Navigating the Rails: A Comprehensive Guide to Rail Tracking Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Rails: A Comprehensive Guide to Rail Tracking Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Rails: A Comprehensive Guide to Rail Tracking Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Rails: A Comprehensive Guide to Rail Tracking Maps

In an era of interconnectedness, the movement of goods and people across vast distances is crucial. Rail transportation plays a vital role in this global network, providing an efficient and environmentally friendly mode of transport. To effectively manage this intricate system, a powerful tool has emerged: the rail tracking map.
Understanding the Essence of Rail Tracking Maps
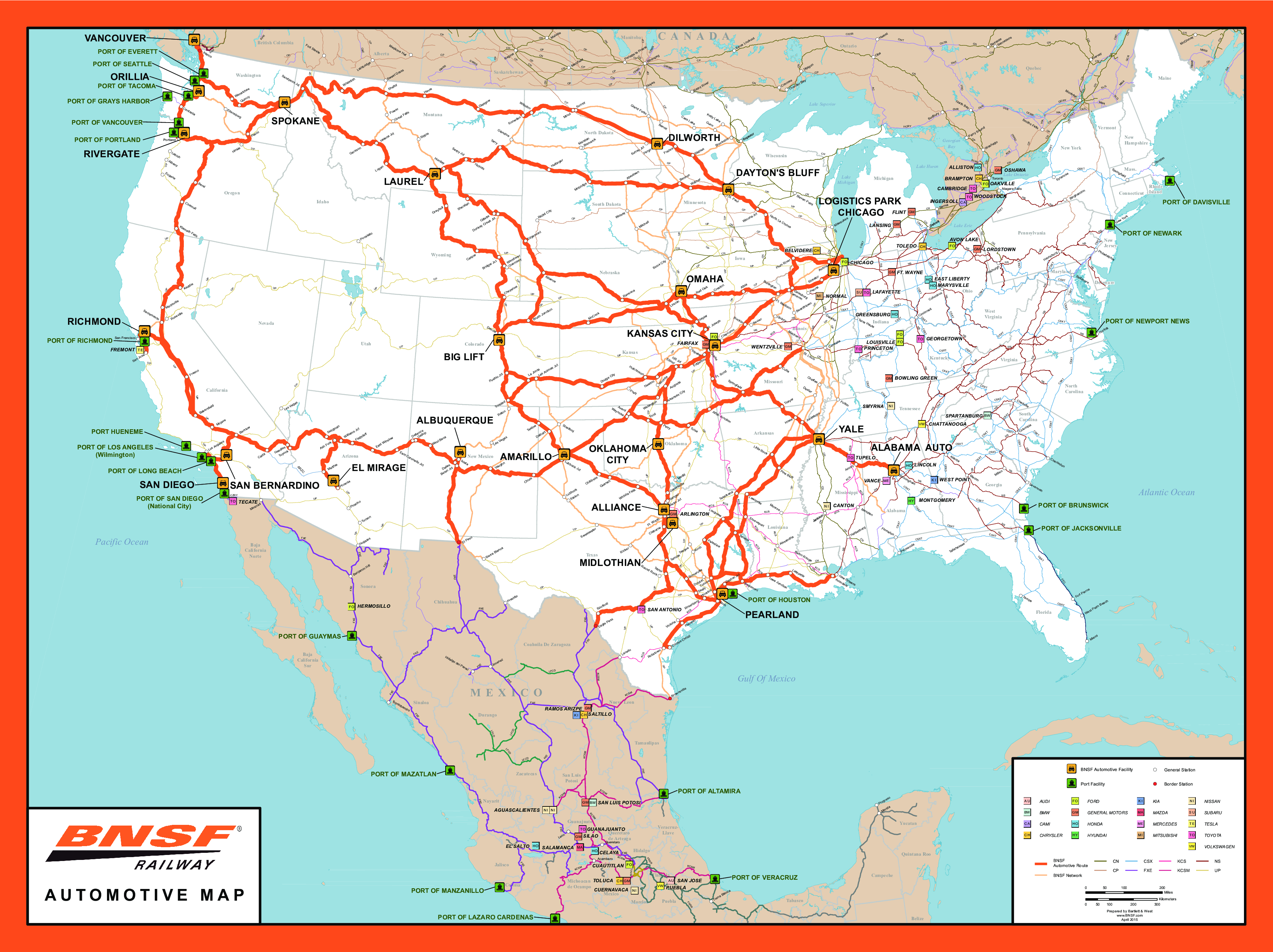
A rail tracking map is a visual representation of a railway network, displaying the intricate web of tracks, stations, and lines that connect different locations. This map serves as a dynamic and interactive platform, providing real-time information on train movements, schedules, and potential disruptions. Its purpose is to enhance transparency, efficiency, and overall control within the railway system.
