The Prime Meridian: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Prime Meridian: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Prime Meridian: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Prime Meridian: A Line Dividing the World
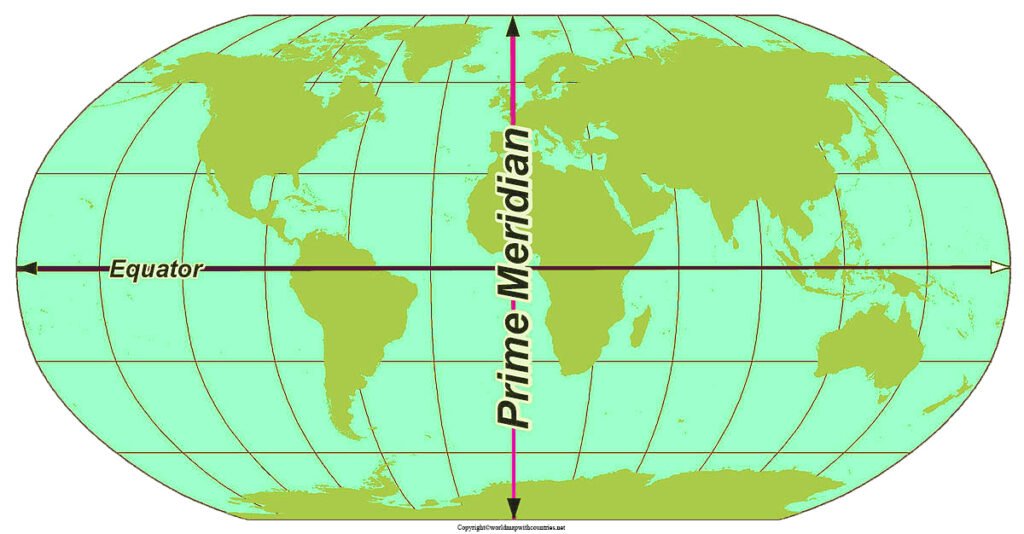
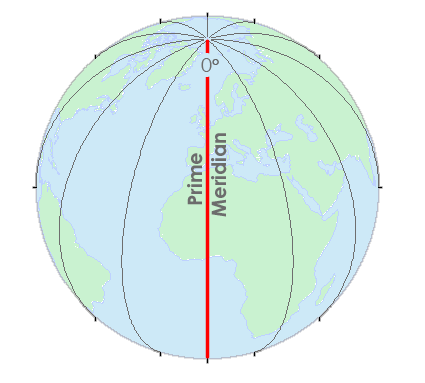
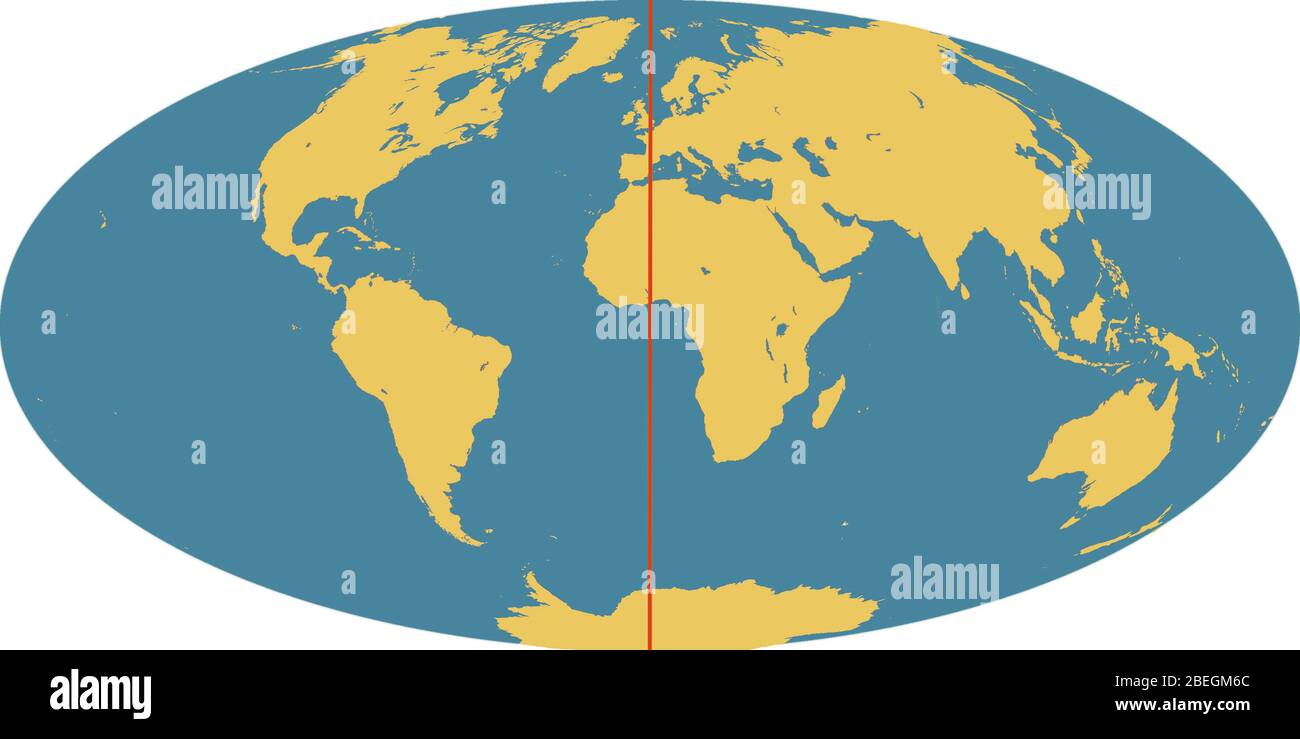
The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, is divided into hemispheres, each defined by a specific line of reference. The Prime Meridian, an imaginary line running from the North Pole to the South Pole, serves as the zero-degree line of longitude, dividing the globe into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. Its significance extends far beyond simple geographical demarcation, playing a crucial role in navigation, timekeeping, and global communication.
