The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Related Articles: The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography

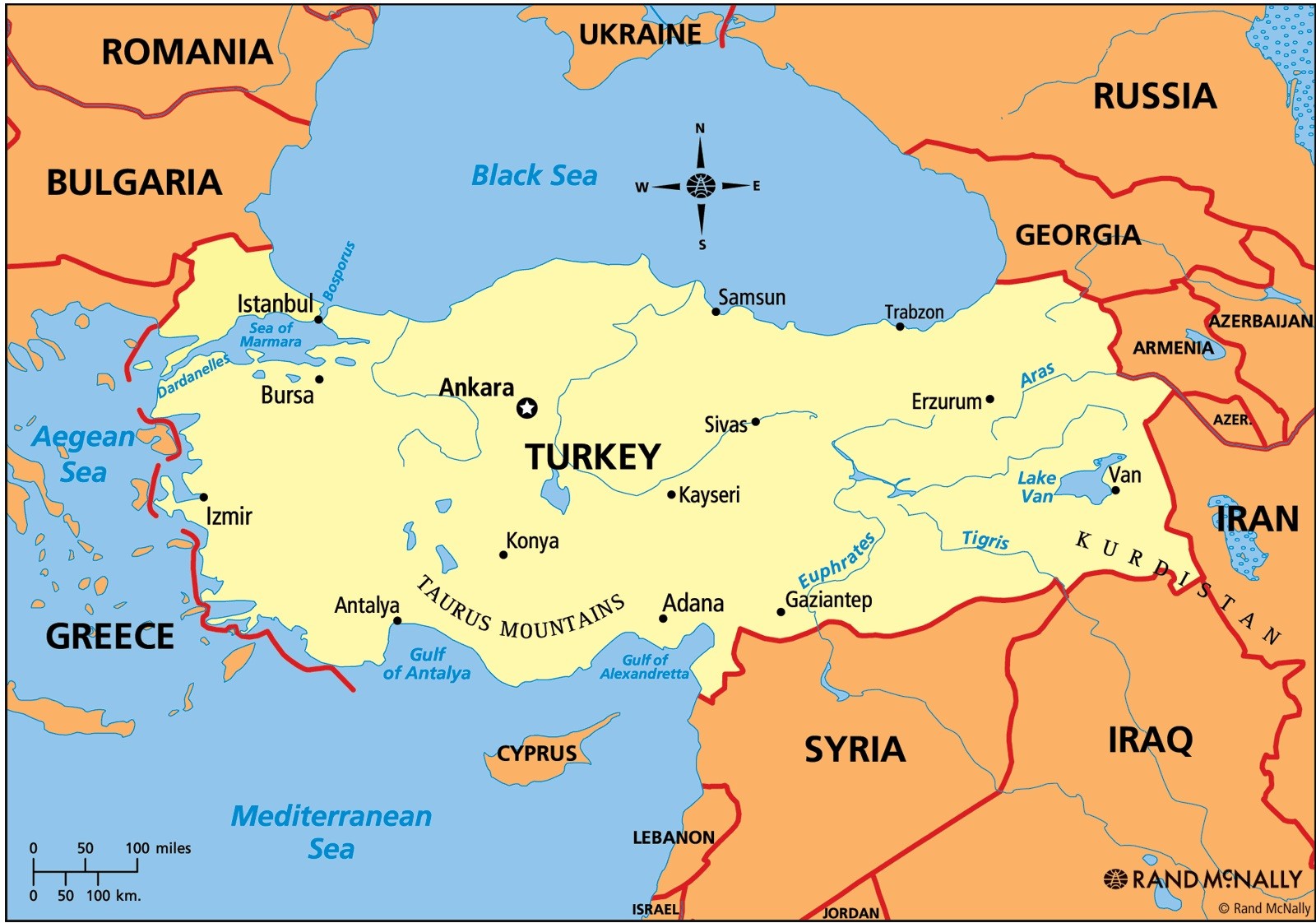
The Anatolian Peninsula, often referred to as Asia Minor, is a geographically and historically significant landmass situated at the easternmost point of the Mediterranean Sea. It serves as a bridge between Europe and Asia, connecting the continents both physically and culturally. This peninsula, encompassing modern-day Turkey, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the development of diverse cultures, and the birth of significant innovations, leaving an indelible mark on the world’s history.
A Land of Contrasts:
The Anatolian Peninsula is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, ranging from the snow-capped peaks of the Taurus Mountains to the fertile plains of the Central Anatolian Plateau. The western coast boasts a coastline dotted with picturesque bays and harbors, while the eastern regions are characterized by rugged terrain and arid landscapes. This geographical variety has shaped the peninsula’s history, influencing its agricultural practices, trade routes, and cultural development.
