Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regions
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regions
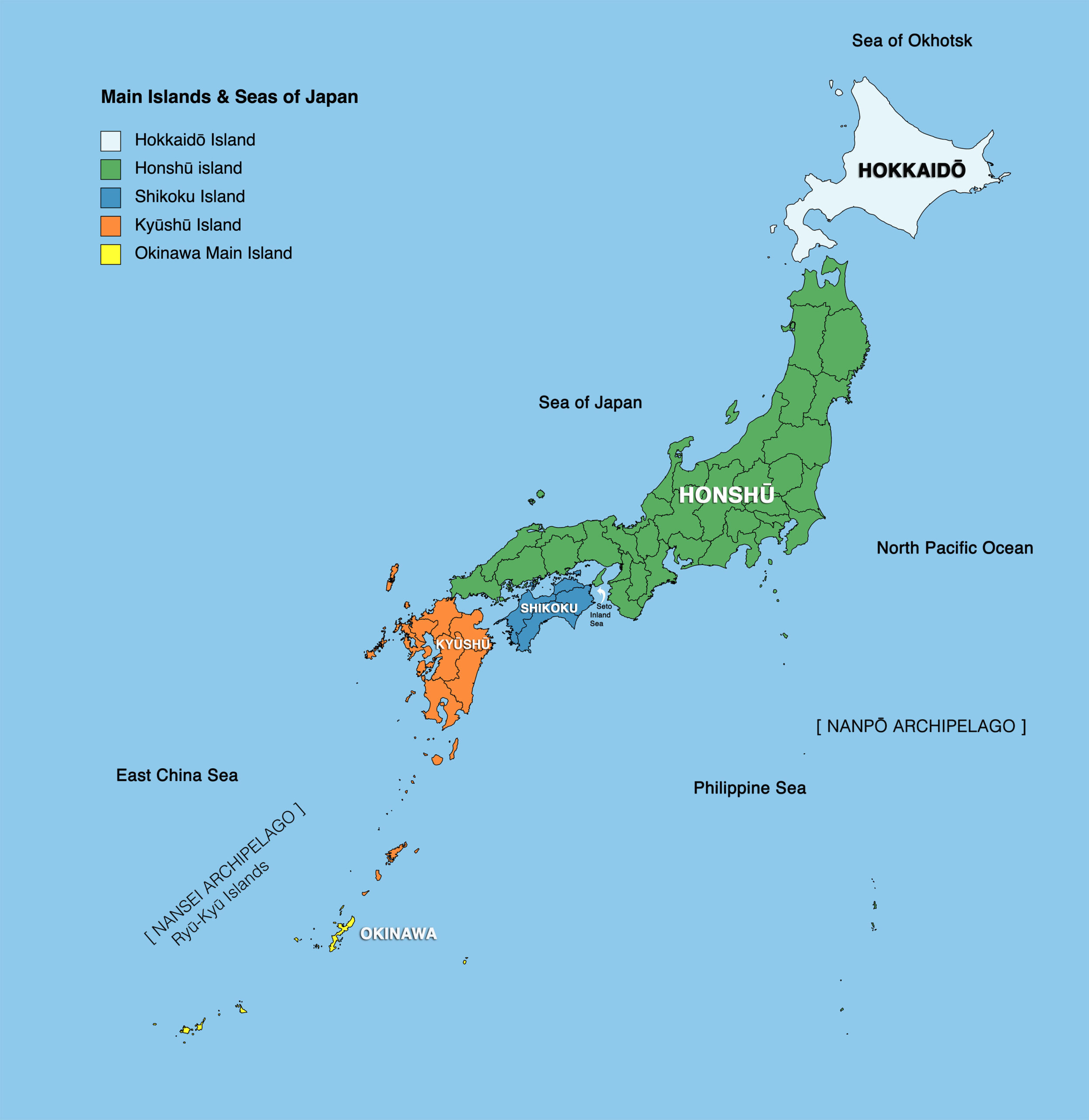
Japan, an island nation rising from the Pacific Ocean, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and rich history. Understanding its geographical structure is essential for appreciating the nation’s multifaceted character. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Japan’s regional divisions, highlighting their unique features and contributions to the nation’s identity.
