The Foundation of Geospatial Understanding: A Deep Dive into Map Sources
Related Articles: The Foundation of Geospatial Understanding: A Deep Dive into Map Sources
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Geospatial Understanding: A Deep Dive into Map Sources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Foundation of Geospatial Understanding: A Deep Dive into Map Sources

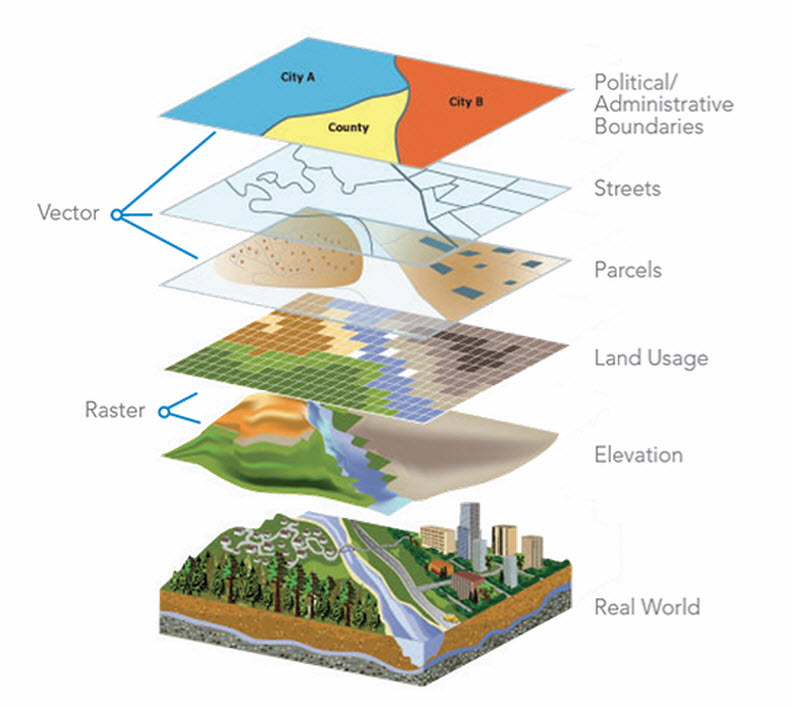
In the digital age, maps are no longer static representations confined to paper. They have evolved into dynamic and interactive tools that empower us to navigate, explore, and understand the world around us. At the heart of this transformation lies the concept of "map source," a crucial element that determines the accuracy, reliability, and richness of the information presented on a map.
Understanding Map Sources: The Building Blocks of Geospatial Data
A map source refers to the origin and nature of the data used to create a map. This data can encompass a wide range of information, including:
- Geographic data: This forms the fundamental framework of a map, defining locations, boundaries, and geographic features such as rivers, mountains, and roads.
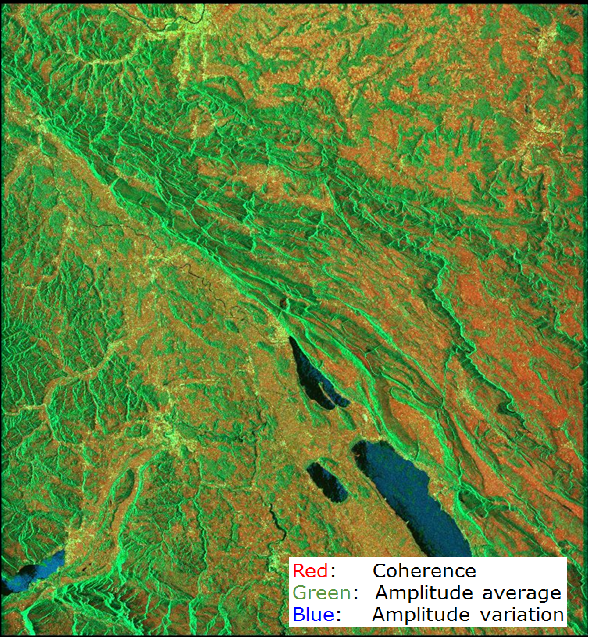
- Satellite imagery: Captured from space, satellite imagery provides a bird’s-eye view of the Earth, offering valuable insights into land cover, urban development, and natural disasters.
- Aerial photography: Taken from airplanes, aerial photographs offer detailed views of the Earth’s surface, often used for mapping, planning, and environmental monitoring.
- LiDAR data: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D representations of the Earth’s surface, invaluable for terrain analysis, infrastructure mapping, and urban planning.