A Historical Journey:
The concept of a Prime Meridian predates the modern era, with ancient civilizations utilizing various reference points for mapping their known world. Early Greek astronomers, for instance, relied on the meridian passing through the island of Rhodes. However, the need for a globally standardized meridian became increasingly apparent with the advent of exploration and trade during the Age of Discovery.
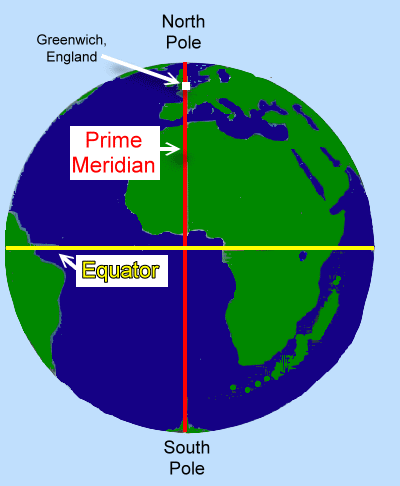
In the 18th century, various countries adopted their own Prime Meridians, leading to confusion and inconsistencies in navigation and cartography. The British, with their vast colonial empire, established Greenwich Observatory in London as the site for their Prime Meridian, a decision that eventually gained international recognition.
The Greenwich Meridian: A Global Standard:
The Greenwich Meridian, passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, was officially adopted as the international Prime Meridian in 1884 at the International Meridian Conference held in Washington, D.C. This momentous decision established a unified system for longitude measurement, simplifying navigation and facilitating global communication.
Navigating the World:
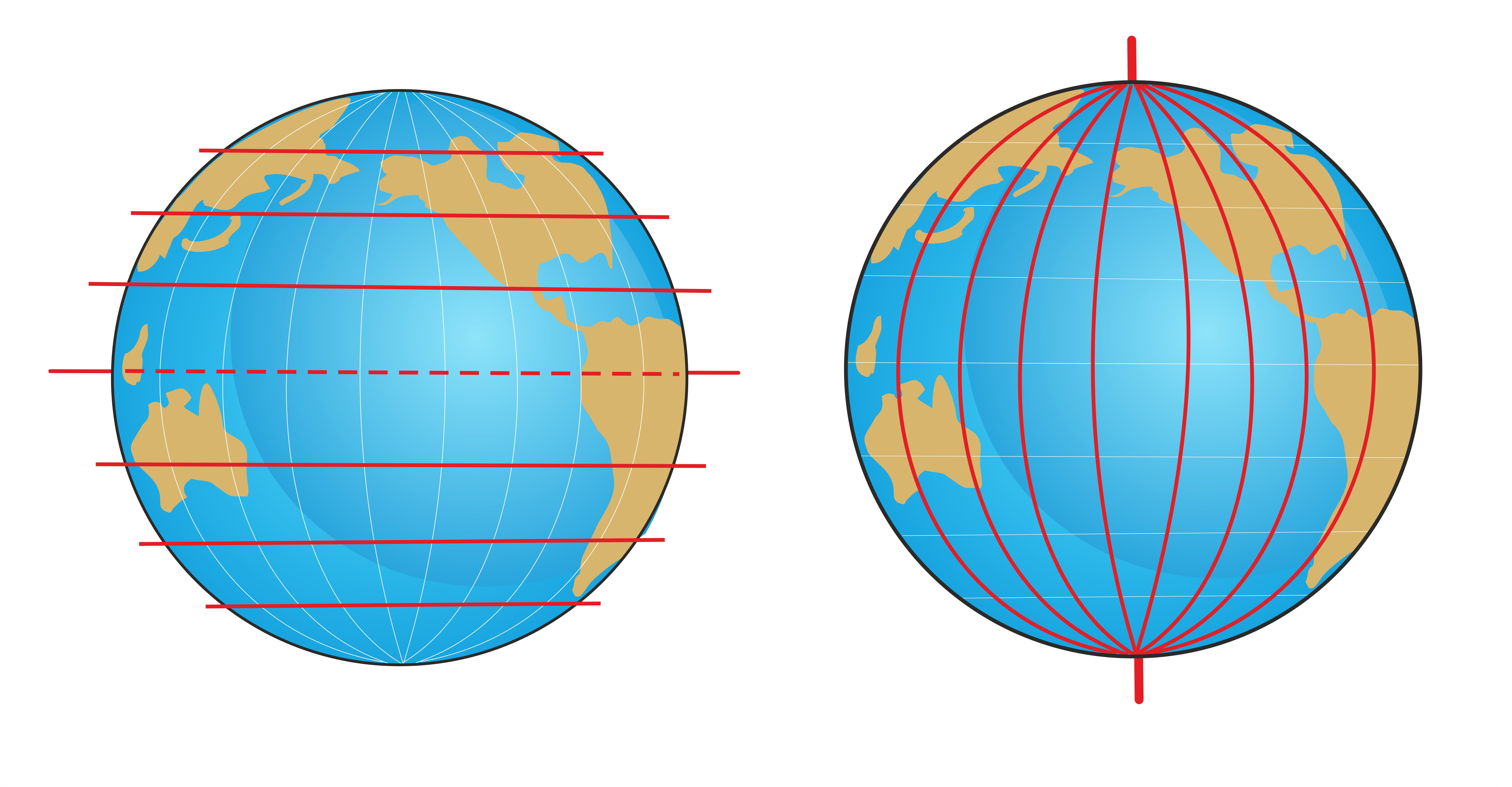
The Prime Meridian acts as the starting point for measuring longitude, with locations east of Greenwich being assigned positive degrees, while those west are assigned negative degrees. This system allows for precise location determination, crucial for navigation, mapping, and timekeeping.