A Land of Islands: The Regional Framework
Japan’s geography is defined by its archipelago, a chain of four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – along with thousands of smaller islands. This physical structure has profoundly influenced the nation’s history, culture, and development. Recognizing the distinct characteristics of each region is crucial for understanding Japan’s complexities.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
The northernmost island, Hokkaido, is a land of rugged mountains, volcanic landscapes, and vast expanses of wilderness. Its relatively recent development, compared to the other main islands, is reflected in its modern infrastructure and agricultural focus. Hokkaido is renowned for its dairy products, seafood, and pristine natural beauty, attracting outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers.
Honshu: The Heart of Japan
The largest island, Honshu, is the cultural and economic powerhouse of Japan. It encompasses the bustling metropolis of Tokyo, the ancient capital of Kyoto, and numerous other major cities. Honshu’s diverse landscape ranges from the snow-capped peaks of the Japanese Alps to the fertile plains of the Kanto region. This island is a microcosm of Japan’s history, tradition, and modernity, showcasing a captivating blend of ancient temples, bustling cities, and natural wonders.
Shikoku: The Island of Pilgrimage
Shikoku, the smallest of the four main islands, is known for its spiritual significance. It is home to the Shikoku Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer circuit of 88 Buddhist temples, attracting pilgrims from across Japan and beyond. Shikoku’s serene landscapes, including rolling hills, lush forests, and picturesque coastlines, offer a tranquil escape from the urban hustle.
Kyushu: The Southern Gateway
Kyushu, the southernmost of the main islands, is characterized by its volcanic activity, subtropical climate, and vibrant culture. It boasts numerous hot springs, active volcanoes, and beautiful beaches. Kyushu is also known for its unique cuisine, including the famous ramen from Hakata and the traditional Kagoshima black pork. This island serves as a gateway to mainland Asia, reflecting a distinct cultural influence from neighboring countries.
Beyond the Main Islands: The Importance of Smaller Islands
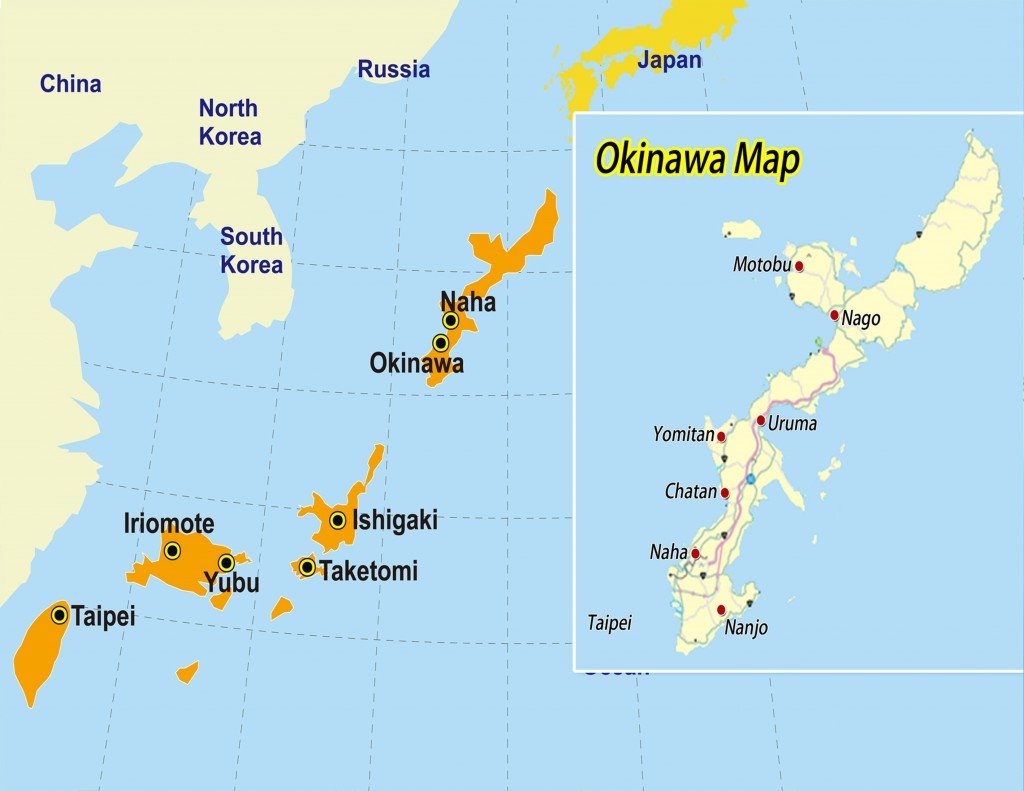
While the four main islands dominate the landscape, numerous smaller islands contribute significantly to Japan’s diverse tapestry. These include the Ryukyu Islands, located southwest of Kyushu, known for their unique culture, stunning beaches, and rich marine life. The Izu Islands, east of Tokyo, offer volcanic landscapes, hot springs, and a secluded island escape. These smaller islands, each with their unique character, contribute to the richness and complexity of Japan’s geography and culture.
