Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map
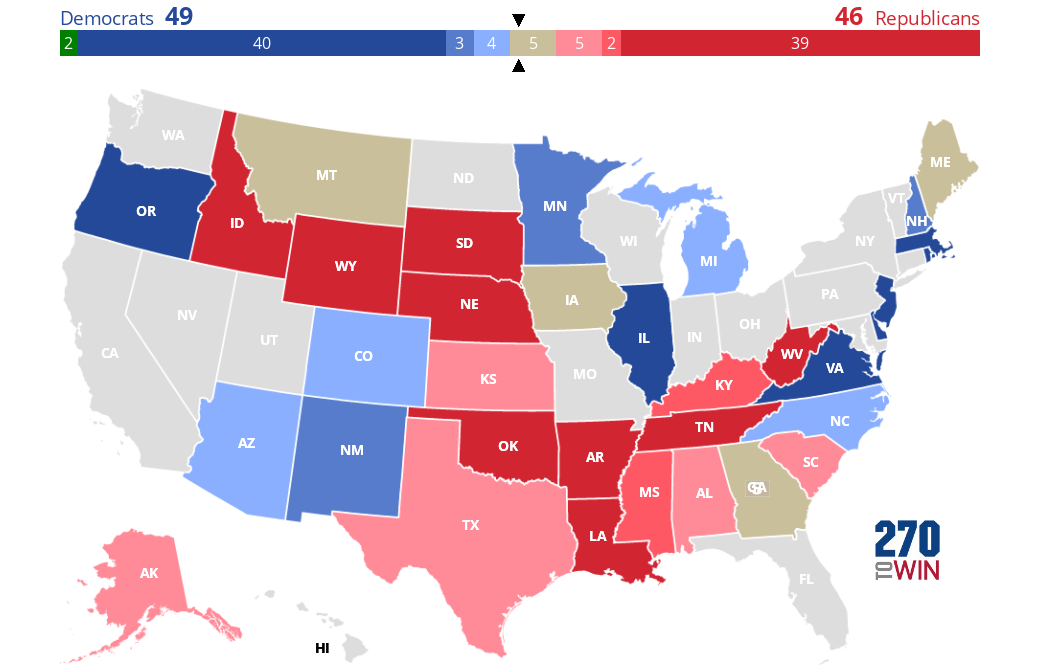
The 2020 US presidential election was a pivotal moment in American history, marked by intense political polarization and a close race. To understand the complex dynamics of the election and its implications, analysts and researchers rely on various tools, including the 2020 Election Consensus Map. This map, a product of data aggregation and analysis, provides a comprehensive and insightful view of the electoral landscape, showcasing the distribution of votes across the nation.
The Foundation of the Consensus Map:
The Consensus Map is not a single entity but rather a compilation of data from multiple reputable sources, each employing their own methodologies for predicting election outcomes. These sources include:
- Polling Data: Surveys conducted by organizations like FiveThirtyEight, RealClearPolitics, and others, which gather information from a sample of voters to gauge their preferences.
- Historical Voting Patterns: Analyzing past election results to identify trends and predict future outcomes based on demographic factors and voting history.
- Economic Indicators: Economic data, such as unemployment rates and GDP growth, can influence voter sentiment and impact election results.
- Expert Analysis: Political analysts and commentators offer insights based on their knowledge of the political landscape, campaign strategies, and voter behavior.
Interpreting the Consensus Map:
The Consensus Map presents a visual representation of the projected electoral outcome, typically displayed as a color-coded map of the United States. Each state is assigned a color based on the probability of a particular candidate winning its electoral votes. For example, a state with a high probability of voting for the Democratic candidate may be shaded blue, while a state with a high probability of voting for the Republican candidate may be shaded red.
The map’s key benefit lies in its ability to synthesize diverse data sources and present a nuanced picture of the electoral landscape. It highlights key battleground states, where the outcome is uncertain and the election could be decided, and identifies states where the outcome is more predictable. This information is crucial for understanding the potential paths to victory for each candidate and assessing the overall likelihood of their success.
Beyond the Colors:
While the Consensus Map provides a valuable snapshot of the electoral landscape, it is important to note that it is not a definitive prediction. The map reflects the current state of knowledge based on available data, but unforeseen events and shifts in voter sentiment could alter the outcome.
Furthermore, the Consensus Map does not capture the full complexity of the election. It focuses primarily on the presidential race, but it does not account for the numerous other races taking place at the state and local levels. It also does not reflect the nuanced political ideologies and voting preferences within each state.
The Importance of the Consensus Map:
Despite its limitations, the Consensus Map remains a valuable tool for understanding the 2020 election. It provides a clear and concise overview of the key battlegrounds, allowing voters, analysts, and political strategists to focus their attention on the areas most likely to influence the outcome.