The Anatomy of a Rail Tracking Map
A typical rail tracking map comprises several key elements:
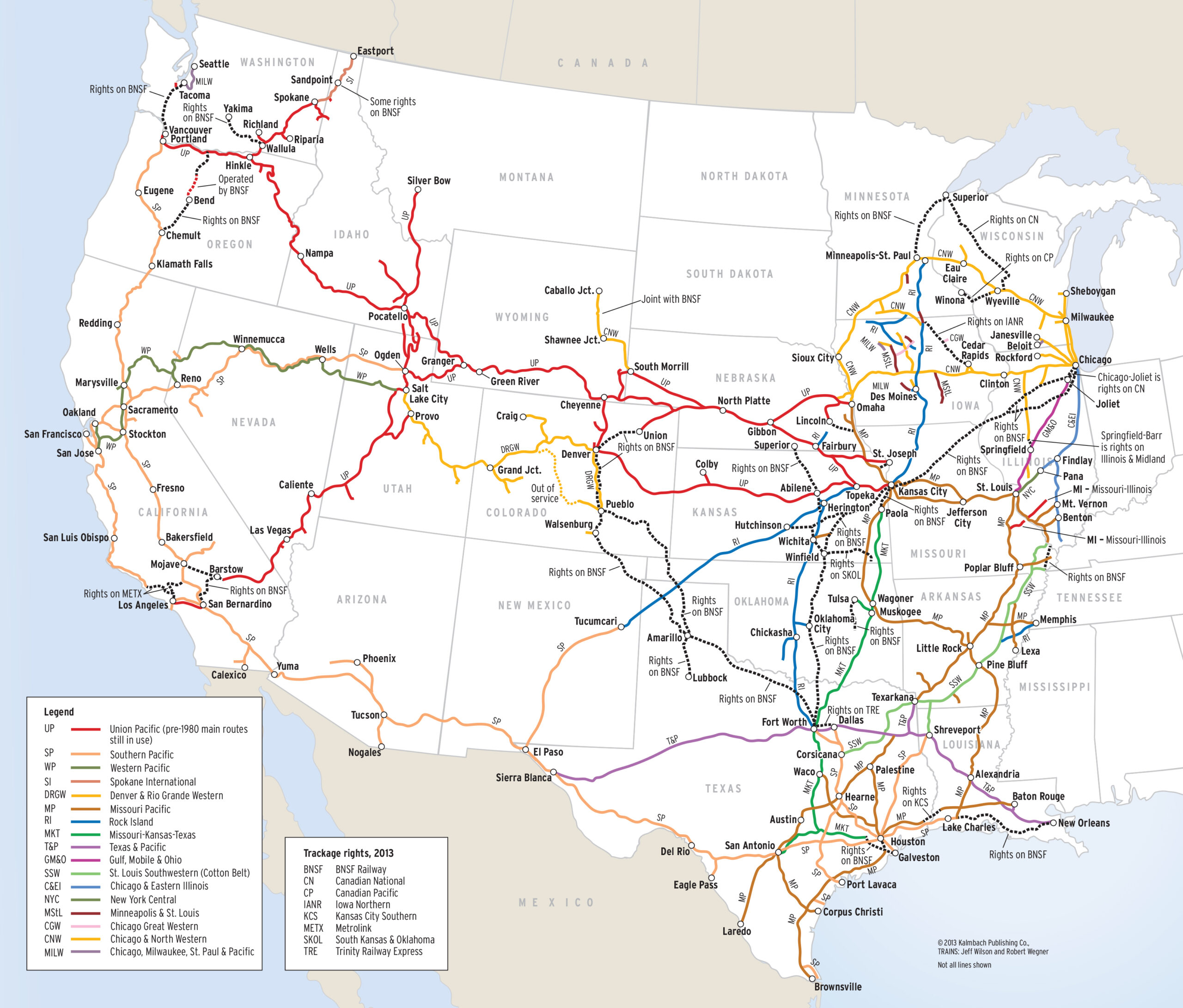
- Railway Network: The map depicts the entire rail network, including mainline tracks, branch lines, and switching yards.
