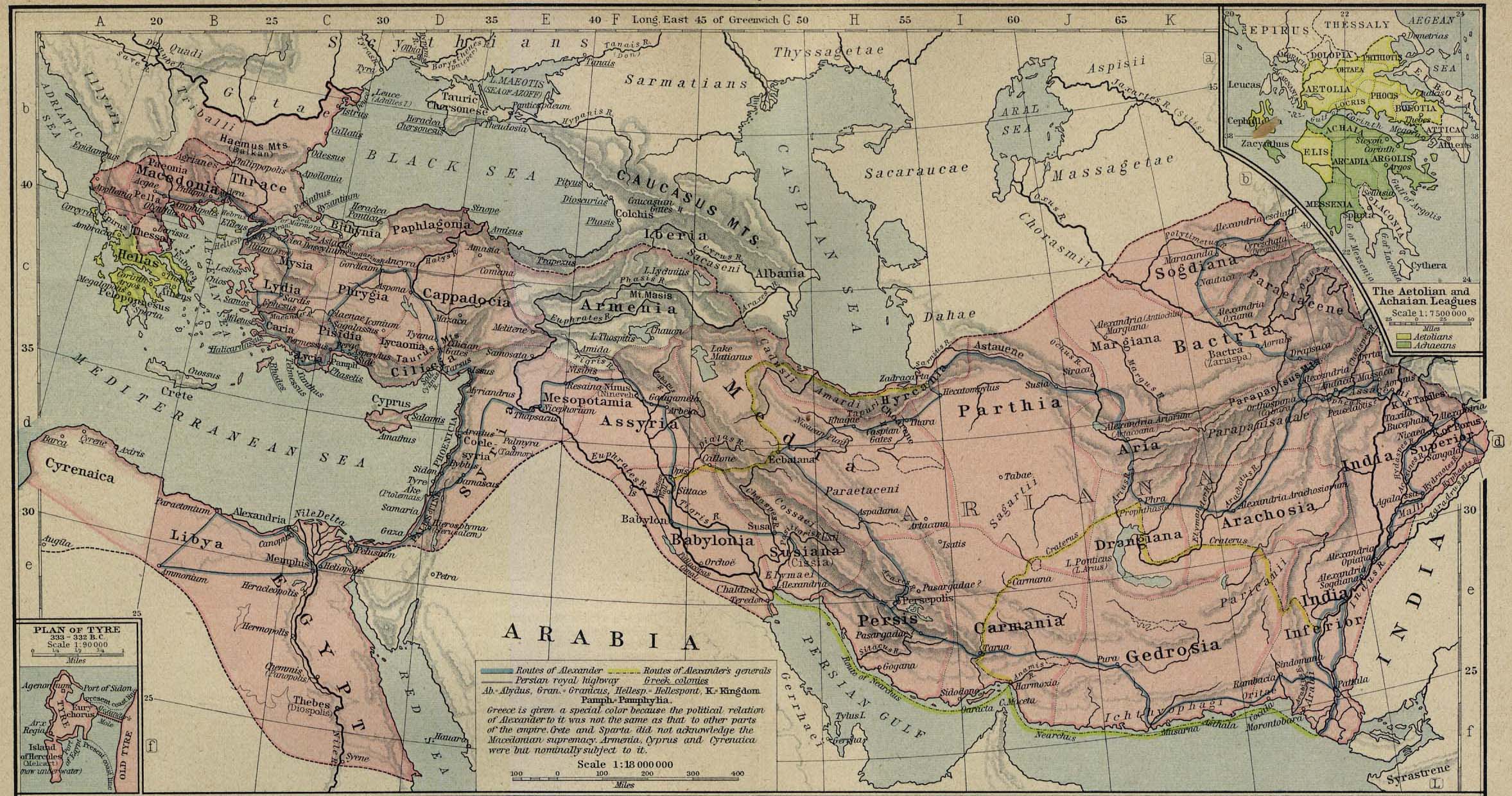
Alexander the Great’s conquests, spanning from Greece to India, dramatically expanded the Macedonian realm. This period, known as the Hellenistic era, witnessed a cultural and intellectual flourishing, as Greek culture spread throughout the conquered territories.
