Taiwan: An Island Nation at the Crossroads of Asia
Related Articles: Taiwan: An Island Nation at the Crossroads of Asia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Taiwan: An Island Nation at the Crossroads of Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Taiwan: An Island Nation at the Crossroads of Asia
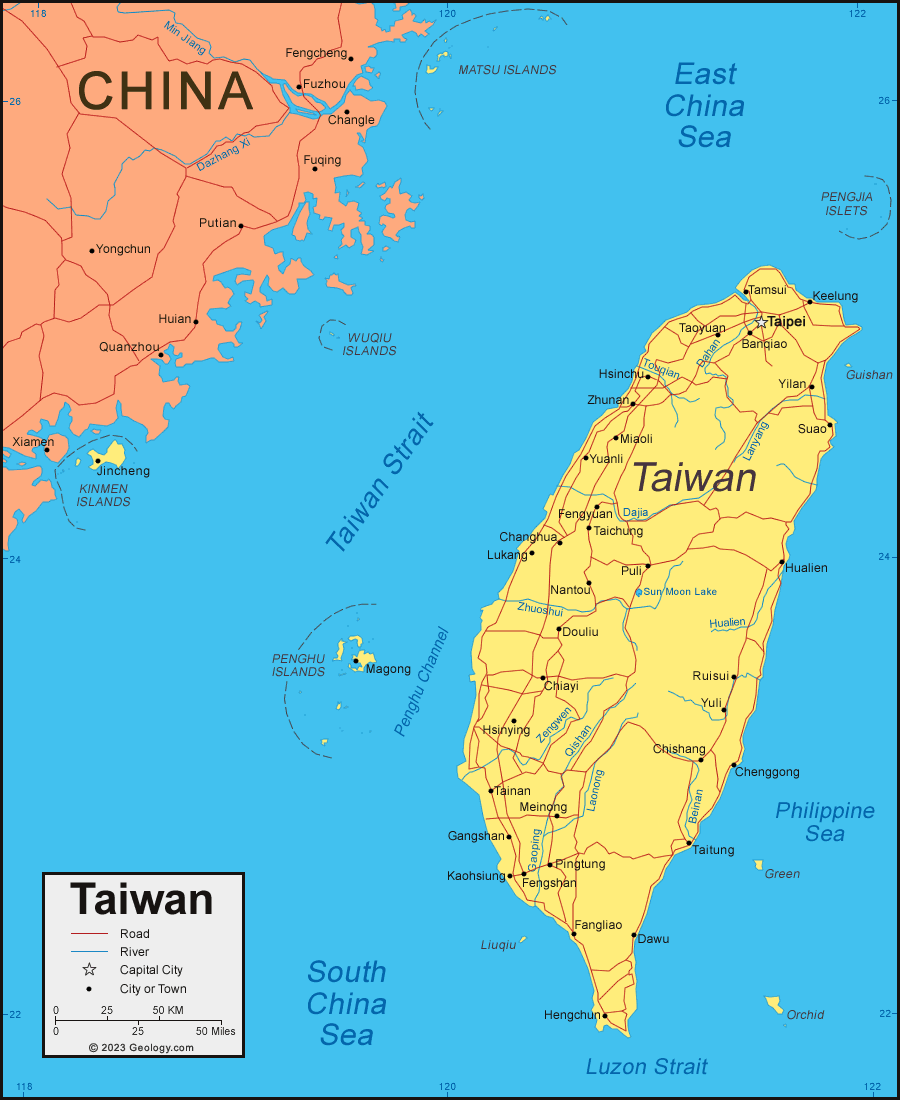
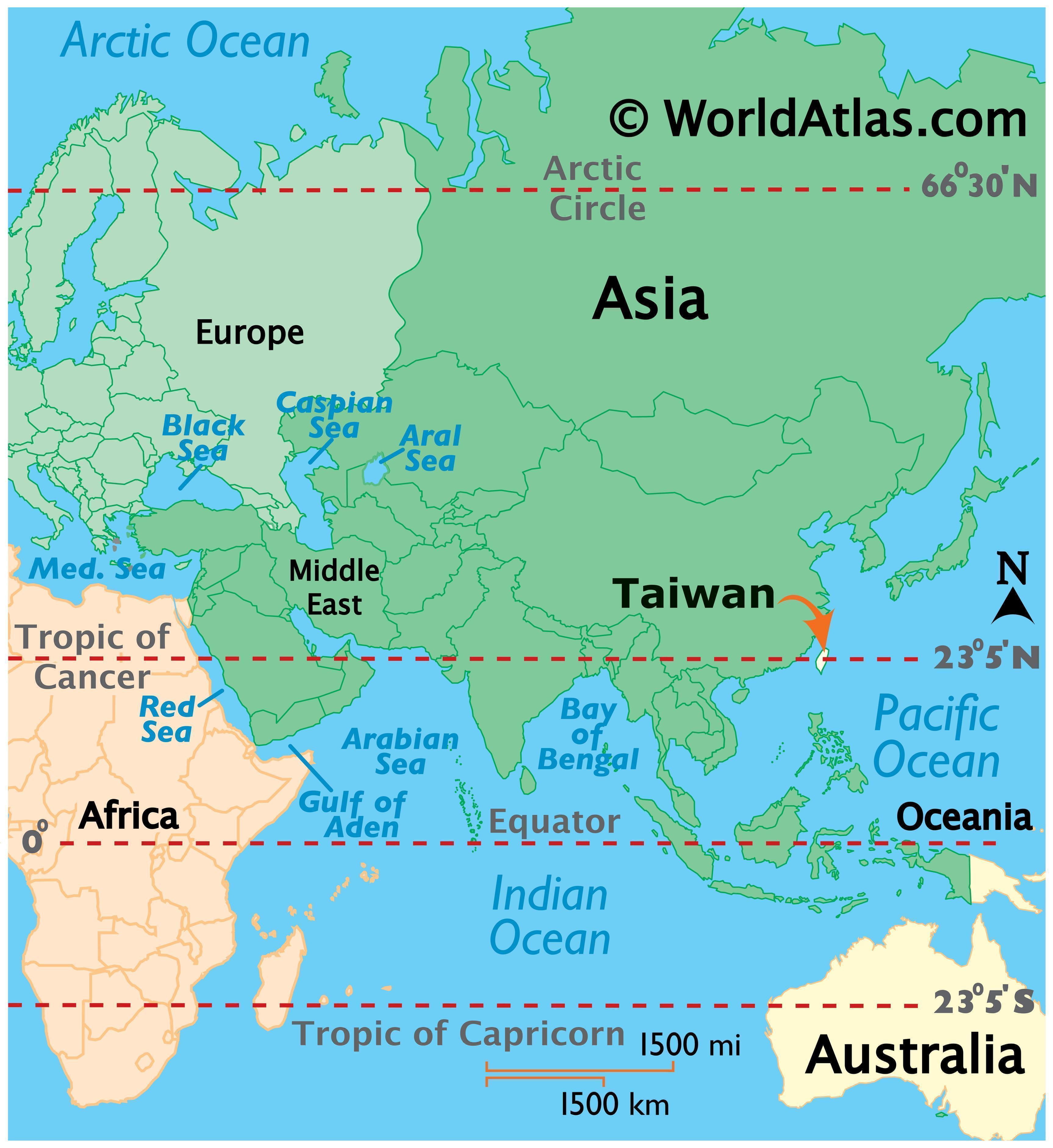
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island nation located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. Its strategic location in East Asia, coupled with its unique history and culture, has made Taiwan a significant player in the global arena.