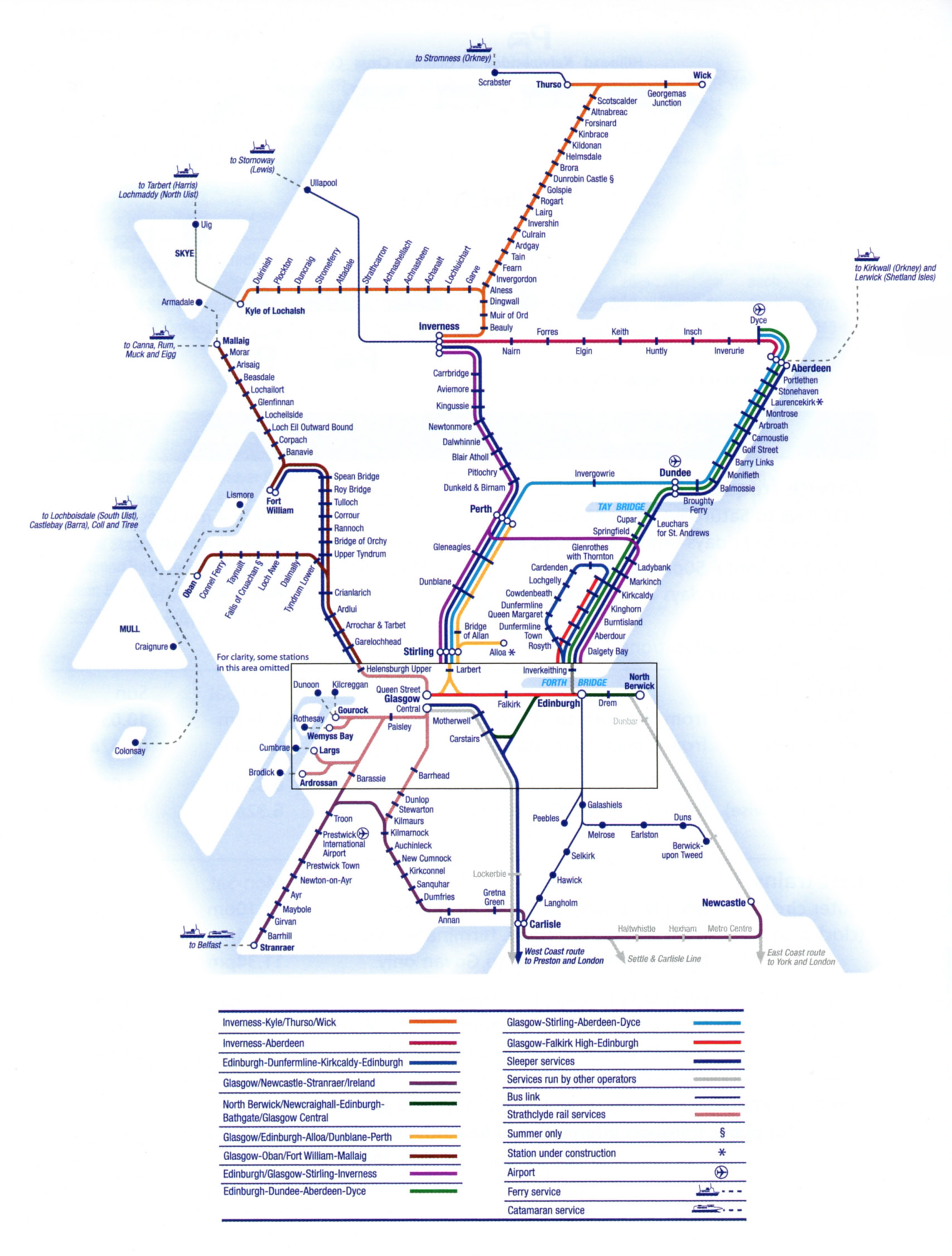
- Stations and Stops: Each station and stop along the route is clearly marked, along with its location and relevant information.
- Train Symbols: Different symbols are used to represent various types of trains, such as passenger, freight, or high-speed trains.
