Navigating the Kingdom: A Comprehensive Look at the Saudi Arabian Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Kingdom: A Comprehensive Look at the Saudi Arabian Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Kingdom: A Comprehensive Look at the Saudi Arabian Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Kingdom: A Comprehensive Look at the Saudi Arabian Map
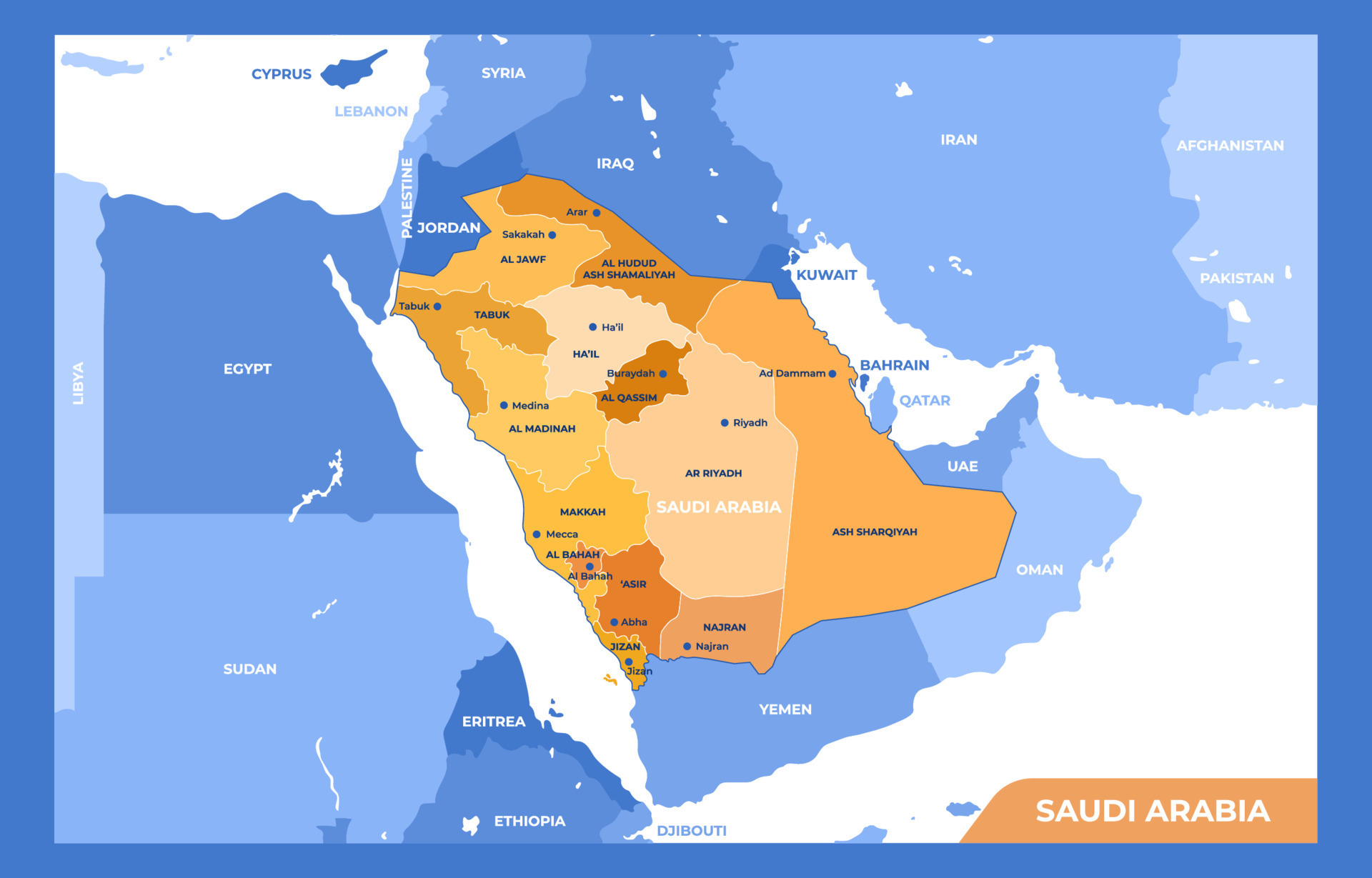
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, a vast and diverse nation in the Arabian Peninsula, is a land of ancient history, vibrant culture, and immense natural resources. Understanding its geography is crucial for appreciating its unique character and appreciating the challenges and opportunities it faces. The Saudi Arabian map, with its distinct features and intricate details, provides a window into the heart of the kingdom, revealing its diverse landscapes, strategic locations, and cultural tapestry.