A Cradle of Civilization:
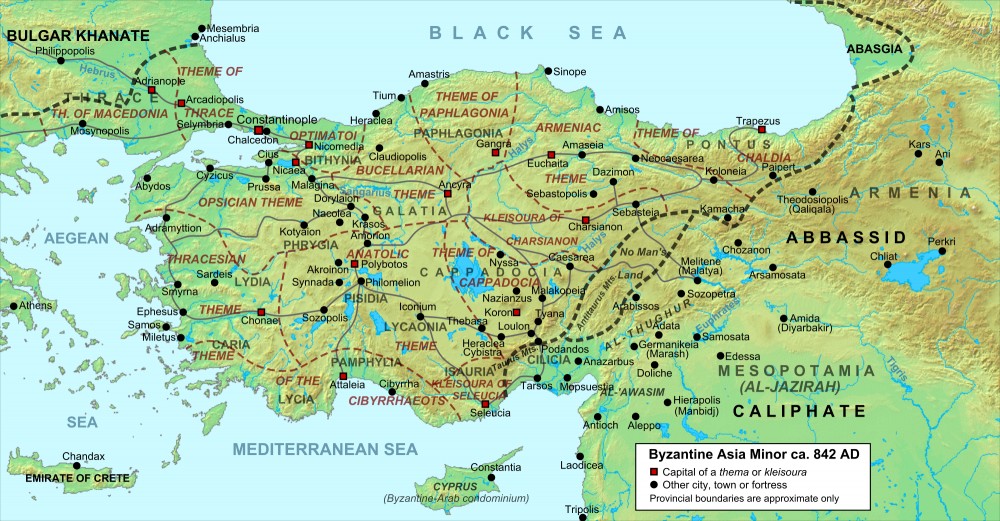
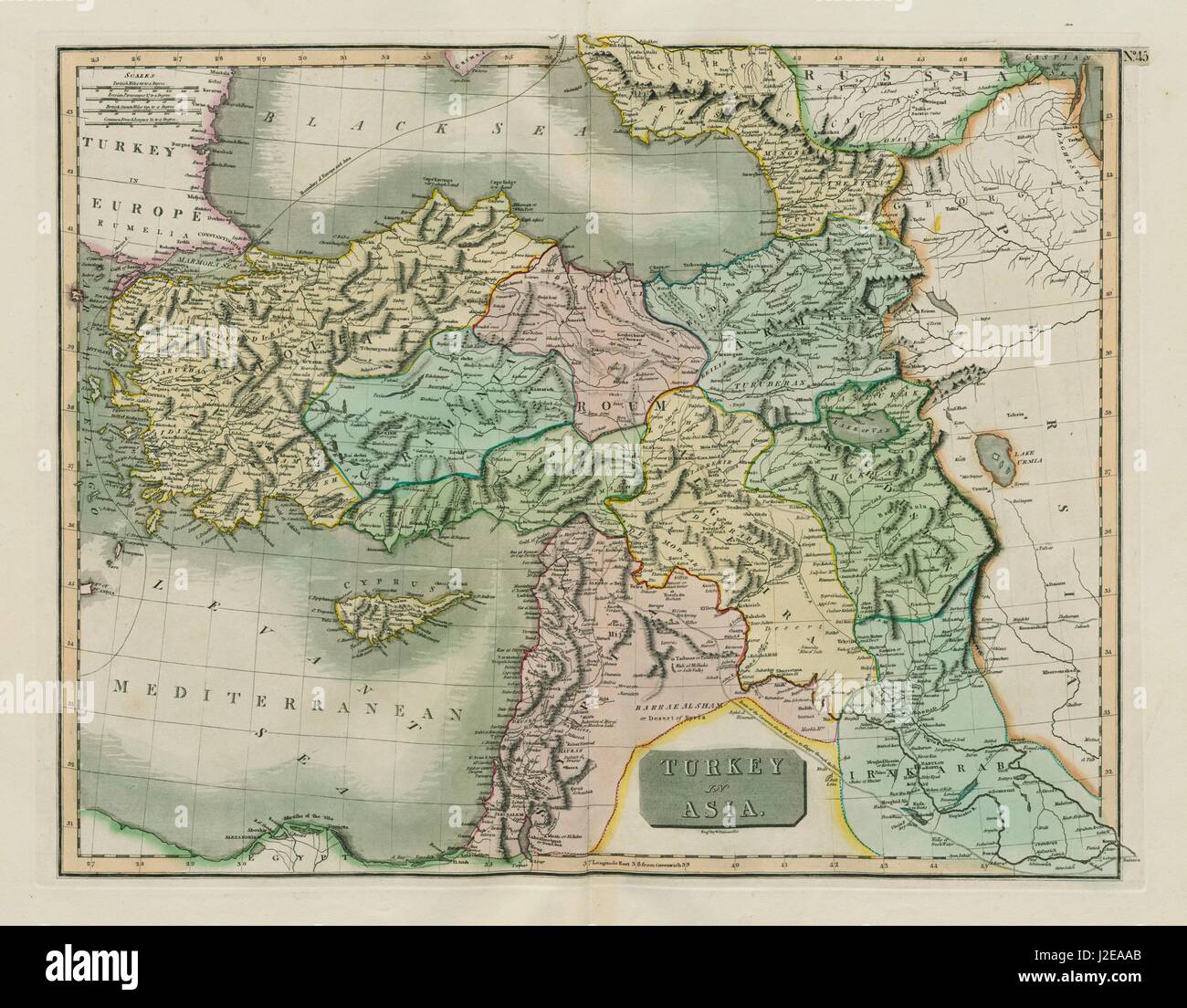
The Anatolian Peninsula has been a home to civilizations since the dawn of human history. The earliest settlements, dating back to the Neolithic period, attest to the region’s early agricultural advancements and the development of complex social structures. The Hittite Empire, with its sophisticated legal system and advanced metallurgy, flourished in the second millennium BCE, leaving behind impressive archaeological remains. The Greeks established colonies along the western coast, contributing to the region’s cultural and linguistic tapestry. The Romans, Persians, Byzantines, and Ottomans, among others, have all left their mark on the peninsula’s history, shaping its political landscape, cultural identity, and architectural legacy.
