The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration
Related Articles: The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration

The North Pole, a singular point at the northernmost extremity of Earth, holds a unique position in geography and human imagination. It serves as a crucial reference point in navigation, a symbol of exploration, and a focal point for scientific research. Understanding its location on a map requires grasping the principles of cartography and the Earth’s spherical nature.
The Earth as a Sphere and the North Pole’s Position:
The Earth is an oblate spheroid, meaning it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. The North Pole, situated at 90 degrees North latitude, is the northernmost point on this sphere. All lines of longitude converge at the North Pole, making it a central point for navigation and cartography.
Representing the North Pole on Maps:
The challenge of representing the Earth’s spherical shape on a flat map leads to various map projections. Each projection distorts the Earth’s surface in different ways, impacting the visual representation of the North Pole.
-
Mercator Projection: A widely used projection for navigation, the Mercator projection distorts areas near the poles, making them appear larger than they actually are. The North Pole is depicted as a point at the top of the map, surrounded by lines of longitude converging at this point.
-
Polar Projection: This projection focuses on the polar regions, with the North Pole placed at the center of the map. Lines of longitude radiate outwards from the center, forming a radial pattern. This projection is ideal for visualizing the North Pole and its surrounding areas.
-
Other Projections: Other map projections, such as the Winkel Tripel projection, attempt to minimize distortion across the globe, including the North Pole. The North Pole is represented as a point at the top of the map, with lines of longitude converging towards it.
The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration:
The North Pole’s unique position makes it a significant point for exploration and research. Its location at the convergence of all lines of longitude allows for a clear understanding of geographical directions and facilitates navigation.
-
Exploration: The North Pole has been a target for explorers for centuries. From the early attempts by explorers like Robert Peary to the modern-day expeditions, the North Pole has challenged human endurance and pushed the boundaries of exploration.
-