Regional Distinctions: Understanding the Tapestry
Each region in Japan has its own distinct characteristics, shaped by historical, geographical, and cultural factors. These differences are reflected in:
- Language and Dialects: While standard Japanese is the official language, regional dialects, known as "ben," are prevalent throughout the country. These dialects often reflect the historical and cultural nuances of each region.
- Cuisine: Japanese cuisine is known for its diversity and regional specialties. From the seafood-centric dishes of Hokkaido to the fiery flavors of Kyushu, each region boasts its unique culinary traditions.
- Culture and Traditions: Regional festivals, art forms, and customs contribute to the vibrant cultural mosaic of Japan. The unique traditions of each region reflect the local history and environment.
- Economy and Industry: The economic landscape of Japan varies significantly across regions. While some regions are known for their industrial centers, others focus on agriculture, tourism, or specialized industries.
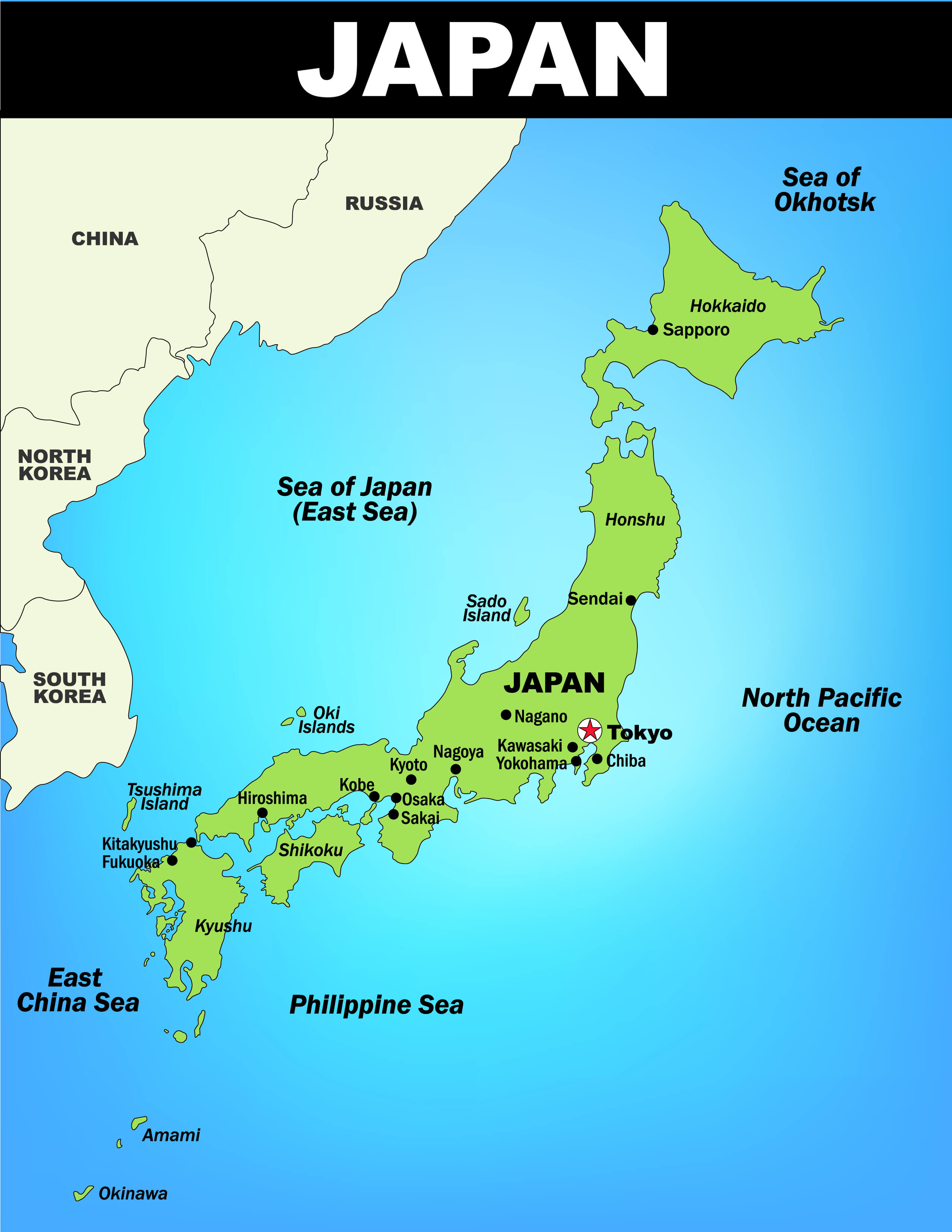
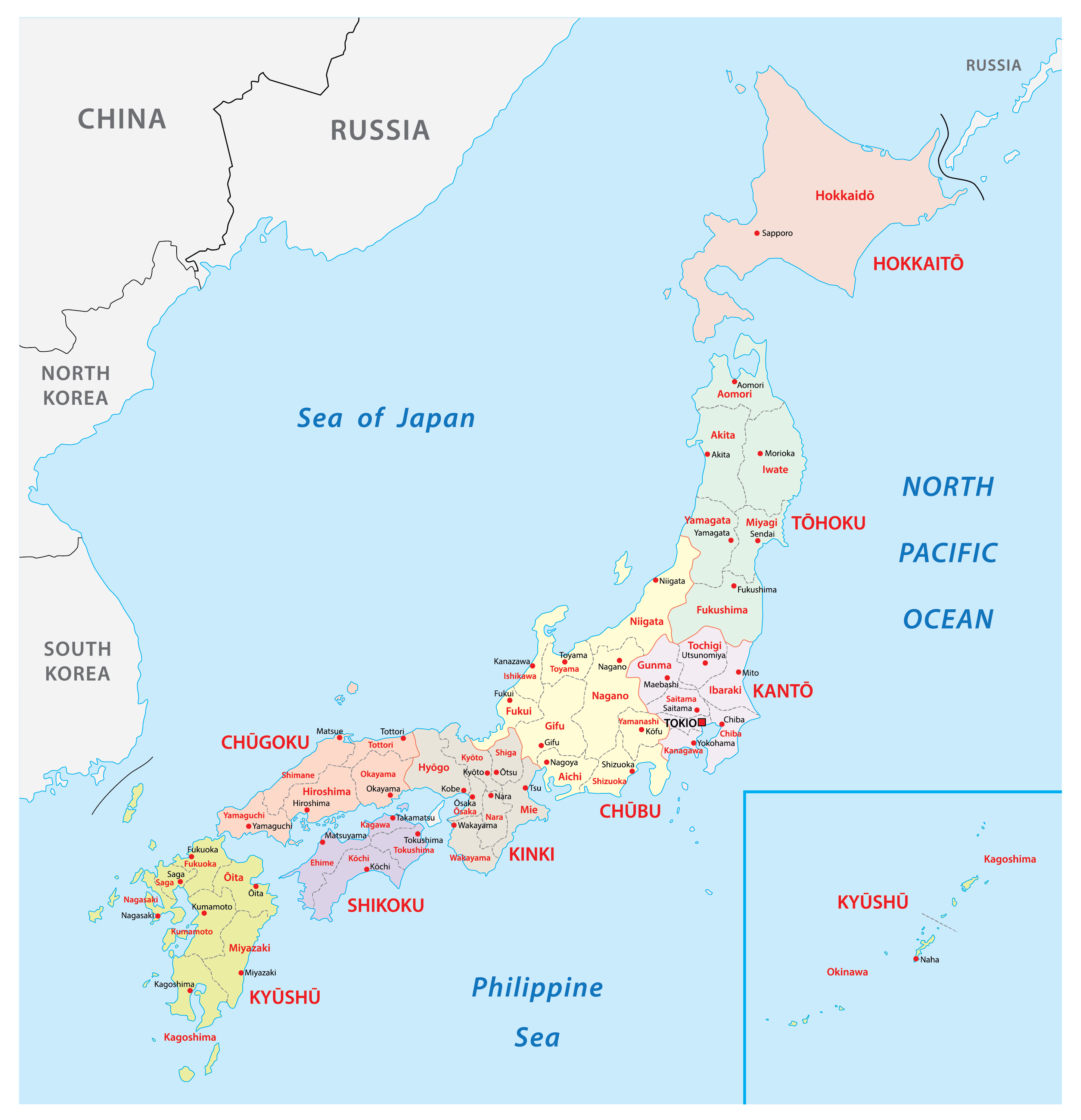