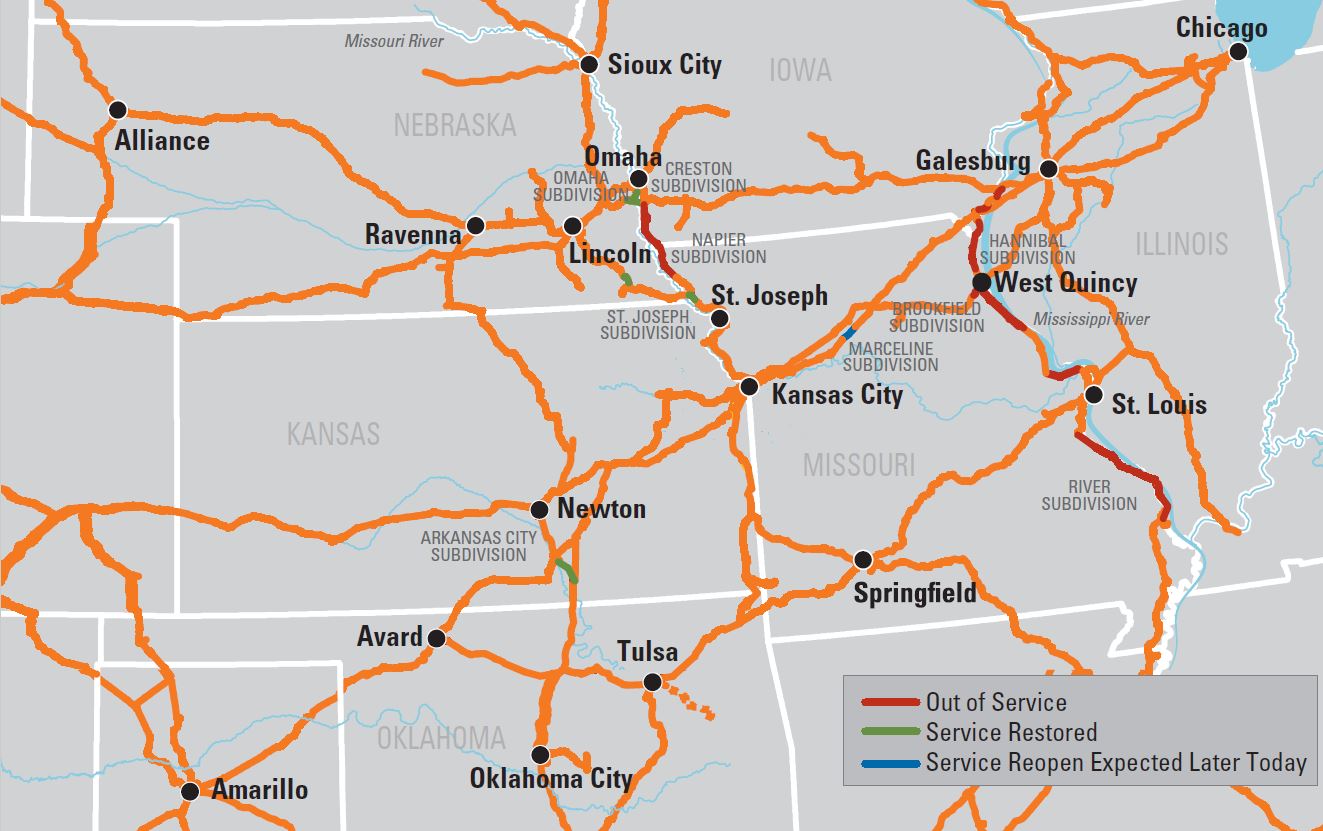
- Real-Time Data: The map displays the current location of trains, their estimated arrival and departure times, and potential delays or cancellations.
- Interactive Features: Many rail tracking maps offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom in and out, pan across the map, and access detailed information about specific trains or stations.
Benefits of Rail Tracking Maps: A Multifaceted Advantage
The implementation of rail tracking maps brings a multitude of benefits to various stakeholders within the railway ecosystem:
For Passengers:
- Improved Journey Planning: Passengers can easily track the progress of their train, anticipate delays, and adjust their travel plans accordingly.
- Enhanced Transparency: Real-time information on train movements provides passengers with a clear understanding of the status of their journey.
- Increased Accessibility: Passengers with disabilities or special needs can leverage the map to plan their travel routes and access station information.
For Rail Operators:
- Optimized Operations: Tracking trains in real-time allows operators to optimize train schedules, manage resources efficiently, and minimize delays.
- Improved Safety: The map enables operators to monitor train movements and identify potential safety hazards, ensuring the safety of passengers and crew.
- Enhanced Communication: Operators can use the map to communicate effectively with passengers about delays, cancellations, or other disruptions.
For Freight Companies:
- Streamlined Logistics: Freight companies can track their shipments in real-time, ensuring timely delivery and optimizing their supply chains.
- Reduced Costs: By minimizing delays and optimizing routes, freight companies can reduce transportation costs and improve overall efficiency.