However, Alexander’s death in 323 BCE ushered in a period of instability and fragmentation. His vast empire was divided among his generals, leading to a series of wars and political upheavals. The Macedonian Empire gradually diminished, succumbing to Roman influence in the 2nd century BCE.
Roman Macedonia: A Province of the Empire:
The Roman conquest of Macedonia marked a significant shift in the region’s political landscape. It became a Roman province, experiencing a period of relative peace and prosperity under Roman rule. The region’s strategic location made it a crucial nexus for trade and communication within the Roman Empire.
The Legacy of the Ancient Macedonian Map:
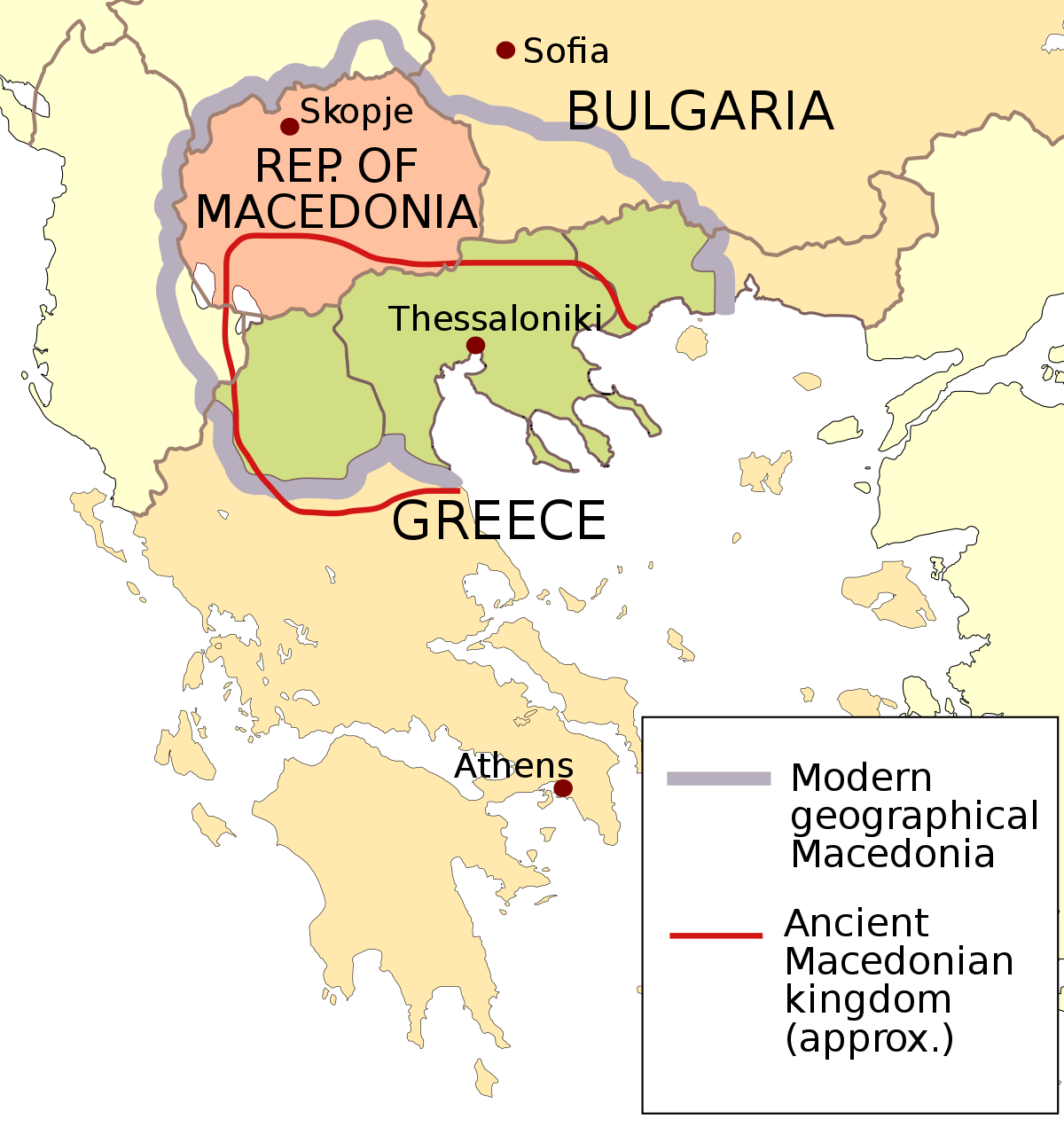
The shifting boundaries and evolving political landscape of ancient Macedonia have left a lasting legacy. The region’s strategic importance, its diverse cultural influences, and its role in shaping the ancient world continue to resonate in modern-day Macedonia and beyond.