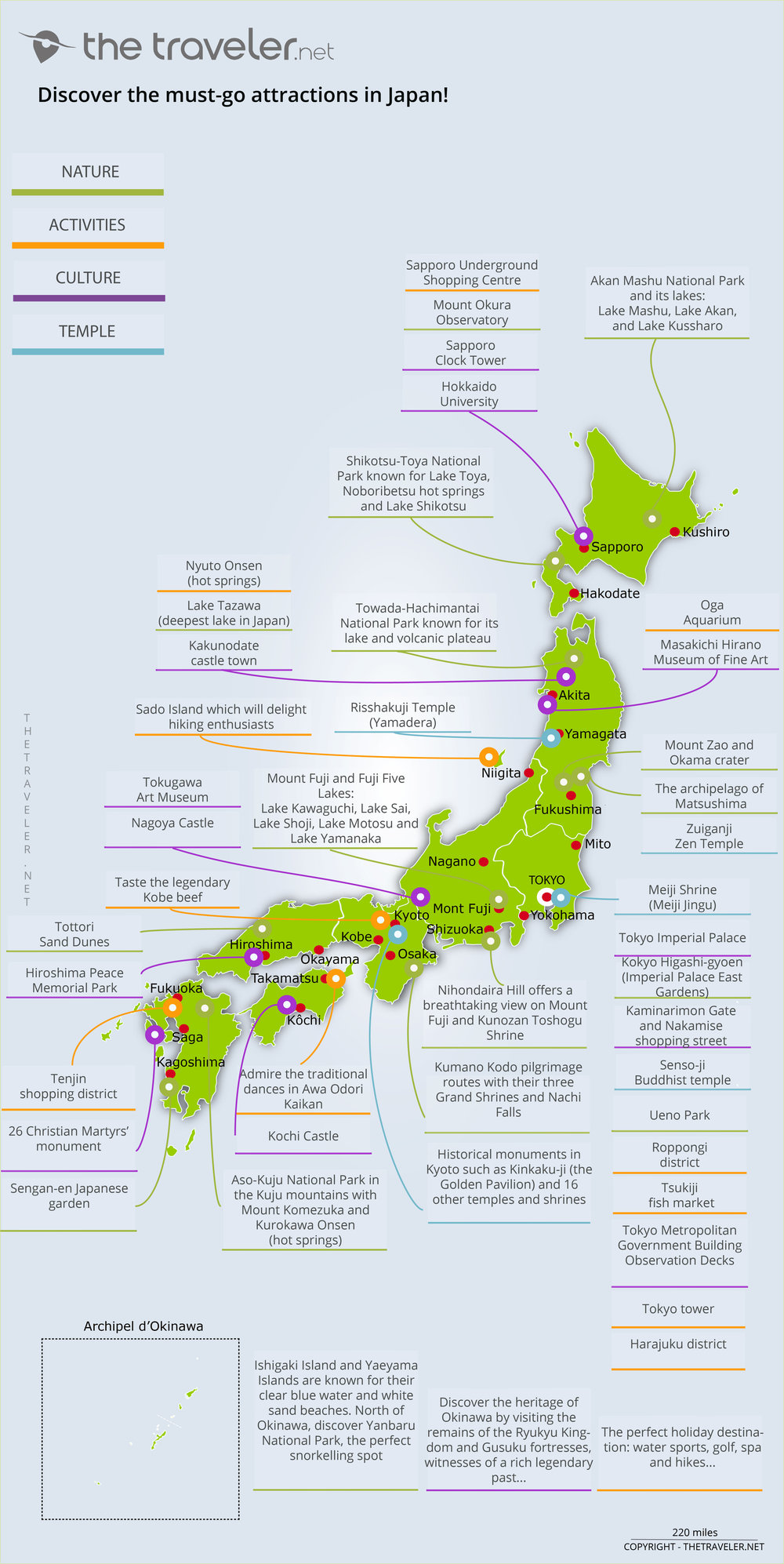
Navigating the Regions: A Map as a Guide
A map of Japan serves as an essential tool for understanding the country’s geographical structure and regional divisions. By visually representing the islands, major cities, and key features, it provides a framework for exploring the diverse landscapes and cultures of Japan.
FAQs: Understanding Japan’s Regional Divisions
1. What are the major islands of Japan?
The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
2. Which island is the largest and most populous?
Honshu is the largest and most populous island, home to the major cities of Tokyo, Kyoto, and Osaka.
3. What are some notable features of Hokkaido?
Hokkaido is known for its rugged mountains, volcanic landscapes, vast wilderness, and dairy products.
4. What is the Shikoku Pilgrimage?
The Shikoku Pilgrimage is a 1,200-kilometer circuit of 88 Buddhist temples located on the island of Shikoku, attracting pilgrims from across Japan and beyond.
5. What are the Ryukyu Islands known for?
The Ryukyu Islands, located southwest of Kyushu, are known for their unique culture, stunning beaches, and rich marine life.
6. How do regional dialects differ from standard Japanese?
Regional dialects, known as "ben," often reflect the historical and cultural nuances of each region, with unique pronunciations, vocabulary, and grammatical structures.
Tips for Exploring Japan’s Regions
- Research and Plan: Before traveling, familiarize yourself with the specific features and attractions of the regions you plan to visit.
- Embrace Local Culture: Immerse yourself in local customs, traditions, and cuisine to gain a deeper understanding of each region’s unique character.
- Consider Regional Transportation: Utilize local transportation options, such as Shinkansen bullet trains, regional trains, and ferries, to efficiently explore different regions.
- Engage with Locals: Interact with local residents to gain insights into their lives, culture, and perspectives.
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, such as bowing and taking off shoes before entering homes or temples.
Conclusion: A Nation of Diverse Landscapes and Cultures
Understanding Japan’s regional divisions is essential for appreciating the nation’s multifaceted character. From the rugged landscapes of Hokkaido to the bustling cities of Honshu, the spiritual heart of Shikoku, and the vibrant culture of Kyushu, each region contributes to the rich tapestry of Japan’s identity. Through exploration and engagement, travelers can gain a deeper understanding of this captivating nation and its diverse landscapes, cultures, and traditions.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!