Scientific Research: The North Pole is an important site for scientific research, providing insights into climate change, sea ice dynamics, and the impact of human activities on the Arctic environment. Research stations and expeditions at the North Pole contribute to our understanding of the planet’s ecosystems and the effects of global warming.
FAQs on the North Pole’s Location:
Q: Is the North Pole a landmass?
A: No, the North Pole is located in the Arctic Ocean, covered by a layer of sea ice.
Q: Can you reach the North Pole by land?
A: No, the North Pole is inaccessible by land. It can only be reached by air, sea, or by traversing the sea ice.
Q: What is the difference between the North Pole and the geographic North Pole?
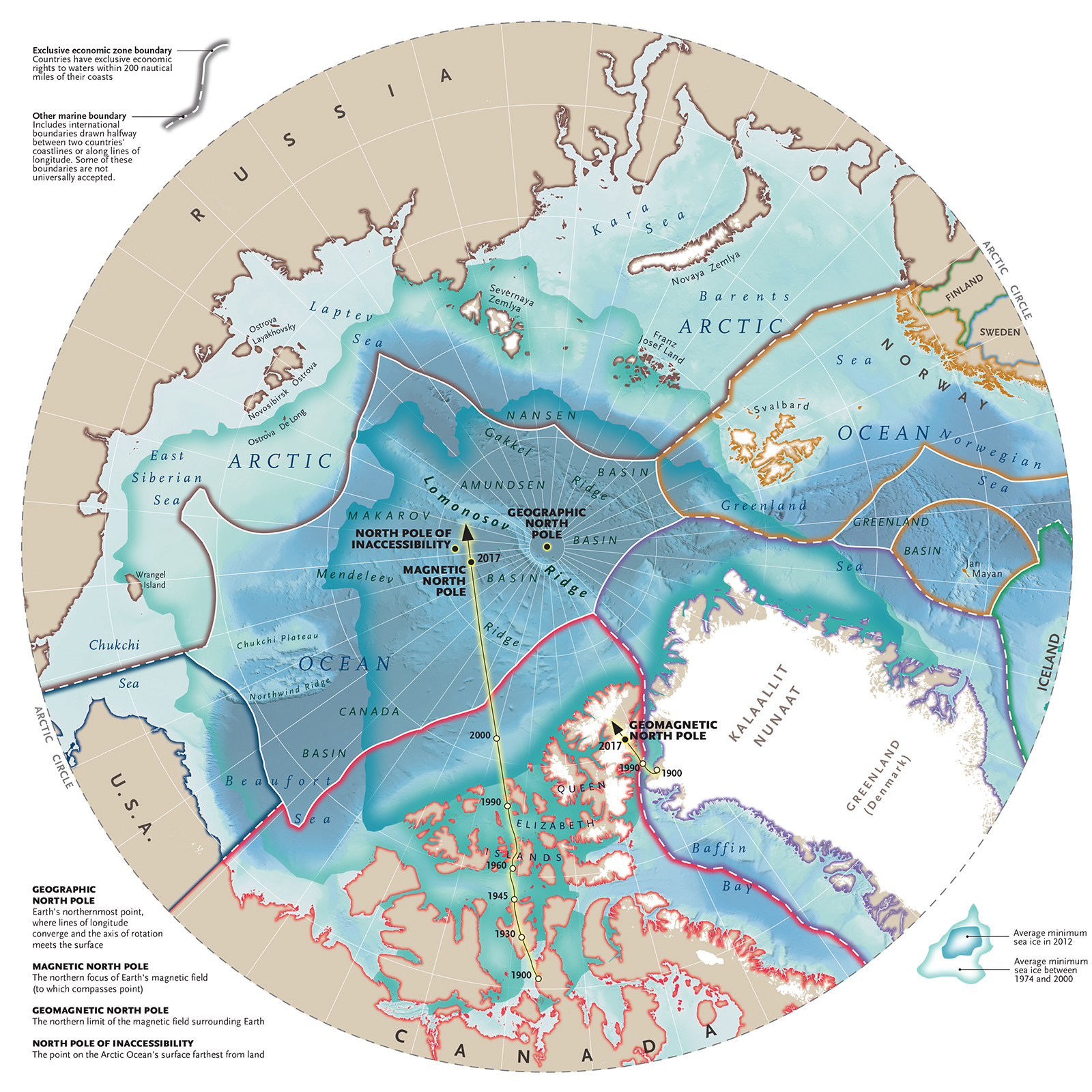
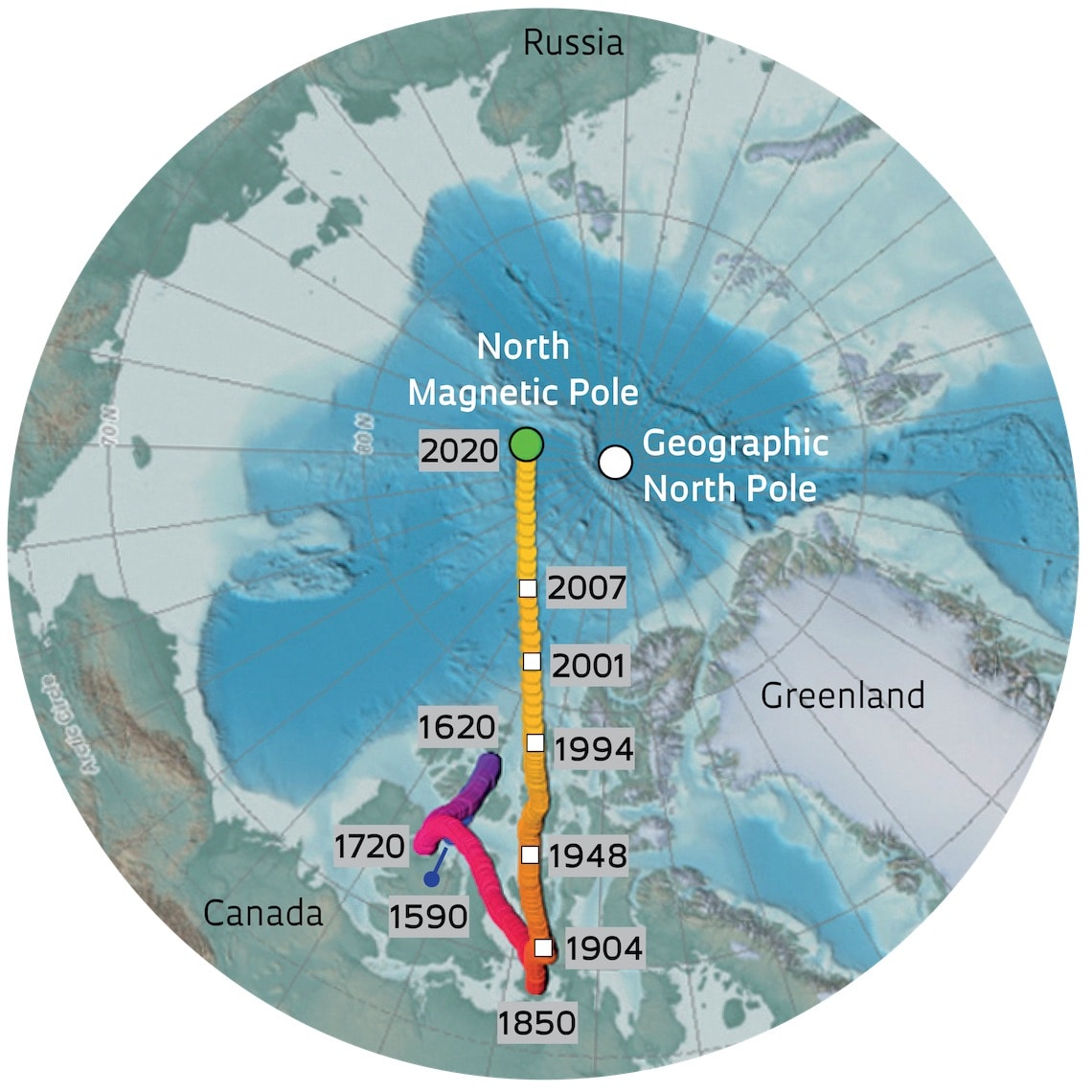
A: The geographic North Pole is the point where all lines of longitude converge. The magnetic North Pole, on the other hand, is the point where the Earth’s magnetic field lines converge. The magnetic North Pole is not fixed and shifts over time.
Q: What are the challenges of reaching the North Pole?
A: Reaching the North Pole presents significant challenges, including extreme cold temperatures, unpredictable weather conditions, and the constant threat of ice movement.
Tips for Understanding the North Pole’s Location:
-
Use a globe: A globe provides a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape than a flat map, helping to visualize the North Pole’s position.
-
Explore different map projections: Compare different map projections to understand how they represent the North Pole and its surrounding areas.
-
Learn about the Arctic region: Research the Arctic region’s geography, climate, and the challenges of exploring and researching in this remote environment.
Conclusion:
The North Pole, a point of convergence and exploration, holds a significant place in our understanding of the Earth. Its location at the northernmost extremity of the planet, its importance in navigation, and its role in scientific research continue to inspire curiosity and exploration. Understanding the North Pole’s location on a map requires appreciating the Earth’s spherical nature and the various ways cartographers represent its surface. By exploring these aspects, we gain a deeper understanding of the world and the challenges and opportunities that lie at the top of our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The North Pole: A Point of Convergence and Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!