Navigating the Risks: Understanding Louisiana’s Flood Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Risks: Understanding Louisiana’s Flood Zone Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Risks: Understanding Louisiana’s Flood Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Risks: Understanding Louisiana’s Flood Zone Map
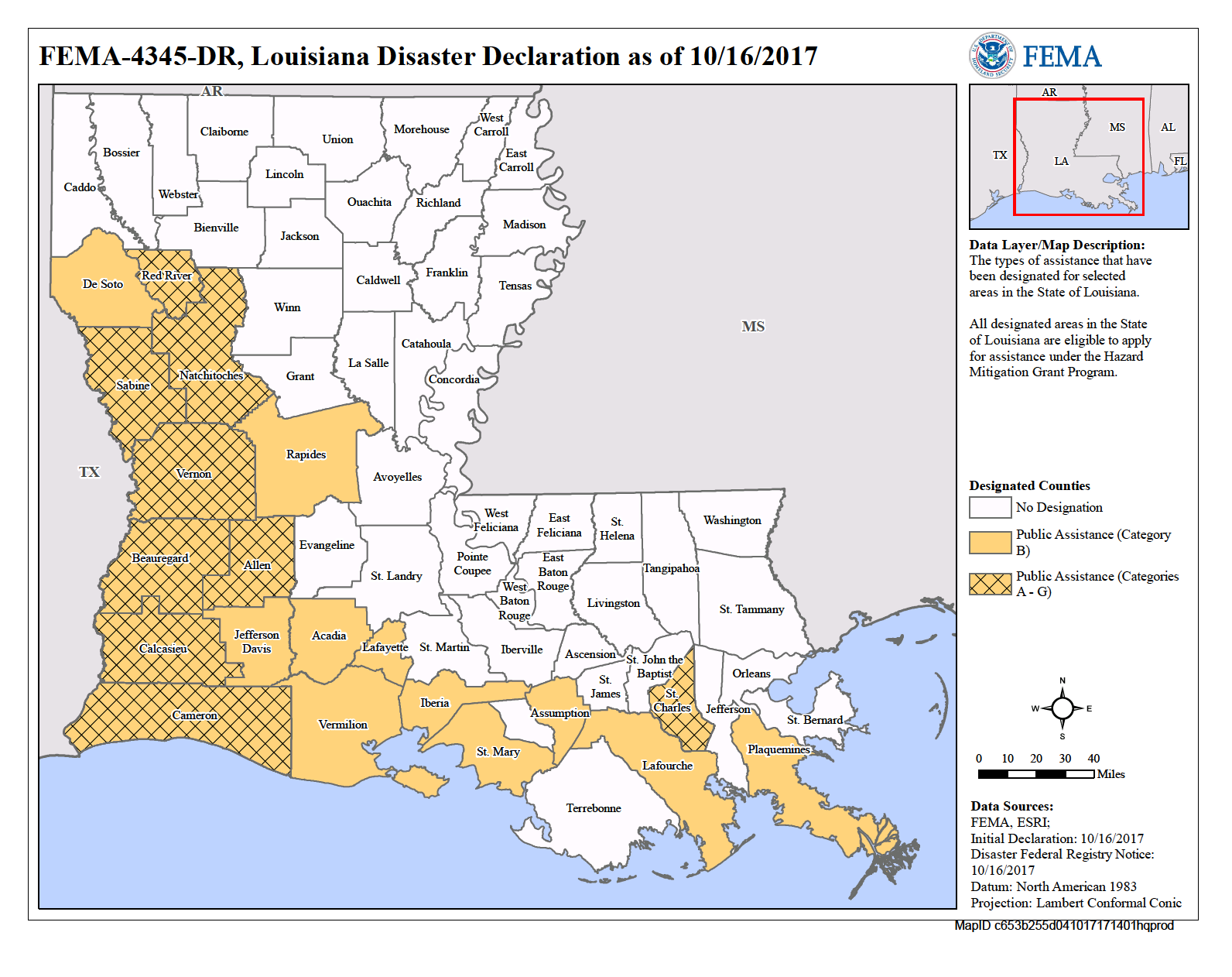
Louisiana, known for its vibrant culture, rich history, and captivating landscapes, also grapples with a significant challenge: the constant threat of flooding. This challenge is amplified by the state’s unique geography, characterized by low-lying coastal areas, extensive river systems, and a vulnerability to hurricanes. To mitigate these risks and guide responsible development, Louisiana utilizes a comprehensive flood zone map, a critical tool for individuals, communities, and policymakers alike.