For centuries, sailors relied on celestial navigation, using stars and the sun to determine their position at sea. The Prime Meridian served as a crucial reference point, allowing them to calculate their longitude and navigate safely across vast oceans.
Timekeeping and the International Date Line:
The Prime Meridian also plays a vital role in timekeeping. The Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours, creating a 360-degree circle. This rotation is divided into 24 hours, with each hour representing 15 degrees of longitude.
The Prime Meridian, being the zero-degree line, marks the starting point for time zones. The time at Greenwich is designated as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), serving as the basis for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the global standard for timekeeping.
The 180th meridian, directly opposite the Prime Meridian, marks the International Date Line. This line serves as the boundary between time zones, where the date changes. Crossing the International Date Line eastward results in losing a day, while crossing westward results in gaining a day.
The Prime Meridian in the Digital Age:
In the digital age, the Prime Meridian remains a vital component of global positioning systems (GPS). Satellites orbiting the Earth continuously transmit signals containing precise time and location data, allowing GPS receivers to determine their coordinates relative to the Prime Meridian.
This technology has revolutionized navigation, enabling accurate location tracking for a wide range of applications, from personal navigation to transportation management, disaster response, and scientific research.
The Enduring Importance of the Prime Meridian:
The Prime Meridian, despite being an imaginary line, has had a profound impact on our understanding of the world. It serves as a foundational element for navigation, timekeeping, and global communication, facilitating trade, exploration, and technological advancement.
Its historical significance, combined with its enduring role in modern society, underscores the importance of standardized reference points in a world increasingly interconnected and reliant on precise location data.
FAQs about the Prime Meridian:
1. Why is Greenwich, England, the location of the Prime Meridian?
The choice of Greenwich as the location for the Prime Meridian was a result of the British Empire’s global influence during the 19th century. The Royal Observatory at Greenwich had already established itself as a leading center for astronomical research and navigation. Its adoption as the international Prime Meridian reflected the prominence of British maritime power and scientific advancements.
2. Does the Prime Meridian actually exist on Earth?
The Prime Meridian is an imaginary line, a concept used for mapping and navigation. It does not physically exist on Earth’s surface.
3. What is the difference between the Prime Meridian and the International Date Line?
The Prime Meridian is the zero-degree line of longitude, dividing the Earth into Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The International Date Line is the 180th meridian, located on the opposite side of the Earth from the Prime Meridian. It serves as the boundary between time zones, where the date changes.
4. Why is the Prime Meridian important for timekeeping?
The Prime Meridian serves as the starting point for time zones. The time at Greenwich is designated as GMT, which serves as the basis for UTC, the global standard for timekeeping.
5. How does the Prime Meridian relate to GPS technology?
GPS satellites transmit signals containing precise time and location data. Receivers on Earth use this information to determine their coordinates relative to the Prime Meridian.
Tips for Understanding the Prime Meridian:
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: Imagine a line running from the North Pole to the South Pole, dividing the Earth into two halves. This is the Prime Meridian.
- Use a globe or map: Study a globe or world map to understand how the Prime Meridian relates to other lines of longitude.
- Consider its impact on navigation and timekeeping: Think about how the Prime Meridian is used to determine location and time throughout the world.
Conclusion:
The Prime Meridian, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds immense significance in shaping our understanding of the world. Its role in navigation, timekeeping, and global communication continues to be vital in the modern era, highlighting the enduring importance of standardized reference points for a connected and technologically advanced society. As we continue to explore the universe and push the boundaries of human knowledge, the Prime Meridian will remain a cornerstone of our understanding of the Earth and its place within the cosmos.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Prime Meridian: A Line Dividing the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!