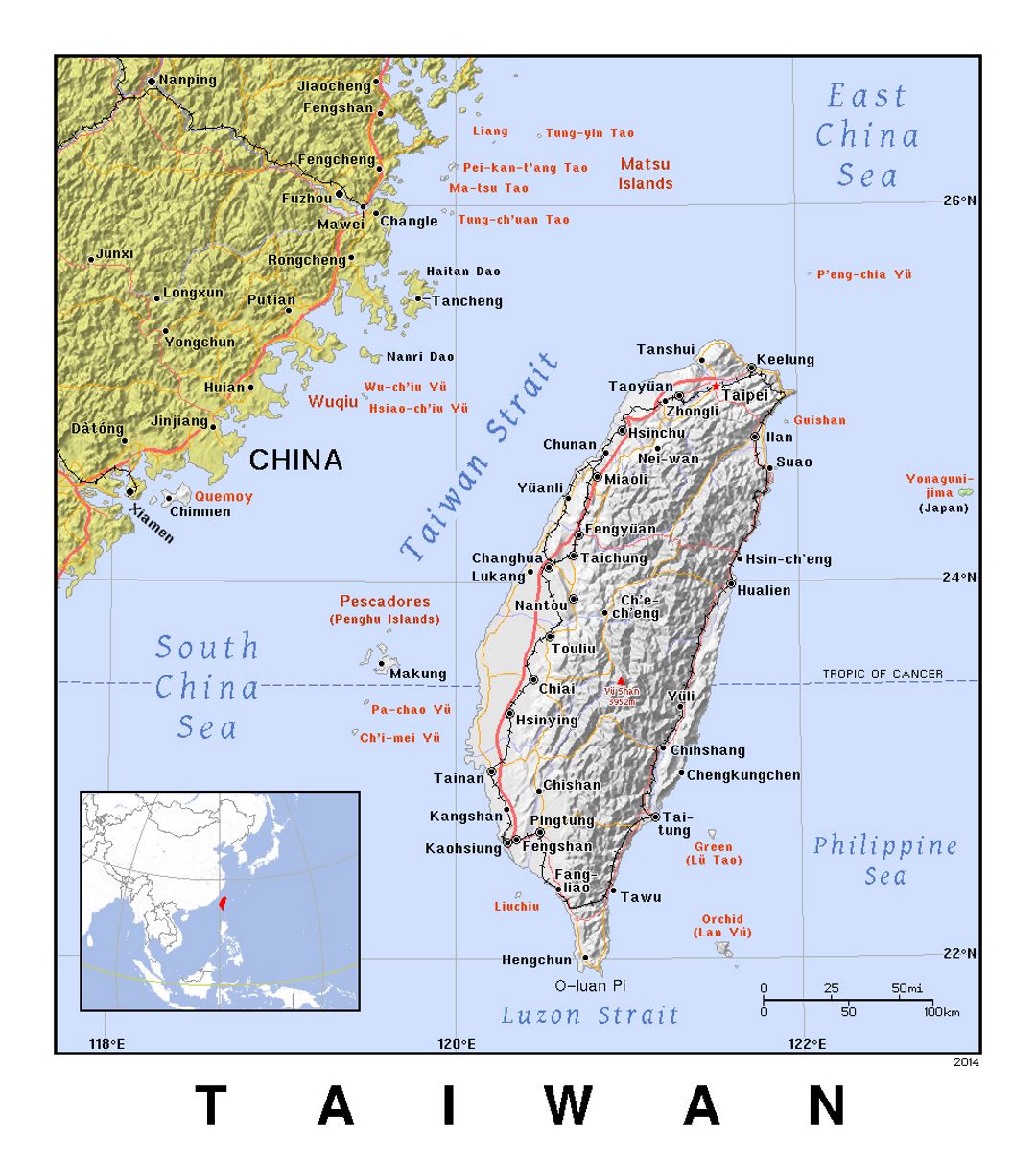
Taiwan’s Geographic Context
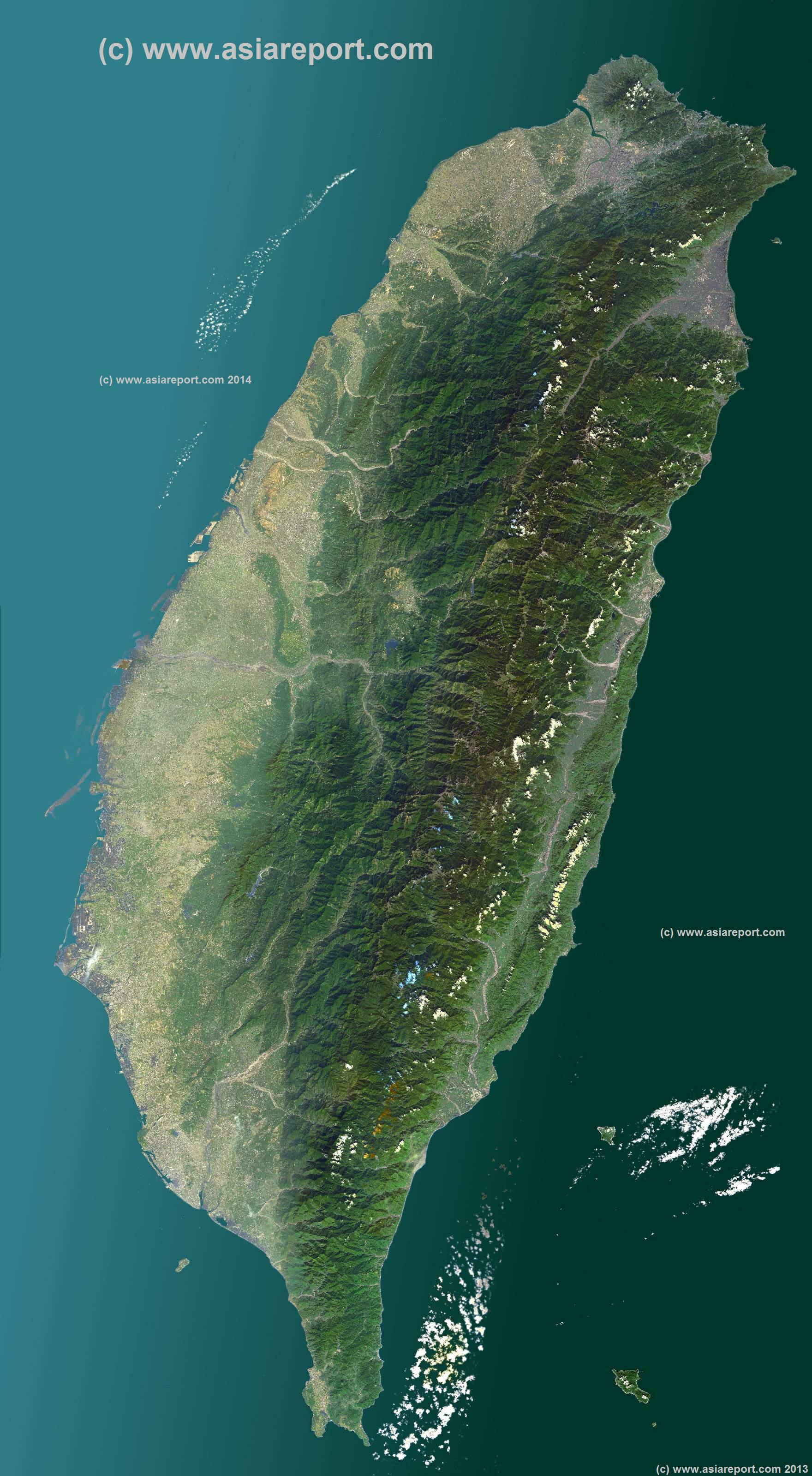
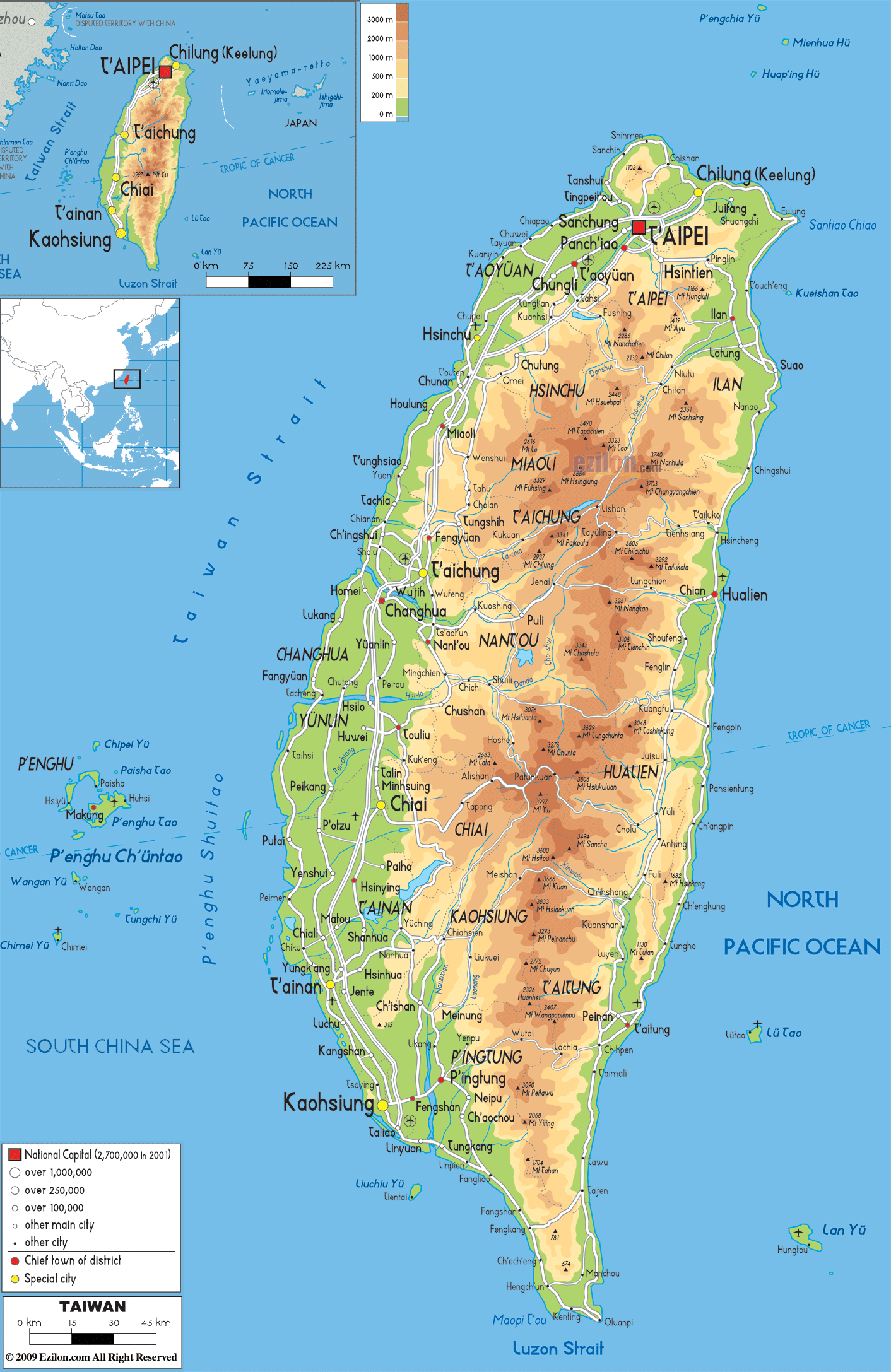
Taiwan’s main island, also known as Formosa, is the largest of the Ryukyu Archipelago, a chain of islands extending from Japan to Taiwan. The island is separated from mainland China by the Taiwan Strait, a body of water approximately 100 miles wide. Taiwan’s geography is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with the Central Mountain Range running along the island’s spine. This range, home to numerous peaks exceeding 3,000 meters, creates a diverse landscape of lush forests, rolling hills, and fertile plains.