- Census data: Population statistics, demographics, and socioeconomic information collected through censuses provide crucial insights into human settlements and societal trends.
- OpenStreetMap data: A collaborative project where users contribute to building a free and open-source map of the world, offering valuable data for navigation, exploration, and community mapping.
The Importance of Map Sources: Shaping Our Understanding of the World
The choice of map source significantly impacts the quality and relevance of the information presented. Understanding the origin and characteristics of the data is crucial for making informed decisions based on the information displayed on a map.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Different map sources possess varying levels of accuracy and reliability. Satellite imagery, for example, can be affected by cloud cover and atmospheric conditions, while LiDAR data offers a higher level of precision.
- Resolution and Detail: The resolution of a map source determines the level of detail visible. High-resolution imagery reveals intricate features, while low-resolution data provides a broader overview.
- Timeliness and Up-to-date Information: Some map sources, like satellite imagery, offer real-time or near-real-time updates, while others, like census data, are updated periodically.
- Data Availability and Accessibility: The availability and accessibility of map sources vary depending on their nature. Open data sources, like OpenStreetMap, are readily available, while others might require subscription or licensing.
Exploring Common Map Sources: A Closer Look at Specific Types
1. Government Agencies and Organizations:
- National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA): The NGA provides a wide range of geospatial data, including maps, imagery, and elevation data, used for defense, intelligence, and civilian applications.
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS is a leading provider of topographic maps, satellite imagery, and geospatial data for scientific research, resource management, and public use.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): NASA’s Earth Observing System provides valuable data from satellites, including land cover, vegetation health, and sea surface temperature, used for environmental monitoring and climate research.
2. Commercial Data Providers:
- Google Maps: A widely used mapping service, Google Maps utilizes a combination of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and user-generated data to provide a comprehensive and interactive map experience.
- Mapbox: A cloud-based mapping platform offering customizable map styles, data visualization tools, and APIs for developers to create and integrate maps into various applications.
- Esri: A leading provider of geospatial software and services, Esri offers a wide range of mapping tools, data management solutions, and spatial analysis capabilities.
3. Open Data Initiatives:
- OpenStreetMap (OSM): A collaborative project where users contribute to building a free and open-source map of the world. OSM data is widely used for navigation, exploration, and community mapping.
- GeoJSON: A format for encoding geographic data structures, enabling the sharing and exchange of geospatial information across different applications.
- Government Open Data Portals: Many governments worldwide provide open access to geospatial data, including maps, imagery, and census data, promoting transparency and citizen engagement.
FAQs about Map Sources:
1. What are the benefits of using multiple map sources?
Combining data from multiple sources can enhance map accuracy, provide a more comprehensive view of a location, and offer different perspectives on the same area. For instance, combining satellite imagery with LiDAR data can create a detailed 3D model of a city, showcasing both the surface features and the underlying terrain.
2. How can I determine the best map source for my needs?
The choice of map source depends on the specific application and the information required. Consider factors like accuracy, resolution, timeliness, data availability, and licensing requirements. For example, if you need highly accurate topographic data for engineering purposes, LiDAR data might be the best option. However, if you need a general overview of a city for navigation, Google Maps might suffice.
3. How can I access and use map source data?
Many map sources offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow developers to access and integrate their data into various applications. Some sources also provide download options for specific data sets. Explore the websites of map source providers to learn about their data access and usage policies.
Tips for Choosing and Using Map Sources Effectively:
- Define your requirements: Clearly identify the specific information you need from a map. This will help you narrow down your search and choose the most appropriate source.
- Evaluate the accuracy and reliability: Consider the source’s reputation, data collection methods, and any known limitations.
- Check the resolution and timeliness: Ensure the map source provides the level of detail and data freshness required for your purpose.
- Explore data visualization tools: Utilize visualization tools to effectively display and analyze the data from different sources.
- Consider data licensing and usage rights: Understand the terms and conditions associated with using specific map sources.
Conclusion: The Power of Map Sources in Shaping our World
Map sources are the foundation of our understanding of the world. They provide the raw data that enables us to navigate, explore, and make informed decisions about our environment. By understanding the origins, characteristics, and applications of various map sources, we can leverage their power to create insightful maps, visualize complex data, and contribute to a more informed and connected world. As technology continues to advance, the world of map sources will undoubtedly evolve further, offering even greater opportunities for exploration, analysis, and innovation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Geospatial Understanding: A Deep Dive into Map Sources. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!