The Majestic Mountains of China: A Geographical Tapestry of Diversity and Significance
Related Articles: The Majestic Mountains of China: A Geographical Tapestry of Diversity and Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Majestic Mountains of China: A Geographical Tapestry of Diversity and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Majestic Mountains of China: A Geographical Tapestry of Diversity and Significance

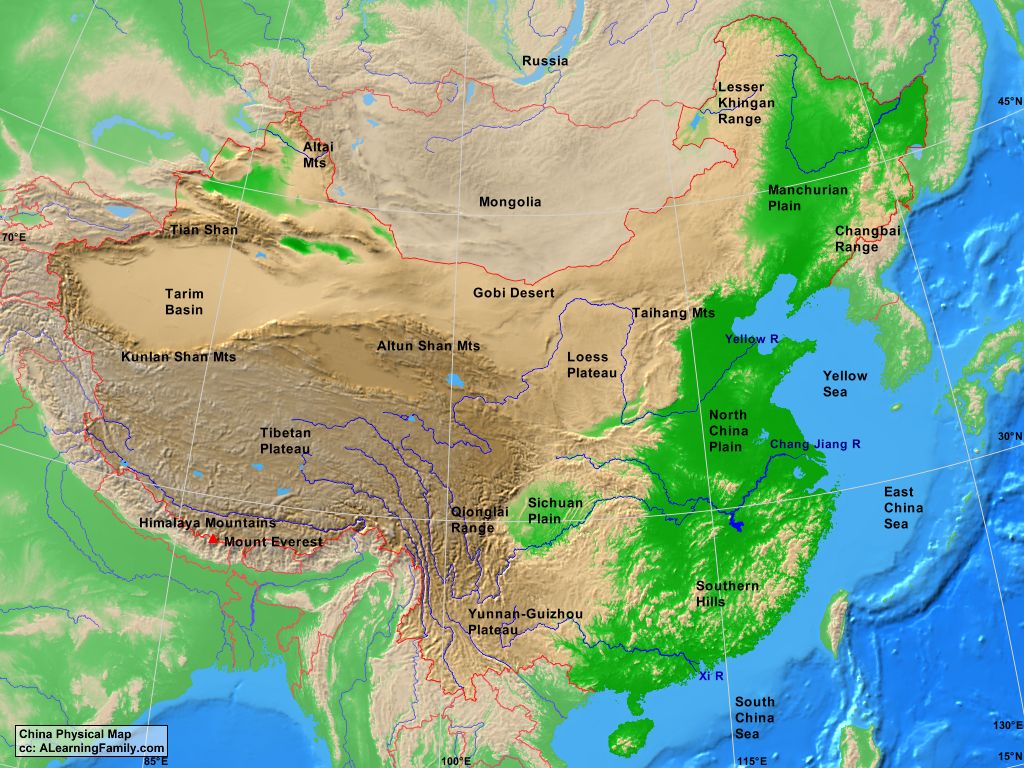
China, the world’s most populous nation, is a land of extraordinary geographic diversity, with its landscape sculpted by towering mountains, vast plains, and fertile river valleys. The mountains of China, in particular, hold a prominent place in the nation’s geography, history, and culture. These majestic peaks, stretching across the vast expanse of the country, form a formidable barrier, shaping the nation’s climate, influencing its biodiversity, and playing a pivotal role in the lives of its people.
A Geographical Overview
The mountains of China can be broadly categorized into three major systems:
-
The Himalayas: This colossal mountain range, home to the world’s highest peak, Mount Everest, forms the southern border of China, separating it from Nepal, India, Bhutan, and Pakistan. The Himalayas are renowned for their sheer scale and rugged beauty, with numerous peaks exceeding 8,000 meters in elevation.
-
The Kunlun Mountains: This vast mountain range, stretching across the western and northwestern parts of China, is considered the "backbone" of the country. The Kunlun Mountains are characterized by their high altitude, arid climate, and rugged terrain, making them a formidable barrier to human settlement.
-
The Tian Shan Mountains: Located in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, the Tian Shan Mountains are a prominent mountain range that extends across the border into Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. The Tian Shan Mountains are known for their high peaks, glaciers, and rich biodiversity.
Beyond these major systems, China boasts numerous other prominent mountain ranges, including:
-
The Qinling Mountains: These mountains, running east-west across central China, mark the boundary between the northern and southern parts of the country, with distinct differences in climate and vegetation.
-
The Taihang Mountains: These mountains, located in the eastern part of China, are known for their steep slopes and rugged terrain, forming a natural barrier between the North China Plain and the Loess Plateau.
-
The Wuling Mountains: Located in the southwest of China, these mountains are known for their lush forests and rich biodiversity, forming a natural border between Sichuan and Hunan provinces.