Historical Significance
Taiwan’s history is marked by periods of foreign rule and internal strife. The island was initially inhabited by indigenous tribes before being claimed by the Dutch in the 17th century. The Qing dynasty of China subsequently took control in 1683, ruling until the late 19th century. Following the First Sino-Japanese War, Japan annexed Taiwan in 1895.
After World War II, Taiwan was returned to Chinese control, but the ensuing Chinese Civil War led to the defeat of the Nationalist government and their retreat to the island in 1949. The Chinese Communist Party, victorious in the mainland, established the People’s Republic of China (PRC), while the Nationalist government continued to govern Taiwan as the Republic of China.
Taiwan’s Political Landscape
The political relationship between Taiwan and mainland China remains a complex and sensitive issue. The PRC claims sovereignty over Taiwan, asserting that it is a breakaway province, while Taiwan maintains its own independent government and democratic system. This unresolved status has led to ongoing tensions between the two entities.
Despite these challenges, Taiwan has established itself as a vibrant democracy with a robust economy. It has a multi-party system, free and fair elections, and a strong commitment to human rights.
Economic Prowess
Taiwan’s economy has transformed from an agricultural base to a highly industrialized one. The country is a global leader in electronics manufacturing, with companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) being at the forefront of the semiconductor industry. Other key sectors include information technology, biotechnology, and tourism.
Cultural Tapestry
Taiwan boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage. Its indigenous populations have contributed their unique traditions, languages, and art forms. Chinese culture, particularly the Hokkien and Hakka dialects, has also had a significant influence. Taiwan’s cultural landscape is further enriched by its blend of traditional and modern influences, reflected in its cuisine, music, and literature.
Taiwan’s Global Role
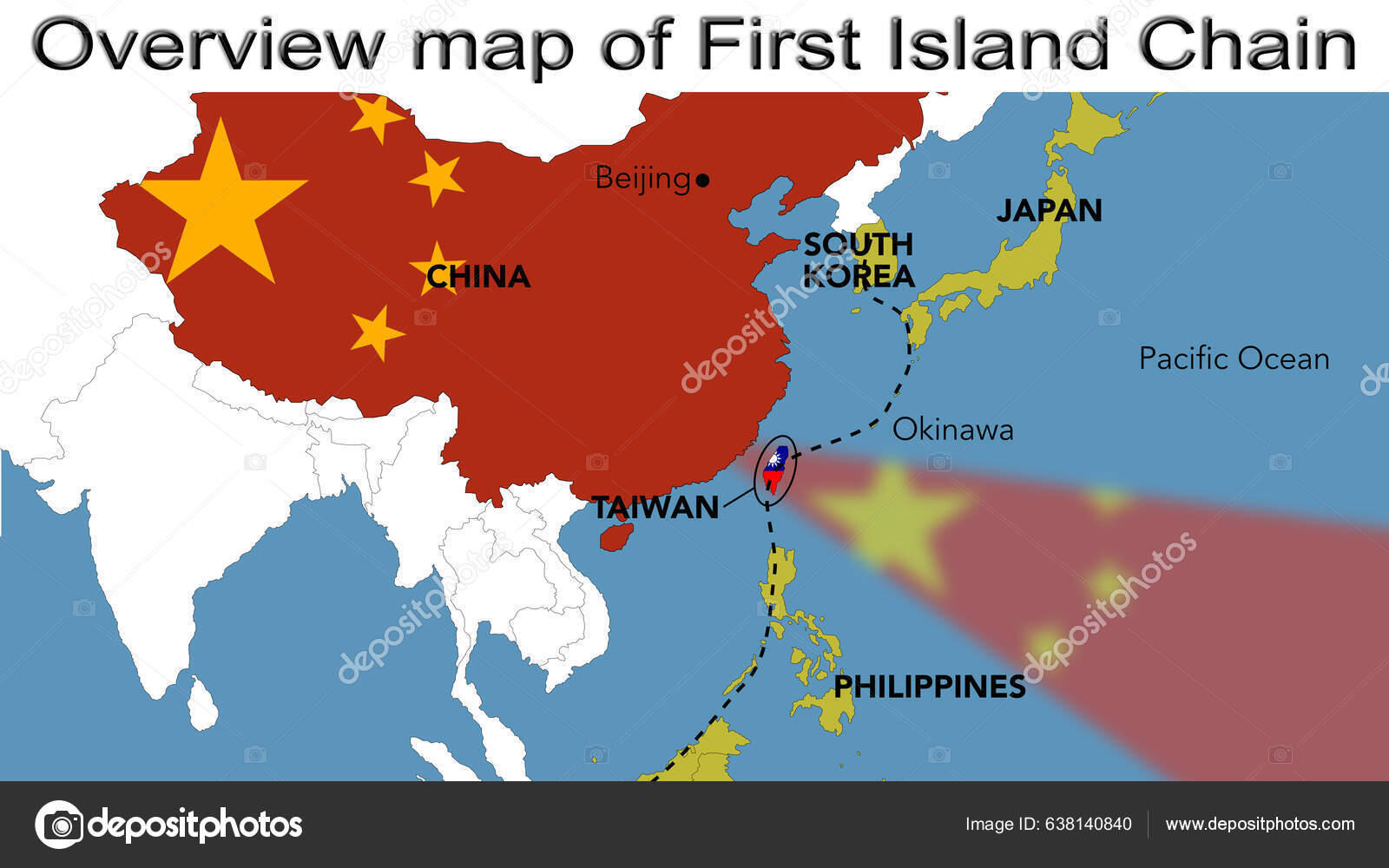
Taiwan plays a crucial role in the global economy and security. It is a major trading partner for many countries, particularly in East Asia. Its technological advancements have positioned it as a leader in innovation. Despite its political status, Taiwan has active diplomatic relations with many countries, including the United States, Japan, and the European Union.