- Improved Customer Service: Real-time tracking allows freight companies to provide customers with accurate information about the status of their shipments.
For Government Agencies:
- Effective Regulation: Government agencies can monitor the performance of the railway system and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Disaster Response: In emergency situations, the map provides a vital tool for coordinating rescue efforts and managing the flow of people and resources.
- Infrastructure Planning: The map can assist in identifying areas requiring infrastructure upgrades or expansion to meet future demand.
Beyond the Map: The Evolution of Rail Tracking Technology
Rail tracking maps are not limited to static, two-dimensional representations. The evolution of technology has ushered in a new era of advanced rail tracking systems:
- GPS Tracking: By integrating GPS technology, trains can be tracked with pinpoint accuracy, providing real-time location data.
- Mobile Apps: Many rail operators have developed mobile applications that allow passengers to access rail tracking maps and other information directly on their smartphones.
- Data Analytics: Advanced data analytics platforms can process vast amounts of data from rail tracking systems to identify trends, optimize operations, and predict potential disruptions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: How accurate are rail tracking maps?
A: The accuracy of rail tracking maps depends on the technology used and the quality of data available. While GPS tracking provides high accuracy, other systems may have limitations. It is important to note that real-time information is subject to change and may not always be completely accurate.
Q: Are rail tracking maps accessible to everyone?
A: Many rail operators provide free access to their rail tracking maps through websites or mobile applications. However, some maps may require registration or subscription fees.
Q: How are rail tracking maps used to improve safety?