Decoding the Map: A Visual Guide to Flood Risk
The Louisiana flood zone map, developed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), serves as a visual representation of areas susceptible to flooding. It categorizes zones based on the probability of flooding during a 100-year storm event, a statistical measure signifying a 1% chance of occurrence in any given year. This map is crucial for:
- Property Owners: Understanding the flood risk associated with their property helps homeowners make informed decisions about purchasing flood insurance, implementing mitigation measures, and planning for potential flooding events.
- Insurance Companies: The map serves as a foundation for setting flood insurance premiums, ensuring that rates accurately reflect the level of risk associated with specific properties.
- Local Governments: This tool assists municipalities in developing land use regulations, zoning ordinances, and infrastructure projects that promote flood resilience and minimize future damage.
- Emergency Responders: The map provides valuable information for planning evacuation routes, deploying resources, and coordinating rescue efforts during flooding events.
Understanding the Zones:
The Louisiana flood zone map utilizes a system of letters and numbers to categorize flood risk:
- Zone A: This zone indicates areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding, known as the "100-year floodplain." Properties within Zone A are generally required to purchase flood insurance if they have a federally backed mortgage.
- Zone B: Areas within Zone B have a lower risk of flooding than Zone A, with a less than 1% annual chance of flooding. While flood insurance is not mandatory, it is strongly recommended for properties in Zone B, as they can still experience flooding.
- Zone C: Properties within Zone C are considered to have a minimal risk of flooding. However, these areas can still be affected by flooding, especially during extreme events.
- Zone X: This zone represents areas outside the 100-year floodplain and is generally considered to have a low risk of flooding.
The Importance of Accuracy and Updates:
The Louisiana flood zone map is a dynamic document, constantly evolving as new data becomes available and flood risks change. FEMA conducts regular updates to the map, incorporating factors such as:
- Changes in Land Use: Development, deforestation, and alterations to natural drainage patterns can influence flood risks.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased precipitation, and more frequent extreme weather events contribute to evolving flood hazards.
- Infrastructure Improvements: Construction of levees, floodwalls, and drainage systems can impact flood zones.
Navigating the Map: A Guide for Homeowners
- Locate Your Property: Use online tools or contact your local parish government to pinpoint your property on the flood zone map.
- Understand Your Risk: Identify the flood zone category your property falls into.
- Consider Flood Insurance: Regardless of your property’s zone, evaluate the potential for flooding and weigh the benefits of flood insurance.
- Implement Mitigation Measures: Implement measures to reduce flood risk, such as elevating your property, installing flood vents, and sealing basement windows.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check for updates to the flood zone map and familiarize yourself with local flood preparedness plans.
FAQs about the Louisiana Flood Zone Map:
1. How do I find my property on the flood zone map?
The Louisiana Office of Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness (GOHSEP) offers an interactive flood zone map online, allowing users to search by address. Additionally, local parish governments maintain copies of the map and can assist with locating specific properties.
2. What does it mean if my property is in a flood zone?
Being located in a flood zone indicates a higher probability of flooding during a 100-year storm event. This means that your property is more likely to experience flooding than properties outside the designated zones.
3. Do I need flood insurance if my property is not in a flood zone?
While flood insurance is not mandatory for properties outside flood zones, it is highly recommended. Even areas with a low risk of flooding can still experience flooding during extreme events.