FAQs
Q: What is the current political status of Taiwan?
A: Taiwan is currently governed by the Republic of China (ROC), which claims sovereignty over mainland China as well. However, the People’s Republic of China (PRC) considers Taiwan a breakaway province and asserts its claim over the island.
Q: What are the main challenges facing Taiwan?
A: The most significant challenge is the unresolved political status of the island, which leads to constant pressure from the PRC. Other challenges include economic competition from mainland China, environmental concerns, and social inequalities.
Q: How is Taiwan’s economy performing?
A: Taiwan has a highly developed and competitive economy, ranking among the top 20 economies in the world by GDP. It is a major exporter of electronics, semiconductors, and other high-tech products.
Q: What is Taiwan’s relationship with mainland China?
A: The relationship between Taiwan and mainland China is complex and often tense. While there is no formal diplomatic recognition, there is a growing economic and cultural exchange between the two sides. However, the PRC’s claim over Taiwan remains a major point of contention.
Tips for Visiting Taiwan
- Explore the diverse landscape: From the towering mountains to the bustling cities, Taiwan offers a variety of experiences for travelers.
- Immerse yourself in the culture: Sample the local cuisine, visit traditional temples, and learn about the island’s rich history.
- Embrace the local language: While English is widely spoken in tourist areas, learning a few basic phrases in Mandarin or Taiwanese can enhance your experience.
- Be mindful of the political situation: While Taiwan is a safe and welcoming destination, it is important to be aware of the sensitive political context.
Conclusion
Taiwan, an island nation at the heart of East Asia, holds a unique position in the global landscape. Its historical significance, economic dynamism, and vibrant culture make it a fascinating and important player on the world stage. While the political status of Taiwan remains a complex issue, the island’s resilience, democratic values, and commitment to progress continue to inspire and shape its future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Taiwan: An Island Nation at the Crossroads of Asia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!