FAQs about the Ancient Macedonian Map:
1. What were the key geographical features of ancient Macedonia?
Ancient Macedonia was characterized by a diverse landscape, encompassing fertile valleys, rugged mountains, and strategic passes. The Axios and Strymon rivers facilitated trade and communication, while the Pindus mountain range provided natural barriers and strategic strongholds.
2. How did the boundaries of ancient Macedonia change over time?
The boundaries of ancient Macedonia fluctuated significantly over centuries, reflecting the rise and fall of various empires and the shifting balance of power. The region’s early kingdoms were often fragmented, but under Philip II, Macedonia expanded its territory to include much of the Greek mainland. Alexander the Great’s conquests further expanded the Macedonian realm, but his death led to the empire’s fragmentation. Eventually, Macedonia became a Roman province, its boundaries defined by the Roman administration.
3. What was the significance of Philip II and Alexander the Great in the history of ancient Macedonia?
Philip II, the father of Alexander the Great, played a pivotal role in unifying the various Macedonian kingdoms and building a formidable military force. His conquests laid the groundwork for the vast empire his son would establish. Alexander the Great’s conquests, spanning from Greece to India, dramatically expanded the Macedonian realm and ushered in the Hellenistic era, a period of cultural and intellectual flourishing.
4. What were the main cultural influences on ancient Macedonia?
Ancient Macedonia was a melting pot of cultures, influenced by its proximity to Greece, Thrace, and the Illyrian tribes. The Macedonians adopted many aspects of Greek culture, including language, art, and literature, while also retaining their own distinct traditions.
5. What was the impact of the Roman conquest on ancient Macedonia?
The Roman conquest of Macedonia marked a significant shift in the region’s political landscape. It became a Roman province, experiencing a period of relative peace and prosperity under Roman rule. The region’s strategic location made it a crucial nexus for trade and communication within the Roman Empire.
Tips for Understanding the Ancient Macedonian Map:
- Focus on the key geographical features: Understanding the role of rivers, mountains, and passes is crucial for comprehending the political and military dynamics of the region.
- Study the different empires and kingdoms: Tracking the rise and fall of empires, such as the early Macedonian kingdoms, the empire of Alexander the Great, and the Roman Empire, is essential for understanding the evolving boundaries of Macedonia.
- Consider the cultural influences: Ancient Macedonia was a meeting point for various cultures, and understanding these influences provides a richer understanding of the region’s history.
- Use maps and timelines: Visual aids, such as maps and timelines, can be invaluable tools for understanding the spatial and temporal dimensions of the ancient Macedonian map.
Conclusion:
The ancient Macedonian map is a testament to the dynamic and fluid nature of power in the ancient world. It reveals a region that was shaped by its geography, its people, and its interactions with neighboring empires. From the early kingdoms to the vast empire of Alexander the Great and the subsequent Roman rule, the history of ancient Macedonia is a story of conquest, cultural exchange, and the constant reshaping of borders. Understanding this complex and fascinating history is essential for appreciating the rich tapestry of the ancient Mediterranean world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Borders of Power: Exploring the Ancient Macedonian Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!