A: By monitoring train movements and identifying potential hazards, rail tracking maps enable operators to take proactive measures to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of passengers and crew.
Q: What are the limitations of rail tracking maps?
A: While rail tracking maps provide valuable information, they may not always capture all aspects of the railway system. For instance, they may not provide information about track conditions, weather conditions, or other factors that could affect train operations.
Tips for Effective Use of Rail Tracking Maps:
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s features: Explore the map’s options and understand how to use its interactive features.
- Check for updates regularly: Real-time information is constantly changing, so it is important to check for updates before making travel plans.
- Use the map for journey planning: Plan your travel routes and anticipate potential delays or disruptions.
- Share the map with others: Share the map with family, friends, or colleagues who may be travelling by train.
- Provide feedback to the operator: If you encounter any inaccuracies or issues with the map, provide feedback to the operator so they can improve their services.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for a Modern Railway System
Rail tracking maps have become an indispensable tool for navigating the complex world of railway transportation. Their ability to provide real-time information, enhance transparency, and optimize operations makes them essential for passengers, operators, freight companies, and government agencies. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and integrated rail tracking systems to emerge, further revolutionizing the way we travel and transport goods by rail.

![]()
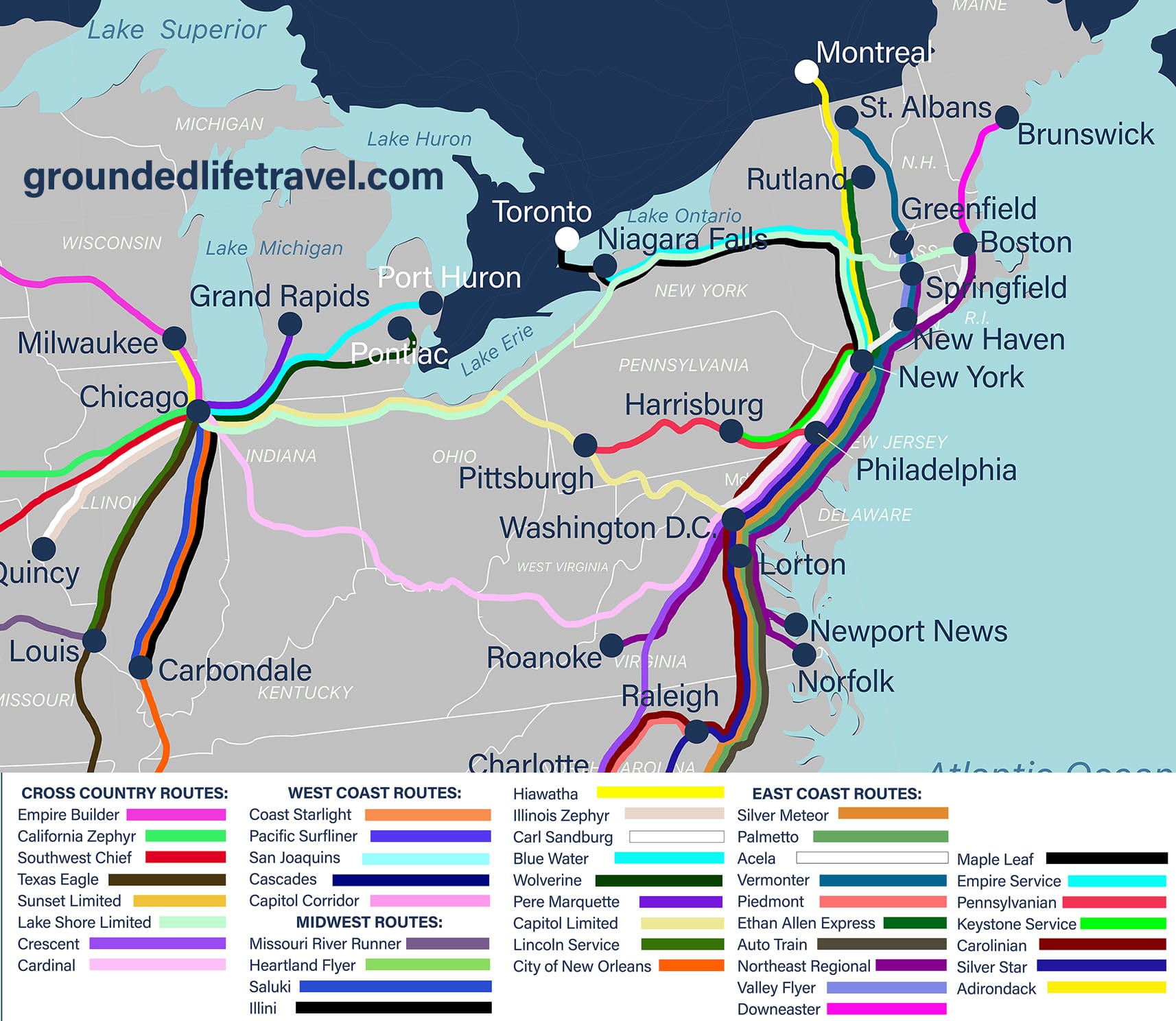
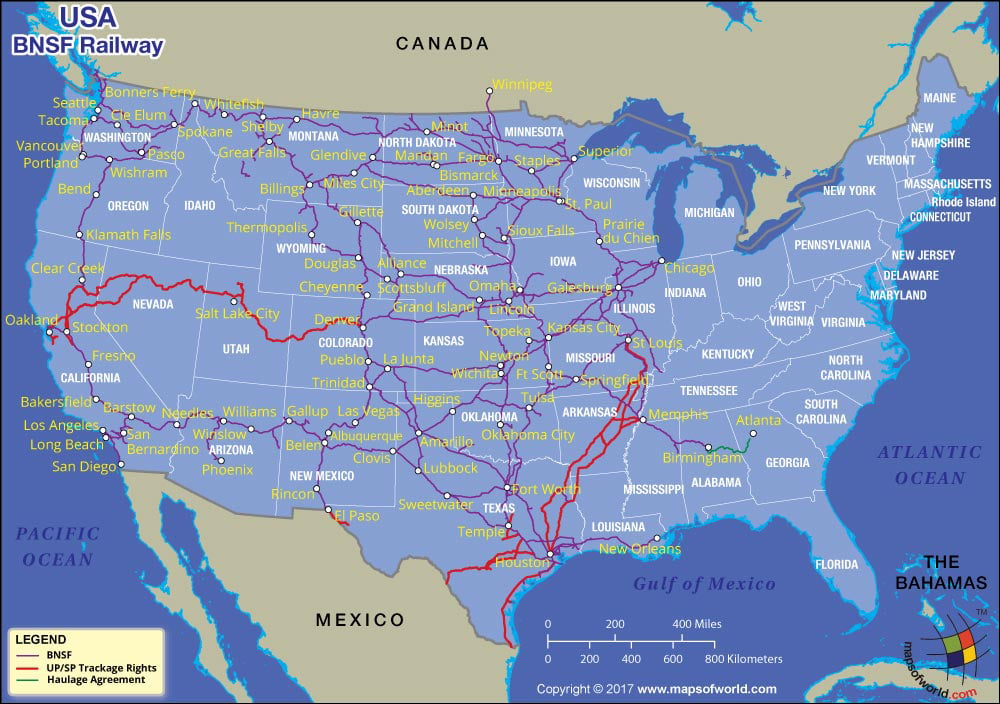
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Rails: A Comprehensive Guide to Rail Tracking Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!