The Significance of Mountains in China
The mountains of China hold immense significance, impacting the nation’s physical geography, ecological diversity, and cultural identity.
1. Shaping the Climate and Environment:
-
Climate Regulation: The mountains act as natural barriers, influencing the flow of air masses and precipitation patterns. The Himalayan range, for instance, acts as a rain shadow, blocking moisture-laden winds from reaching the Tibetan Plateau, creating a dry and arid climate. Conversely, the southeastern mountains receive abundant rainfall, contributing to the lush vegetation of the region.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: The mountains provide diverse habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna. The Himalayas, for example, are home to a unique ecosystem, with alpine meadows, dense forests, and glaciers, supporting a rich diversity of plant and animal life.
-
Water Resources: The mountains are the source of numerous rivers, providing essential water resources for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. The Yangtze River, for example, originates in the Tibetan Plateau and flows through the heart of China, providing irrigation for vast agricultural lands.
2. Cultural and Historical Significance:
-
Ancient Civilizations: The mountains have played a significant role in the development of ancient Chinese civilization. The Yellow River, originating in the Kunlun Mountains, flows through the North China Plain, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting the rise of ancient Chinese civilizations.
-
Spiritual Significance: The mountains hold deep spiritual significance in Chinese culture, often associated with deities and mythical creatures. The Kunlun Mountains, for example, are revered as the "mother mountain" in Chinese mythology, believed to be the source of all life and the abode of immortals.
-
Traditional Practices: The mountains have shaped traditional practices in various regions. The mountainous regions of southwest China, for example, are known for their unique agricultural practices, including terraced farming, adapted to the challenging terrain.
3. Economic Importance:
-
Mineral Resources: The mountains are rich in mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, and copper. The mining industry plays a significant role in the economies of many mountainous regions.
-
Tourism: The scenic beauty of the mountains attracts millions of tourists each year, contributing to the local economies. The Himalayas, for instance, are a popular destination for trekking and mountaineering enthusiasts.
-
Hydropower: The rivers originating from the mountains are harnessed for hydropower generation, providing a significant source of clean energy. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River, for example, is the world’s largest hydroelectric power station.
FAQs on the Mountains of China
Q1: What are the highest mountains in China?
The highest mountain in China is Mount Everest, which straddles the border between China and Nepal. Other notable high peaks include Mount Lhotse, Mount Makalu, and Mount Cho Oyu, all located in the Himalayas.
Q2: What is the impact of the mountains on the Chinese climate?
The mountains play a crucial role in shaping the climate of China. They act as barriers, influencing the flow of air masses and precipitation patterns. The Himalayas, for instance, block moisture-laden winds from reaching the Tibetan Plateau, creating a dry and arid climate. Conversely, the southeastern mountains receive abundant rainfall, contributing to the lush vegetation of the region.
Q3: How do the mountains contribute to China’s biodiversity?
The mountains provide diverse habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna, making them biodiversity hotspots. The Himalayas, for example, are home to a unique ecosystem, with alpine meadows, dense forests, and glaciers, supporting a rich diversity of plant and animal life.
Q4: What is the role of the mountains in Chinese culture?
The mountains hold deep spiritual significance in Chinese culture, often associated with deities and mythical creatures. The Kunlun Mountains, for example, are revered as the "mother mountain" in Chinese mythology, believed to be the source of all life and the abode of immortals.
Q5: What are some of the economic benefits of the mountains?
The mountains are rich in mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, and copper. The mining industry plays a significant role in the economies of many mountainous regions. Additionally, the scenic beauty of the mountains attracts millions of tourists each year, contributing to the local economies. The rivers originating from the mountains are also harnessed for hydropower generation, providing a significant source of clean energy.
Tips for Exploring the Mountains of China
-
Research thoroughly: Before embarking on any mountain expedition, it is crucial to research the specific region, its altitude, climate, and required permits.
-
Choose the right equipment: Depending on the type of expedition, ensure you have the necessary equipment, including appropriate clothing, footwear, and gear.
-
Be aware of altitude sickness: Altitude sickness is a common concern at high altitudes. Consult with a doctor and take necessary precautions to prevent or manage the condition.
-
Respect the environment: Leave no trace behind. Pack out all trash and avoid disturbing the natural environment.
-
Hire a local guide: Hiring a local guide can enhance your experience and ensure your safety, especially in remote areas.
Conclusion
The mountains of China are a testament to the nation’s extraordinary geographical diversity and hold immense significance for its climate, environment, culture, and economy. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the rugged terrain of the Kunlun Mountains, these majestic landscapes have shaped the lives of the Chinese people for centuries, influencing their history, culture, and daily lives. Understanding the role of these mountains is crucial for appreciating the unique tapestry of China’s geography and its impact on the nation’s development and future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Majestic Mountains of China: A Geographical Tapestry of Diversity and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!