A Land of Extremes: Understanding the Topography
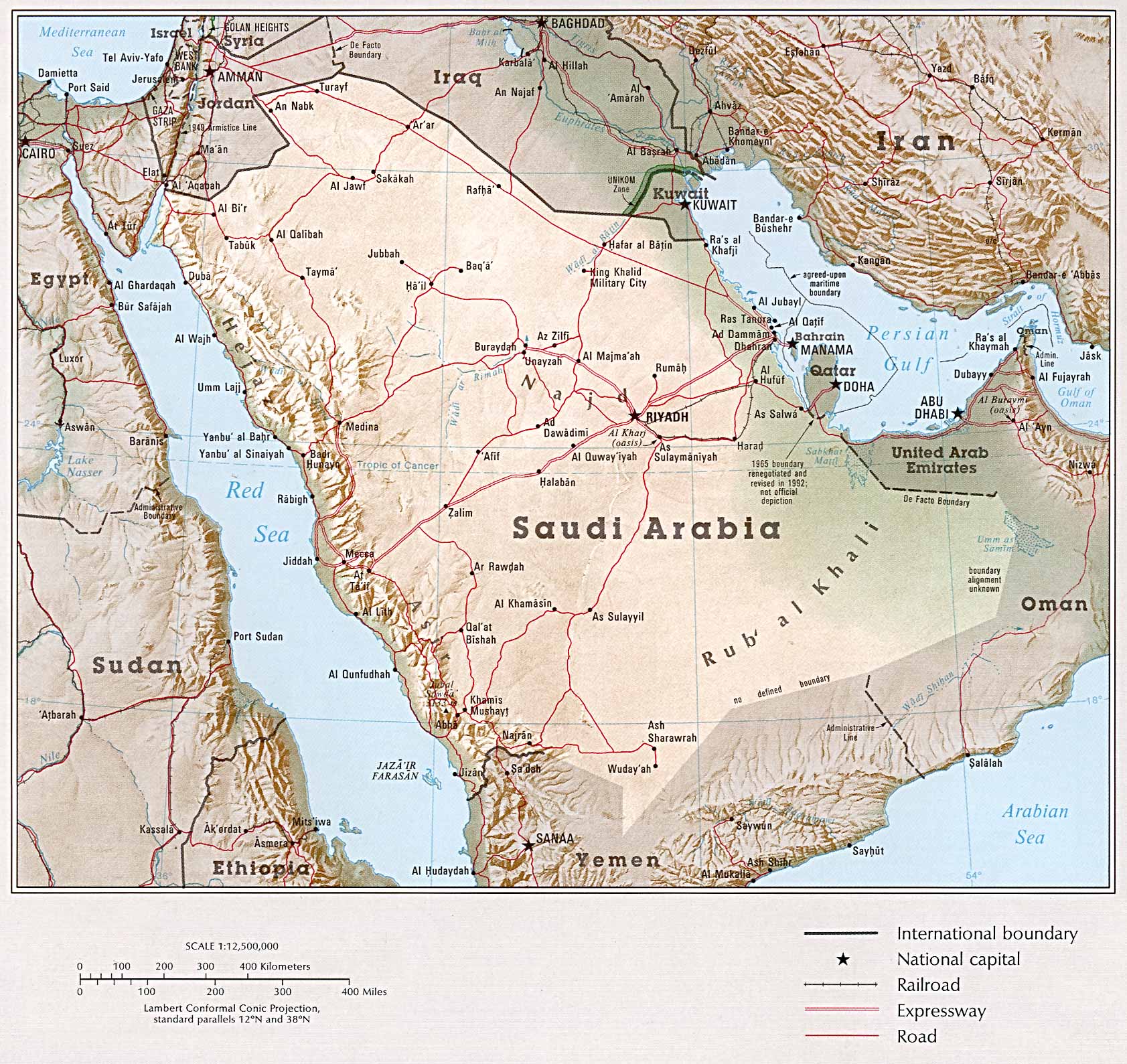
The Saudi Arabian map reveals a land sculpted by millennia of geological forces, resulting in a diverse topography that ranges from towering mountains to vast deserts. The country is dominated by the Arabian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient Precambrian rock that forms the western and central regions. This shield is characterized by rugged mountains, deep canyons, and fertile valleys, home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna.
The eastern region of the kingdom, known as the Eastern Province, is dominated by the Arabian Gulf, a strategic waterway that has played a pivotal role in the country’s history and economy. The coastline is characterized by vast stretches of sand dunes and coastal plains, while the interior is dotted with oases and salt flats.
To the south, the Empty Quarter, the largest sand desert in the world, stretches across the country, creating a vast and unforgiving landscape. This region, characterized by its extreme temperatures and lack of vegetation, serves as a stark reminder of the challenges posed by the harsh environment.
Strategic Locations: The Importance of Geography
The strategic location of Saudi Arabia is evident on the map. Situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, the kingdom holds a pivotal position in the global energy market and international trade. Its proximity to major shipping lanes, including the Suez Canal and the Bab el-Mandab Strait, makes it a vital link in the global supply chain.