A Strategic Crossroads:
The Anatolian Peninsula’s location has made it a strategic crossroads throughout history. Its proximity to Europe, Asia, and Africa has facilitated trade and cultural exchange, connecting empires and civilizations. The Silk Road, a vital trade route connecting the East and West, traversed the peninsula, bringing goods and ideas from across the continent. Its strategic importance has also led to numerous conflicts, with empires vying for control of its resources and strategic locations.
A Tapestry of Cultures:
The Anatolian Peninsula is a melting pot of cultures, reflecting its long history of diverse influences. The region’s archaeological sites, ancient cities, and historical monuments provide a glimpse into the rich tapestry of civilizations that have called it home. From the ancient ruins of Troy and Ephesus to the Hagia Sophia and the Blue Mosque, the peninsula’s architectural legacy is a testament to the region’s artistic and cultural achievements.
A Land of Natural Beauty:
Beyond its historical significance, the Anatolian Peninsula offers breathtaking natural beauty. The turquoise waters of the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas, the snow-capped peaks of the Taurus Mountains, the fertile plains of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and the rugged landscapes of eastern Turkey offer a diverse range of landscapes for exploration and recreation. The peninsula’s natural resources, including fertile land, abundant water resources, and diverse flora and fauna, continue to support a rich and varied ecosystem.
The Anatolian Peninsula Today:
Today, the Anatolian Peninsula, encompassing modern-day Turkey, is a vibrant and dynamic region. Its strategic location continues to make it a crucial player in global affairs, while its rich cultural heritage attracts tourists and scholars from around the world. The country’s diverse population, blending elements of Eastern and Western cultures, reflects its unique historical legacy. The peninsula’s economic growth, driven by its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and growing tourism industry, is shaping its future prospects.
FAQs about the Anatolian Peninsula:
Q: What is the significance of the Anatolian Peninsula in world history?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula has been a crossroads of civilizations, witnessing the rise and fall of empires and the development of diverse cultures. Its strategic location facilitated trade and cultural exchange between continents, shaping the course of world history.
Q: What are some of the major civilizations that have inhabited the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The Hittites, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans, among others, have left their mark on the peninsula’s history, shaping its political landscape, cultural identity, and architectural legacy.
Q: What are some of the major geographical features of the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The peninsula features diverse landscapes, including the Taurus Mountains, the Central Anatolian Plateau, and the coastlines of the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas.
Q: What are some of the major economic activities in the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The peninsula’s economy is based on agriculture, tourism, manufacturing, and trade. Its strategic location and natural resources continue to drive economic growth.
Q: What are some of the major challenges facing the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The peninsula faces challenges related to political instability, economic inequality, and environmental degradation. However, its resilient population and strategic location continue to offer opportunities for growth and development.
Tips for Exploring the Anatolian Peninsula:
- Explore the ancient ruins and historical sites: Visit the ancient cities of Ephesus, Troy, and Pergamum to experience the peninsula’s rich history firsthand.
- Experience the natural beauty: Hike in the Taurus Mountains, explore the turquoise waters of the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas, or visit the diverse landscapes of eastern Turkey.
- Immerse yourself in the culture: Explore the bustling cities of Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir, and experience the unique blend of Eastern and Western cultures.
- Sample the local cuisine: Indulge in the delicious Turkish cuisine, featuring fresh ingredients, flavorful dishes, and aromatic spices.
- Learn about the region’s history: Visit museums and historical sites to gain a deeper understanding of the peninsula’s rich past.
Conclusion:
The Anatolian Peninsula stands as a testament to the enduring power of geography and history. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage have shaped its past, present, and future. The peninsula continues to be a vibrant and dynamic region, offering a fascinating blend of history, culture, and natural beauty for exploration and discovery. As a bridge between continents, the Anatolian Peninsula continues to play a crucial role in shaping the world’s future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!