The map also fosters informed discourse by providing a common framework for understanding the election. It facilitates discussions about the potential impact of various factors on the outcome and encourages deeper analysis of the political landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions about the 2020 Election Consensus Map:
1. How is the Consensus Map created?
The Consensus Map is generated by aggregating data from multiple reputable sources, including polling data, historical voting patterns, economic indicators, and expert analysis. Each source employs its own methodology for predicting election outcomes, and the Consensus Map combines these predictions to provide a comprehensive view of the electoral landscape.
2. How accurate is the Consensus Map?
The accuracy of the Consensus Map depends on the accuracy of the underlying data sources and the effectiveness of the aggregation process. While it is a valuable tool for understanding the election, it is not a guaranteed prediction. Unforeseen events and shifts in voter sentiment can influence the outcome.
3. How does the Consensus Map differ from individual predictions?
The Consensus Map combines multiple predictions into a single representation, providing a more nuanced and comprehensive view of the electoral landscape. Individual predictions may focus on specific factors or methodologies, while the Consensus Map aims to incorporate a wider range of perspectives.
4. What are the limitations of the Consensus Map?
The Consensus Map is a snapshot of the electoral landscape at a particular point in time. It does not account for unforeseen events, shifts in voter sentiment, or the complex political dynamics within each state. Furthermore, it focuses primarily on the presidential race and does not reflect the numerous other races taking place at the state and local levels.
5. How can the Consensus Map be used?
The Consensus Map can be used by voters, analysts, and political strategists to understand the key battlegrounds, assess the potential paths to victory for each candidate, and engage in informed discussions about the election.
Tips for Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map:
- Consider the source: Pay attention to the data sources used to create the Consensus Map and their respective methodologies.
- Look for trends: Observe changes in the map over time to identify shifts in voter sentiment and potential turning points in the election.