The country’s vast oil and gas reserves, located primarily in the Eastern Province, have made it a major player in the global energy market. Its strategic location, coupled with its abundant natural resources, has positioned Saudi Arabia as a key player in regional and global politics.
Cultural Tapestry: Reflecting Diversity on the Map
The Saudi Arabian map reveals a diverse cultural landscape, shaped by centuries of interaction between different communities and traditions. The country is home to a variety of ethnic groups, including Arabs, Africans, and Asians, each contributing to the rich cultural mosaic of the kingdom.
The map highlights the importance of pilgrimage in Saudi culture. Mecca, the holiest city in Islam, is located in the western region of the country and serves as the focal point for the annual Hajj pilgrimage, which attracts millions of Muslims from around the world. Medina, the second holiest city, is also located in the western region and holds significant religious importance.
Navigating the Kingdom: A Closer Look at the Regions
1. The Western Region (Hejaz): This region is characterized by its mountainous terrain, fertile valleys, and coastal plains. It is home to the holy cities of Mecca and Medina, as well as the historic port city of Jeddah. The region is also known for its rich agricultural production and its traditional Bedouin culture.
2. The Central Region (Najd): This region is dominated by the Arabian Shield, with its rugged mountains, deep canyons, and fertile valleys. It is home to the capital city of Riyadh, as well as several other important cities, including Buraidah and Hail. The region is known for its traditional culture, its strong tribal ties, and its role as the heartland of the kingdom.
3. The Eastern Province: This region is characterized by its vast oil and gas reserves, its strategic location on the Arabian Gulf, and its diverse population. It is home to the city of Dammam, the commercial hub of the region, as well as the cities of Khobar and Al-Ahsa. The region is known for its modern infrastructure, its bustling economy, and its vibrant cultural life.
4. The Southern Region (Asir): This region is known for its mountainous terrain, its fertile valleys, and its diverse population. It is home to the city of Abha, the regional capital, as well as several other important cities, including Khamis Mushait and Najran. The region is known for its unique architecture, its rich agricultural production, and its traditional culture.
5. The Northern Region (Tabuk): This region is characterized by its mountainous terrain, its vast deserts, and its strategic location on the border with Jordan and Iraq. It is home to the city of Tabuk, the regional capital, as well as several other important cities, including Al-Jouf and Sakaka. The region is known for its rich history, its traditional culture, and its role as a gateway to the kingdom.
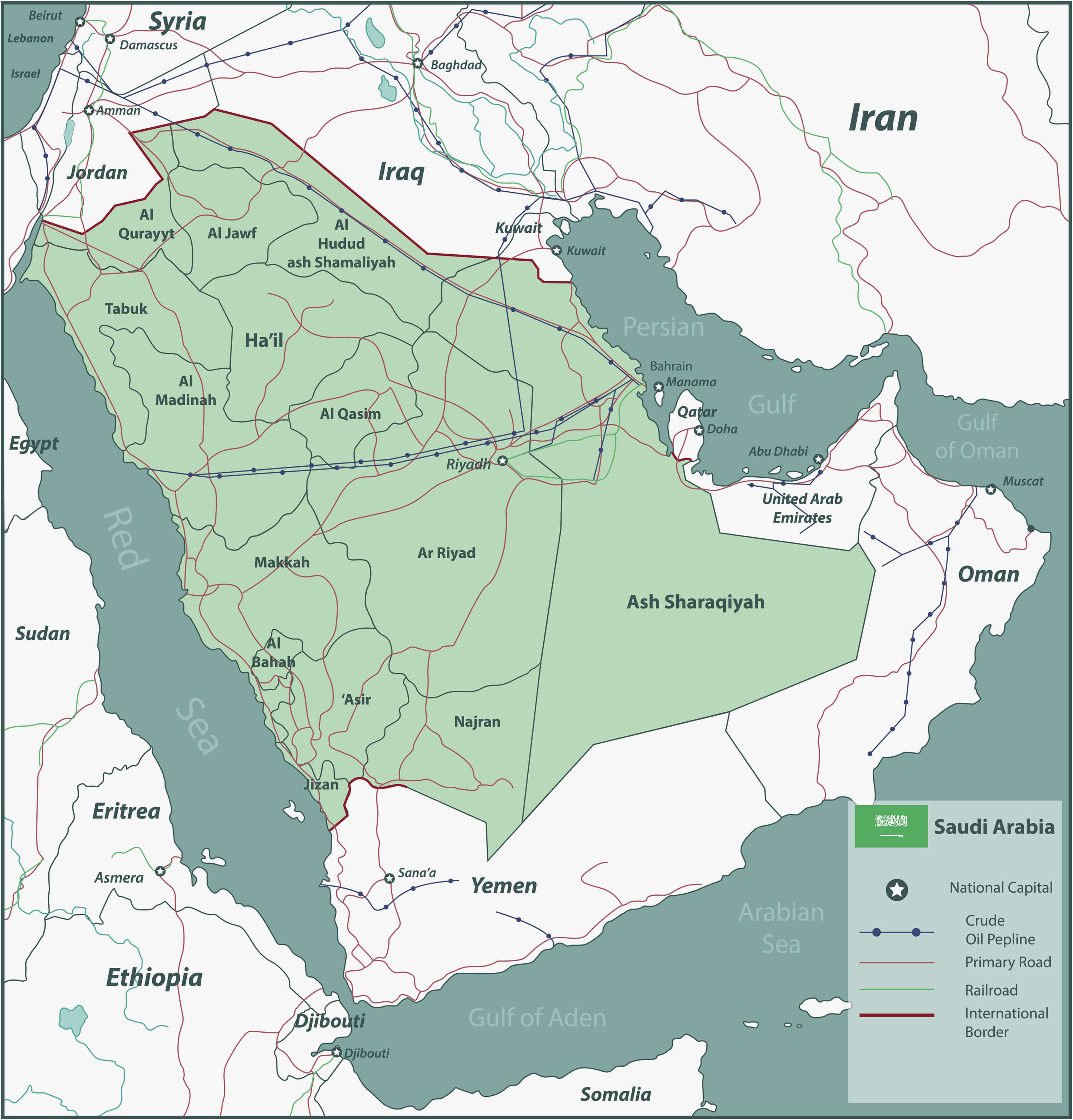
Navigating the Kingdom: Key Features on the Map
1. The Red Sea Coast: This coastline, stretching along the western border of the kingdom, is characterized by its stunning coral reefs, its diverse marine life, and its strategic importance in the global shipping network.
2. The Arabian Gulf Coast: This coastline, stretching along the eastern border of the kingdom, is characterized by its vast oil and gas reserves, its strategic location in the Persian Gulf, and its role as a major center for trade and commerce.
