Navigating the Political Landscape of Southeast Asia: A Geographic Overview
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Southeast Asia: A Geographic Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape of Southeast Asia: A Geographic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape of Southeast Asia: A Geographic Overview
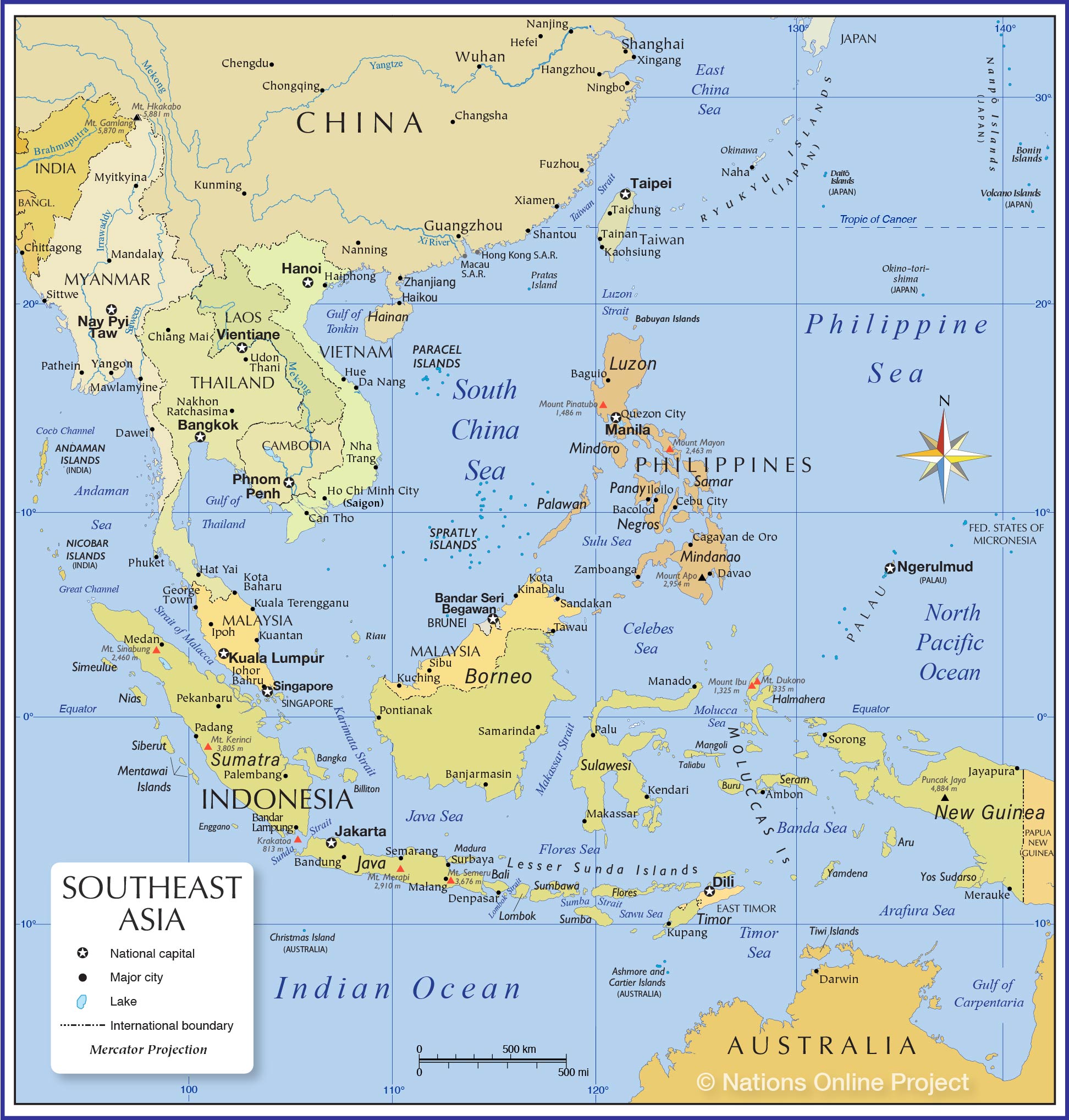
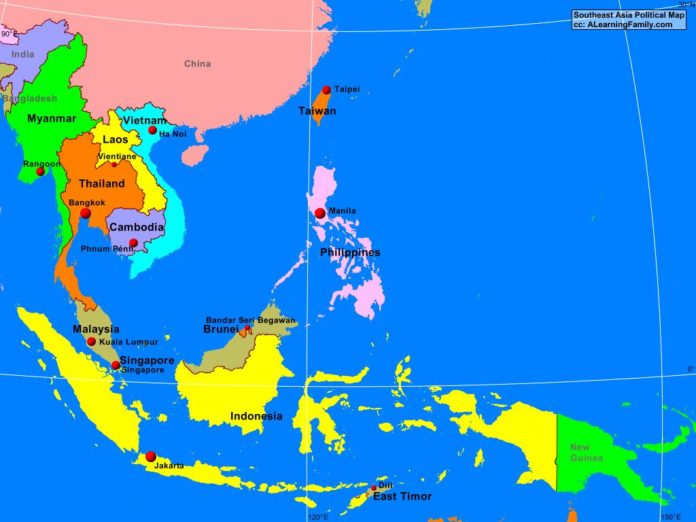
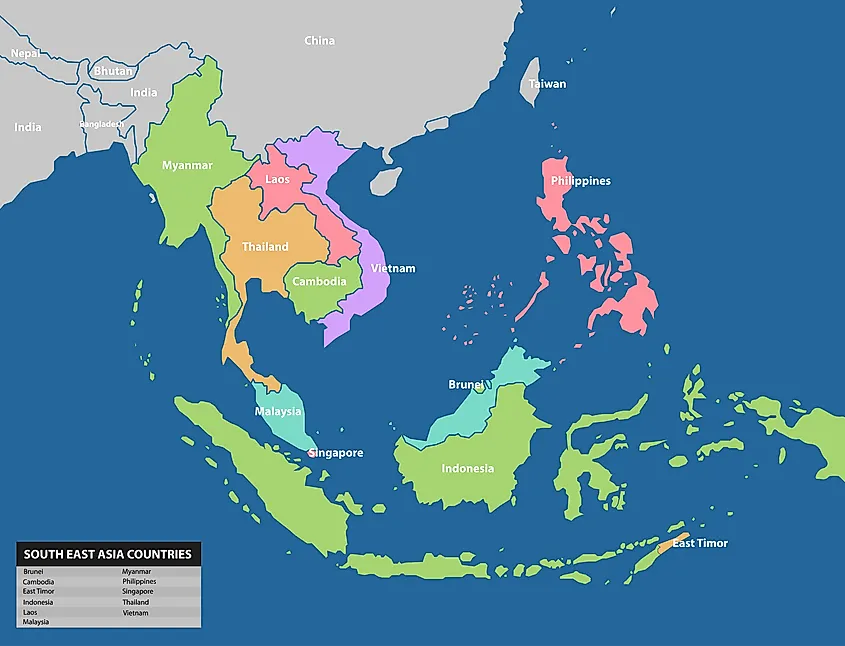
Southeast Asia, a region spanning the Malay Peninsula and numerous islands, boasts a diverse tapestry of cultures, languages, and political systems. Understanding the political map of this dynamic region is crucial for comprehending its history, current affairs, and future trajectory. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the political landscape of Southeast Asia, highlighting key features, historical influences, and contemporary challenges.
A Diverse Political Landscape
Southeast Asia is home to eleven sovereign states, each with its unique history, political structure, and challenges. These states are:
- Brunei Darussalam: A sultanate with a constitutional monarchy, Brunei enjoys significant oil and gas reserves, contributing to its high per capita income.
- Cambodia: A constitutional monarchy with a strong central government, Cambodia is recovering from a tumultuous past, grappling with political instability and economic disparities.
- Indonesia: The world’s largest archipelago nation, Indonesia operates as a unitary presidential republic with a diverse population and a complex political system.