- Focus on battleground states: Pay close attention to states where the outcome is uncertain, as these states are likely to determine the election’s result.
- Remember the limitations: The Consensus Map is a valuable tool but not a definitive prediction. It is essential to remain aware of its limitations and consider other factors that may influence the outcome.
Conclusion:
The 2020 Election Consensus Map provides a valuable framework for understanding the complex political landscape of the election. It synthesizes diverse data sources and presents a comprehensive picture of the electoral landscape, highlighting key battlegrounds and identifying potential paths to victory for each candidate. While it is not a guaranteed prediction, the Consensus Map serves as a valuable tool for informed discourse and analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of the election and its implications.
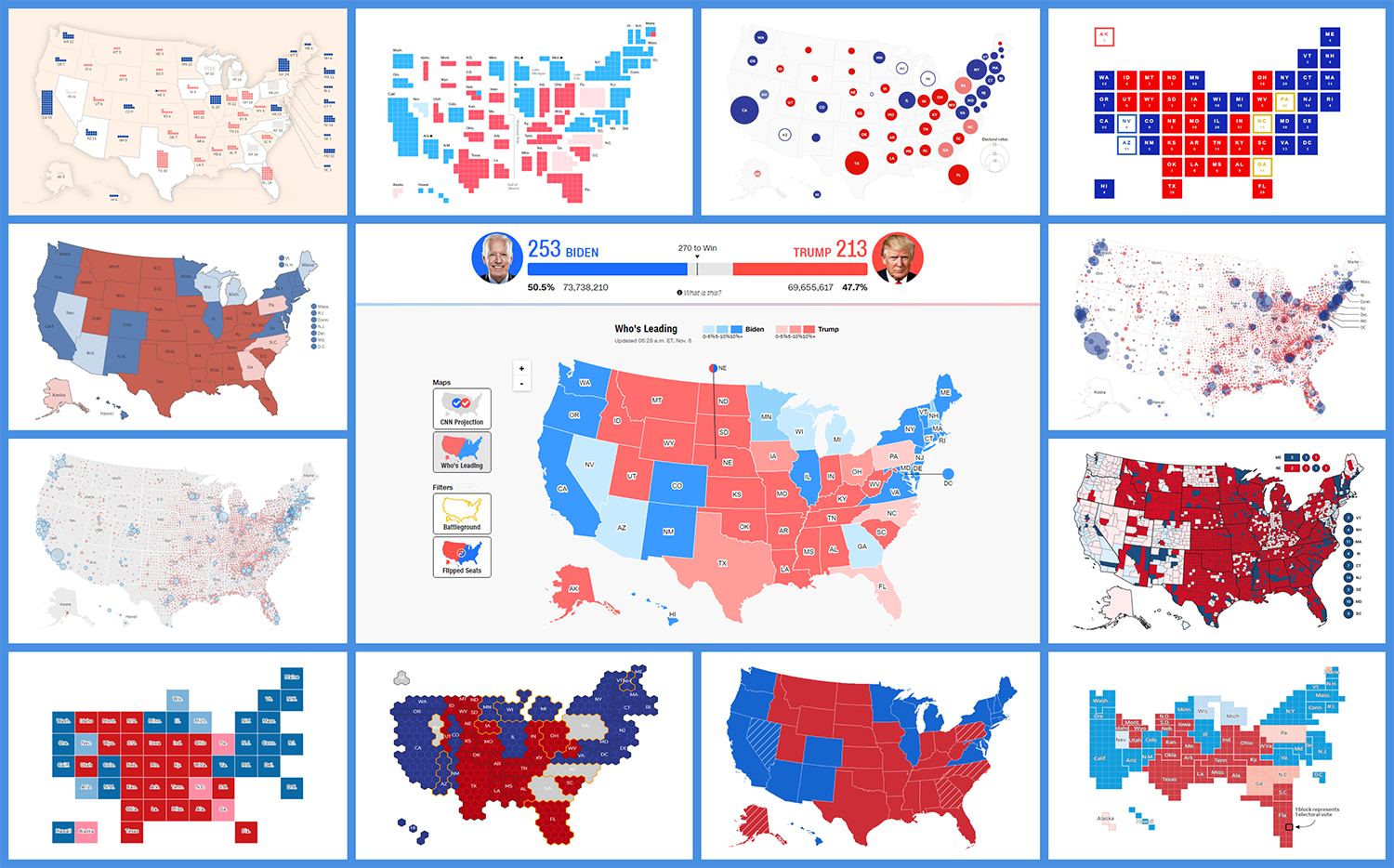
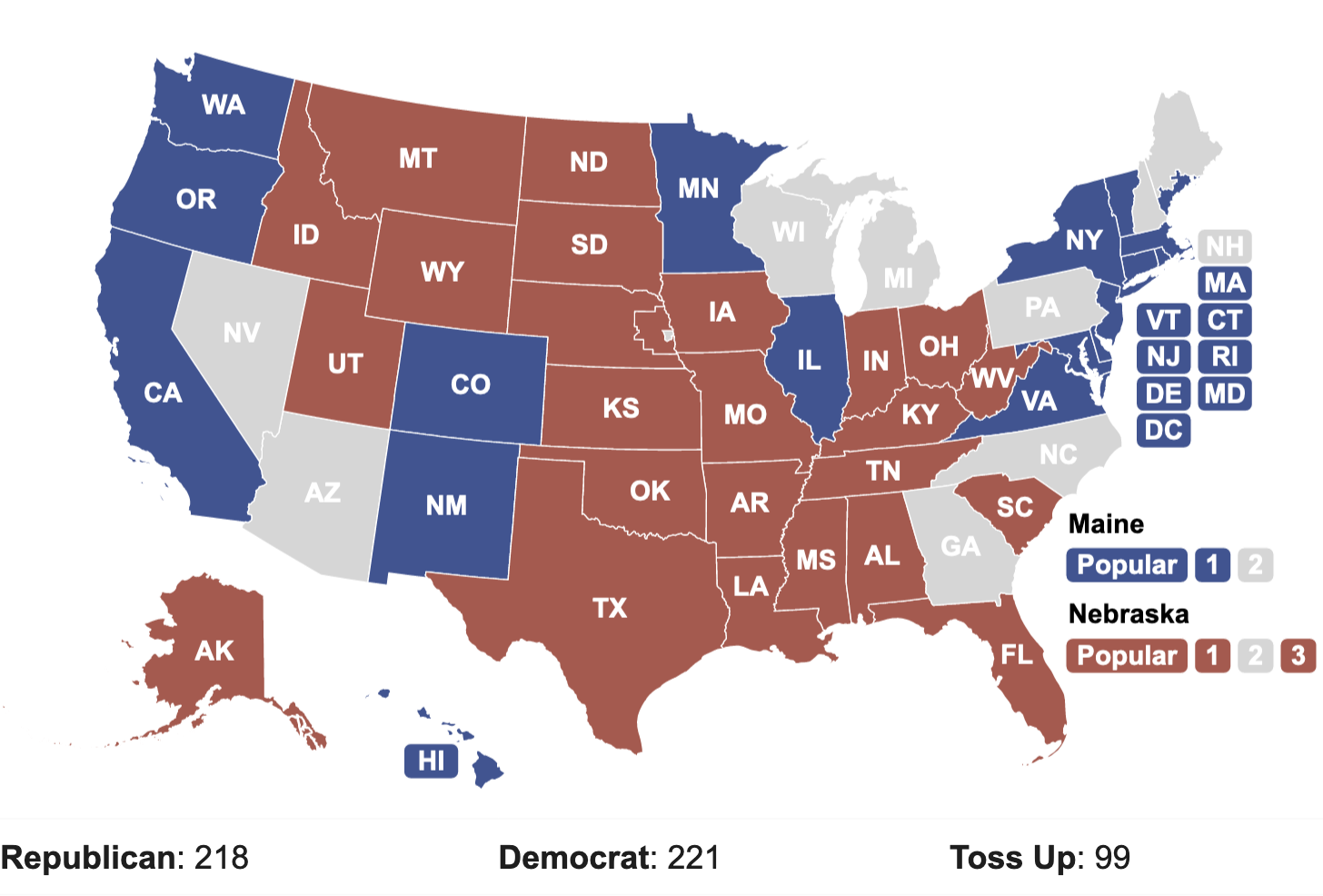
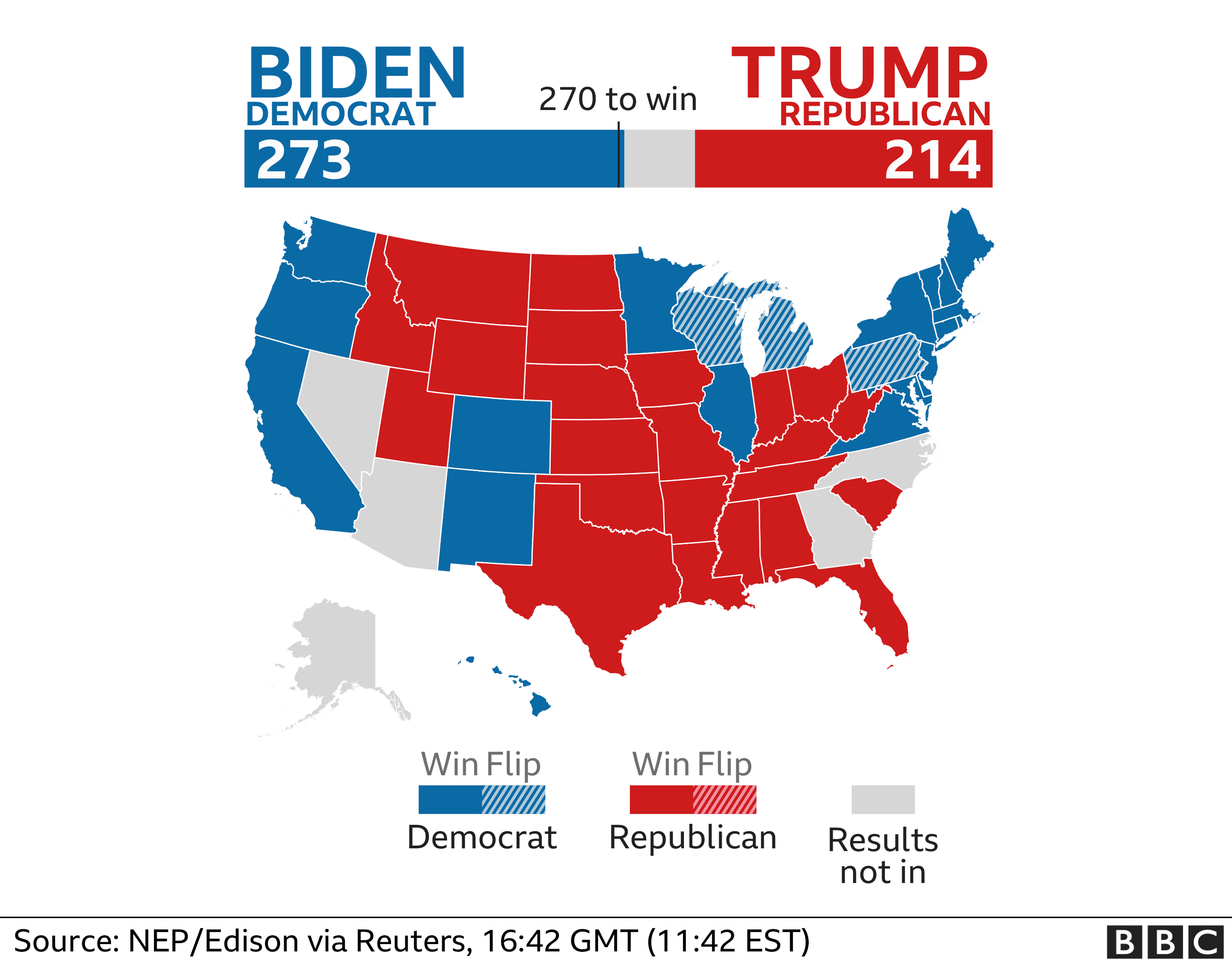




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape: Understanding the 2020 Election Consensus Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!