3. The Empty Quarter: This vast and unforgiving desert, located in the southern region of the kingdom, is characterized by its extreme temperatures, its lack of vegetation, and its role as a barrier to human settlement.
4. The Arabian Shield: This ancient geological formation, covering a vast area of the western and central regions of the kingdom, is characterized by its rugged mountains, its deep canyons, and its fertile valleys.
5. The Rub’ al Khali: This vast and unforgiving desert, located in the southern region of the kingdom, is characterized by its extreme temperatures, its lack of vegetation, and its role as a barrier to human settlement.
Navigating the Kingdom: FAQs
1. What is the capital of Saudi Arabia?
The capital of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh, located in the central region of the country.
2. What are the major cities in Saudi Arabia?
Besides Riyadh, other major cities in Saudi Arabia include Jeddah, Mecca, Medina, Dammam, Khobar, Abha, and Tabuk.
3. What are the major geographical features of Saudi Arabia?
The major geographical features of Saudi Arabia include the Arabian Shield, the Empty Quarter, the Red Sea Coast, the Arabian Gulf Coast, and the Rub’ al Khali desert.
4. What is the climate like in Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia has a desert climate, characterized by hot summers and mild winters. Temperatures can reach extreme levels in the interior regions, particularly during the summer months.
5. What are the major industries in Saudi Arabia?
The major industries in Saudi Arabia include oil and gas production, petrochemicals, manufacturing, and tourism.
Navigating the Kingdom: Tips for Travelers
1. Respecting Local Customs: Saudi Arabia is a conservative society, and it is important for visitors to respect local customs and traditions. Women should dress modestly, and both men and women should avoid public displays of affection.
2. Obtaining a Visa: Visitors to Saudi Arabia need to obtain a visa prior to arrival. Visa requirements vary depending on the nationality of the visitor.
3. Understanding the Language: The official language of Saudi Arabia is Arabic. While English is widely spoken in major cities, it is helpful to learn a few basic Arabic phrases.
4. Planning Your Itinerary: Saudi Arabia is a vast country, and it is important to plan your itinerary carefully. Consider the distances between different destinations and the time required for travel.
5. Staying Safe: Saudi Arabia is generally a safe country to visit. However, it is important to be aware of your surroundings and to take precautions against petty crime.
Conclusion: A Land of Opportunity
The Saudi Arabian map is a powerful tool for understanding the kingdom’s unique geography, its strategic location, and its diverse cultural landscape. It reveals a nation poised for growth and development, embracing its rich heritage while navigating the challenges of the 21st century. As Saudi Arabia continues to evolve, its map will continue to be a vital resource for understanding its past, present, and future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Kingdom: A Comprehensive Look at the Saudi Arabian Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!