- Laos: A landlocked nation with a communist government, Laos has experienced significant economic growth in recent years, driven by hydropower and tourism.
- Malaysia: A constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system, Malaysia is a major economic force in the region, known for its diverse ethnicities and strong trade ties.
- Myanmar: A republic with a military junta currently in control, Myanmar faces significant challenges including political instability, human rights violations, and ongoing conflict in ethnic minority regions.
- Philippines: A presidential republic with a strong Catholic influence, the Philippines is a vibrant democracy with a diverse population and a rapidly growing economy.
- Singapore: A city-state and a parliamentary republic, Singapore is renowned for its economic prowess, high standard of living, and efficient governance.
- Thailand: A constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system, Thailand is a major tourist destination and a regional economic hub, but faces challenges related to political instability and social inequality.
- Timor-Leste: A young nation that gained independence in 2002, Timor-Leste is a presidential republic with a focus on rebuilding its infrastructure and promoting economic development.
- Vietnam: A socialist republic with a single-party system, Vietnam has experienced remarkable economic growth, transforming itself into a major manufacturing hub.
Historical Influences on the Political Map
The political map of Southeast Asia is shaped by a confluence of historical factors, including:
- Colonialism: European powers, particularly the British, French, Dutch, and Spanish, exerted significant influence on the region for centuries, leaving behind legacies of political structures, legal systems, and administrative practices.
- Cold War: The Cold War saw Southeast Asia become a battleground for ideological rivalry, with the region divided between communist and capitalist blocs. This division has left lasting effects on political alignments and economic development.
- Regionalism: The emergence of regional organizations like ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) has fostered cooperation and integration among member states, leading to increased economic interdependence and political stability.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
The political map of Southeast Asia is constantly evolving, facing numerous challenges and opportunities:
- Economic Disparities: Despite significant economic growth in recent years, Southeast Asia continues to grapple with significant economic disparities between countries and within them. This disparity can lead to social unrest and political instability.
- Political Instability: Political instability is a recurring challenge in many Southeast Asian countries, often fueled by ethnic tensions, religious conflicts, and corruption.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the region’s environment and sustainable development.
- Regional Security: Territorial disputes in the South China Sea and the ongoing conflict in Myanmar contribute to regional tensions and complicate security dynamics.
- Globalization and Integration: Southeast Asia is increasingly integrated into the global economy, presenting both opportunities and challenges related to trade, investment, and cultural exchange.
Understanding the Importance of the Political Map
The political map of Southeast Asia is not merely a collection of borders and names; it represents a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and economic factors. Understanding this map is essential for:
- Informed Policy Making: Policymakers need to understand the political landscape of Southeast Asia to develop effective strategies for trade, development, and security cooperation.
- Business and Investment: Businesses and investors need to be aware of the political risks and opportunities associated with different countries in the region.
- International Relations: Understanding the political dynamics of Southeast Asia is crucial for fostering diplomatic relations and promoting regional stability.
FAQs
Q: What are the main political systems in Southeast Asia?
A: Southeast Asia features a diverse array of political systems, including constitutional monarchies, presidential republics, parliamentary republics, and socialist republics.
Q: What are the major regional organizations in Southeast Asia?
A: ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) is the most significant regional organization, promoting economic integration, political stability, and cooperation among member states. Other organizations include the Mekong River Commission, the ASEAN Regional Forum, and the East Asia Summit.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the region?
A: Southeast Asia faces numerous challenges, including economic disparities, political instability, environmental degradation, regional security threats, and the impact of globalization.
Q: What are the prospects for the future of Southeast Asia?
A: Despite challenges, Southeast Asia has a promising future, driven by economic growth, technological advancements, and regional integration. However, addressing issues like political instability, environmental degradation, and inequality is crucial for realizing this potential.
Tips for Navigating the Political Map of Southeast Asia
- Stay Informed: Follow news and analysis from reputable sources to stay updated on political developments in the region.
- Engage with Experts: Consult with academics, analysts, and practitioners specializing in Southeast Asian politics to gain deeper insights.
- Consider Regional Context: Understand how individual countries within Southeast Asia are interconnected and influenced by regional dynamics.