4. How often is the flood zone map updated?
FEMA regularly updates the flood zone map based on new data and evolving flood risks. These updates can occur at different intervals depending on the specific region and the changes being incorporated.
5. What if my property is in a flood zone, but I don’t have a mortgage?
Flood insurance is not mandatory for properties without a federally backed mortgage. However, it is still strongly recommended to protect against potential flood damage.
6. How can I reduce my flood risk?
Implementing flood mitigation measures can significantly reduce your risk of flood damage. These measures can include elevating your property, installing flood vents, sealing basement windows, and ensuring proper drainage around your home.
Tips for Using the Louisiana Flood Zone Map:
- Consult with Professionals: Engage with engineers, architects, and insurance agents to understand the implications of your property’s flood zone designation.
- Collaborate with Neighbors: Discuss flood risks and mitigation strategies with your neighbors to enhance community resilience.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and flood warnings issued by local authorities and GOHSEP.
- Participate in Community Programs: Engage in flood preparedness programs and community initiatives to improve preparedness and response.
Conclusion:
The Louisiana flood zone map is an essential tool for understanding and mitigating flood risks across the state. By utilizing this resource, individuals, communities, and policymakers can make informed decisions, implement effective mitigation strategies, and strengthen resilience against the ever-present threat of flooding. The map serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of preparedness, promoting a proactive approach to managing flood risks and safeguarding lives and property.
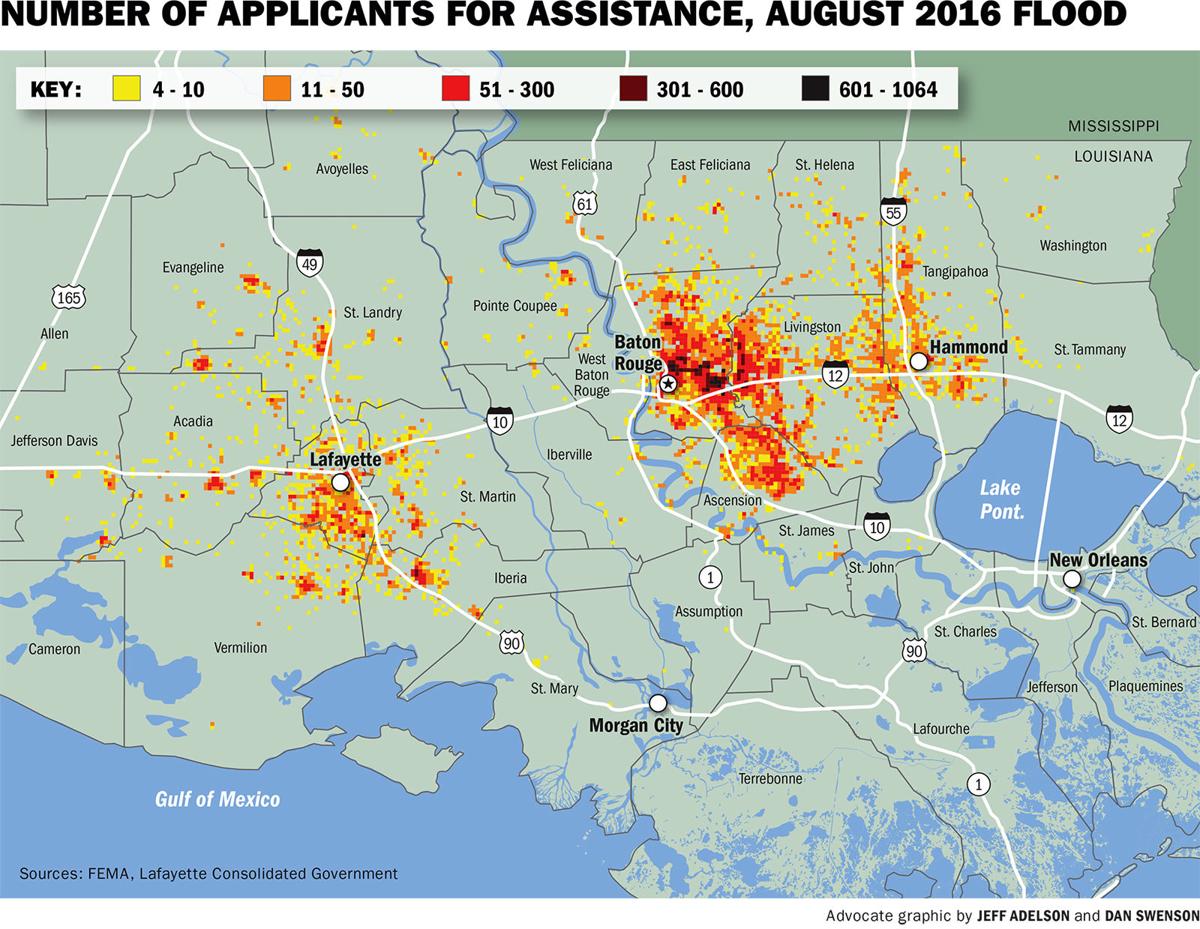

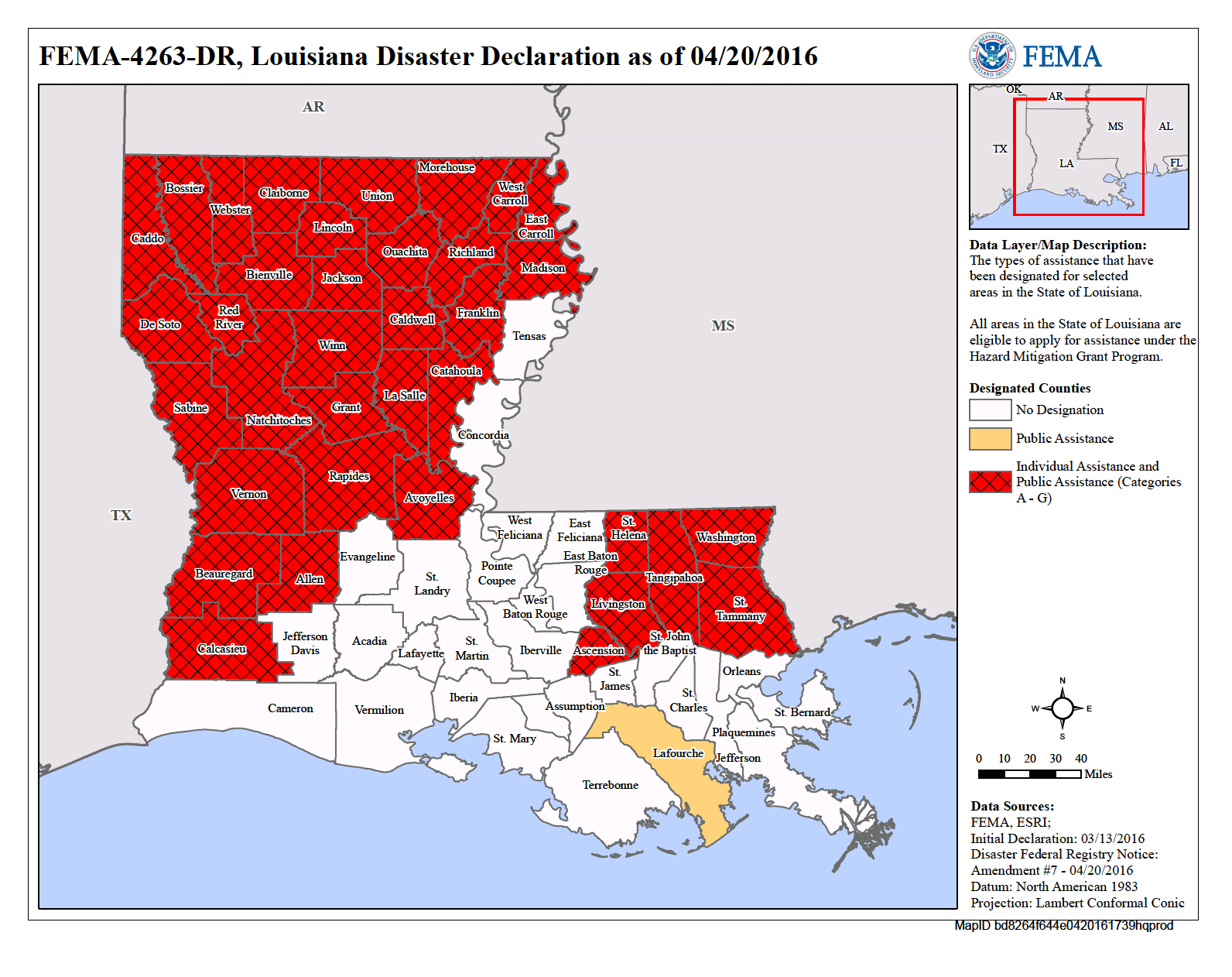

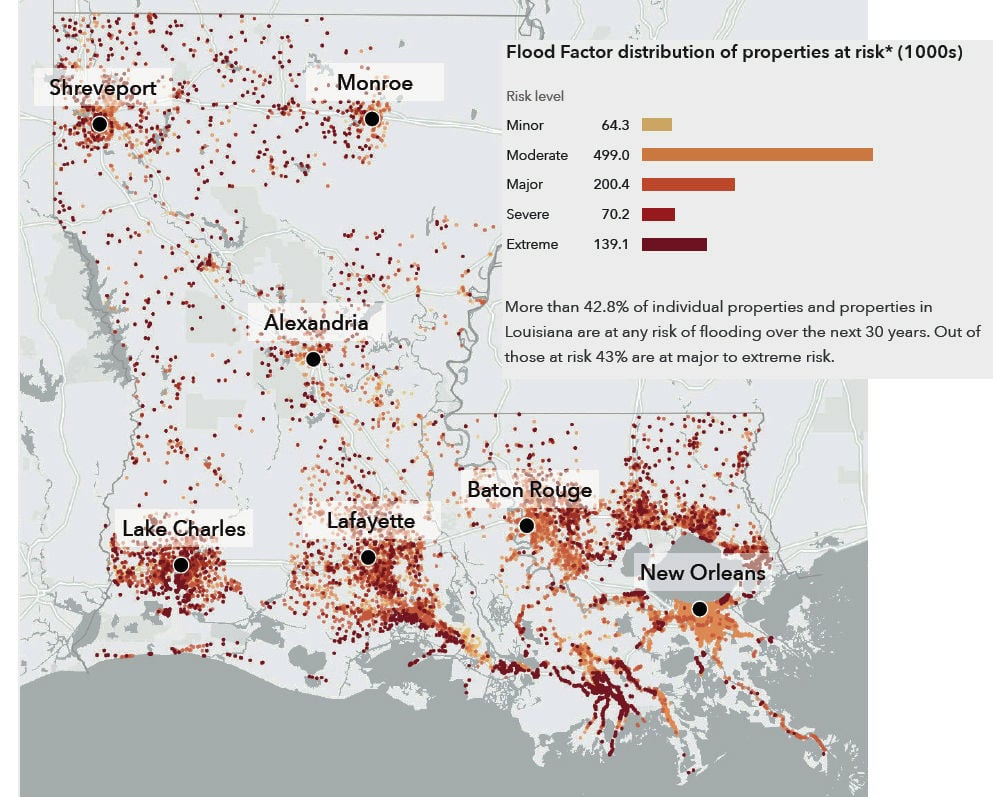
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Risks: Understanding Louisiana’s Flood Zone Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!