- Embrace Diversity: Recognize and appreciate the cultural and political diversity of the region, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes.
Conclusion
The political map of Southeast Asia is a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and economic factors. Understanding this map is essential for navigating the region’s intricate political dynamics, fostering regional cooperation, and promoting sustainable development. By recognizing the challenges and opportunities presented by this dynamic region, policymakers, businesses, and individuals can contribute to a more stable, prosperous, and peaceful Southeast Asia.
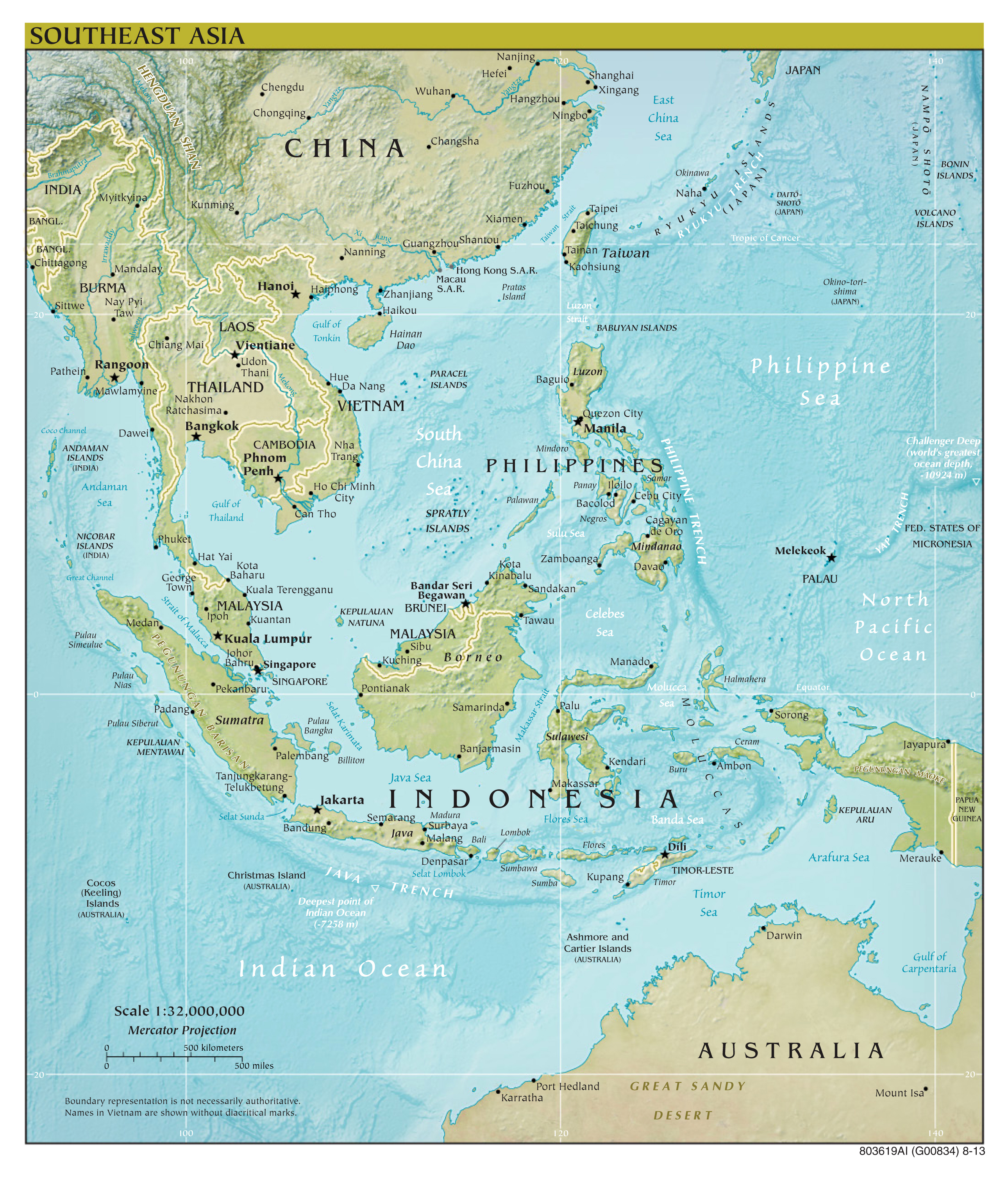
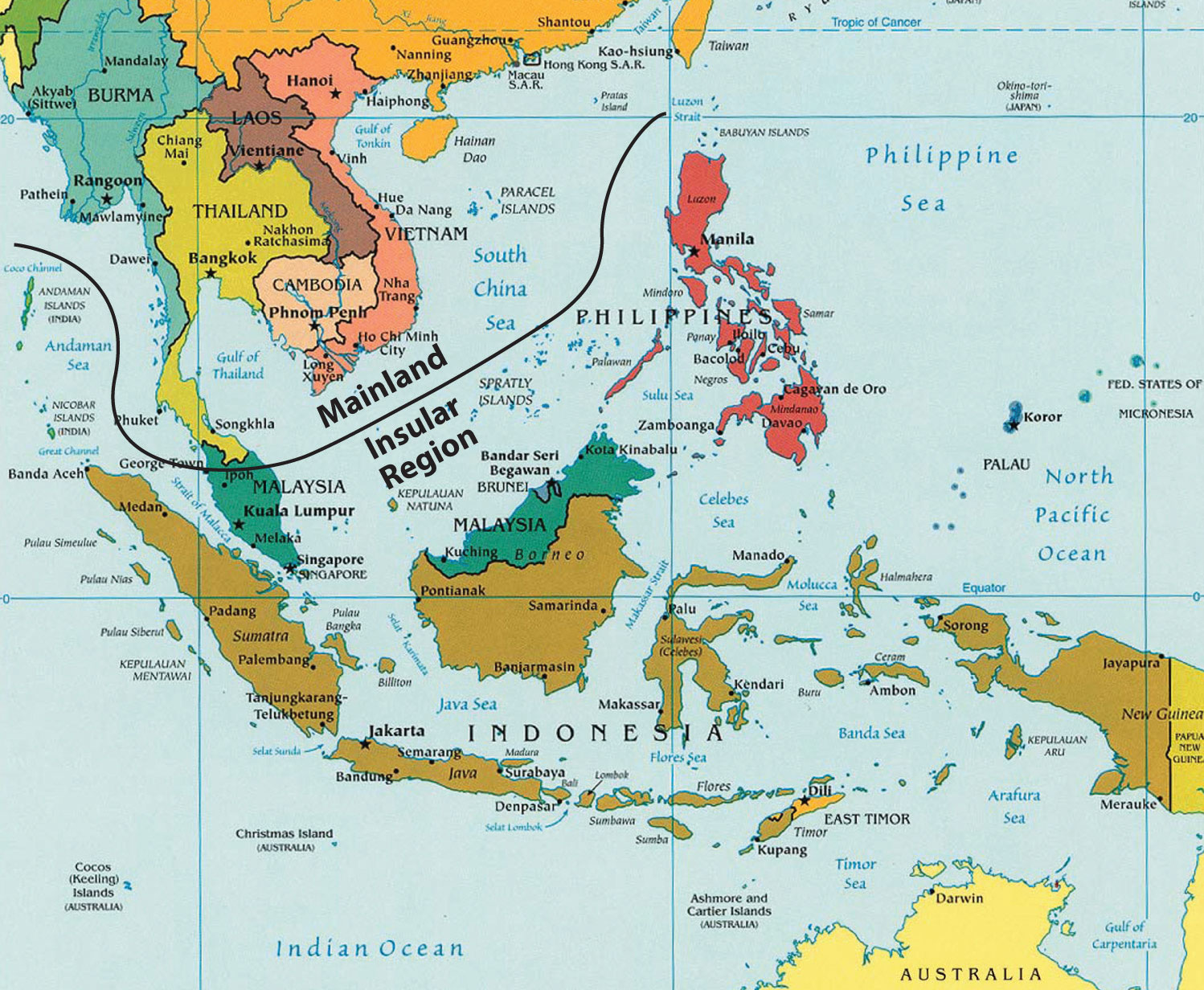
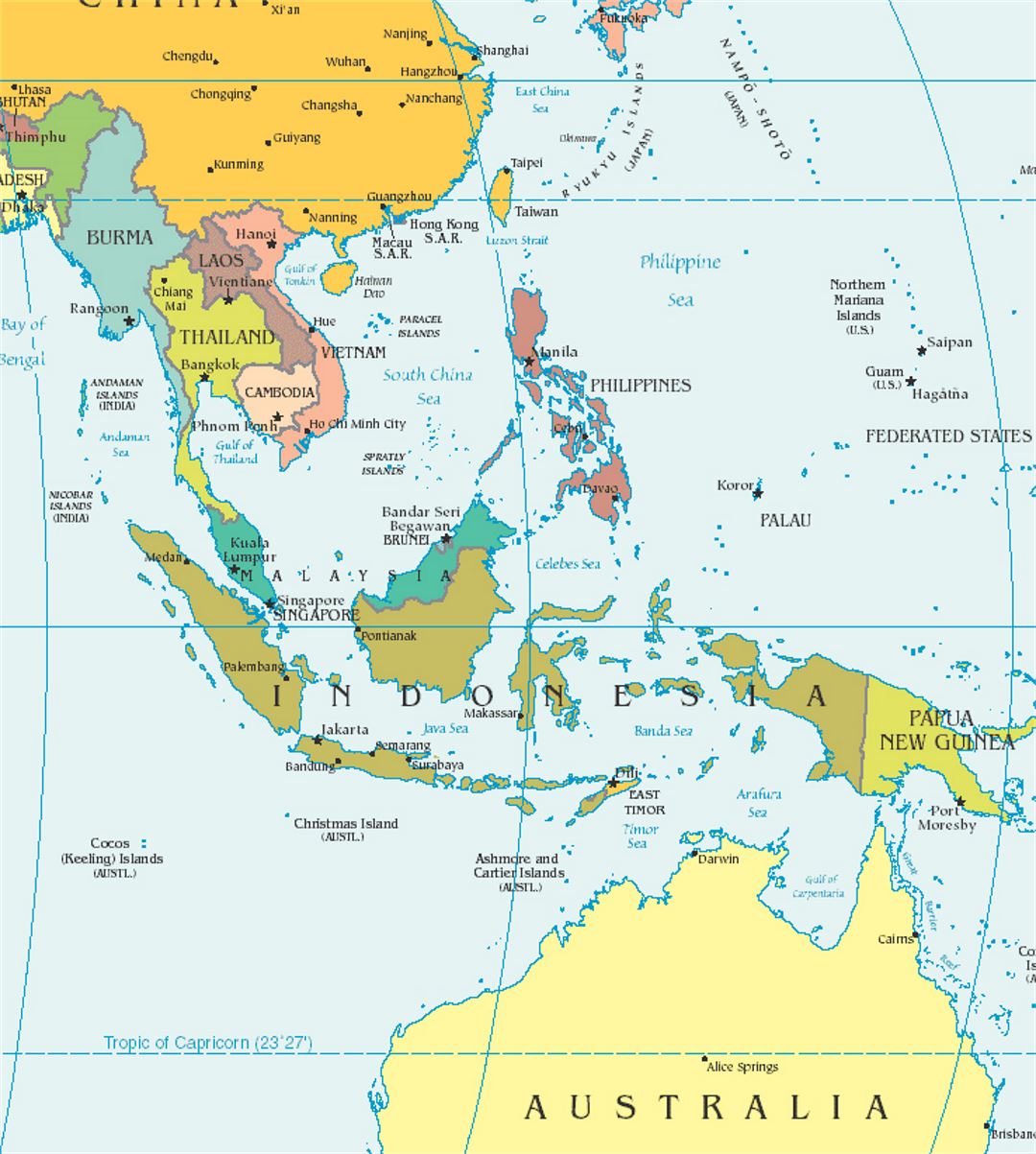


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape of Southeast Asia: A Geographic Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!