Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to List Maps
Related Articles: Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to List Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to List Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to List Maps

In the realm of information management and knowledge representation, the ability to organize and visualize complex data is paramount. List maps, a powerful tool in the arsenal of information architects and knowledge engineers, offer a structured and intuitive way to represent hierarchical relationships within data sets. This article delves into the intricacies of list maps, exploring their construction, applications, benefits, and potential limitations.
Understanding the Essence of List Maps
At its core, a list map is a visual representation of a hierarchical structure. It presents information in a clear and concise manner, breaking down complex data into manageable units. Each element within the map is a "list," which can contain sub-lists, creating a multi-level structure. The arrangement of these lists, often depicted as nodes connected by lines or arrows, reveals the relationships and dependencies between different pieces of information.
The Building Blocks of a List Map
Constructing a list map involves a methodical approach, ensuring clarity and accuracy in the representation. The key components of a list map are:
- Root List: This is the top-level list, serving as the starting point for the entire structure. It represents the broadest category or concept being explored.
- Sub-Lists: These lists branch out from the root list, representing subcategories or more specific concepts. Each sub-list can contain further sub-lists, creating a hierarchical network.
- Items: Each list comprises individual items, which are the fundamental units of information within the map. These items can be text, numbers, images, or other forms of data.
- Links: These connections between lists and items establish the relationships within the structure. They can be represented by lines, arrows, or other visual cues, indicating the hierarchy and dependencies.
Applications of List Maps: A Wide Spectrum of Possibilities
List maps find application in diverse domains, serving as a versatile tool for organizing and communicating information. Some notable examples include:
- Knowledge Management: List maps facilitate the organization and retrieval of knowledge within organizations, enabling efficient knowledge sharing and decision-making. They can be used to map out organizational structures, project plans, or knowledge domains.
- Information Architecture: In the realm of web design and content management, list maps are crucial for structuring websites and content hierarchies. They help ensure clear navigation, logical information flow, and user-friendly interfaces.
- Data Analysis: List maps can be employed to visualize and analyze complex data sets, revealing patterns, relationships, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden. They are particularly useful for exploring hierarchical data structures, such as customer segmentation or product categories.
- Education and Training: List maps aid in the teaching and learning process, providing a structured framework for presenting complex information in a digestible and engaging manner. They can be used for outlining course content, explaining concepts, or summarizing key points.
Benefits of Utilizing List Maps: A Clearer Picture
The adoption of list maps brings numerous advantages to the table, enhancing clarity, efficiency, and understanding within various contexts. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Clarity: List maps present information in a clear and structured manner, eliminating ambiguity and facilitating comprehension. The hierarchical arrangement allows for easy identification of key concepts and their relationships.
- Improved Organization: By breaking down complex data into manageable units, list maps promote efficient organization and information management. They provide a framework for categorizing, classifying, and structuring information, ensuring logical flow and easy retrieval.
- Facilitated Communication: List maps serve as a powerful tool for communicating information effectively. They provide a visual representation that can be easily understood by diverse audiences, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing a clear and concise overview of complex data, list maps support informed decision-making. They enable stakeholders to identify key factors, assess relationships, and make informed choices based on the presented information.
- Increased Efficiency: List maps streamline processes by providing a structured framework for organizing tasks, managing projects, and tracking progress. They enhance collaboration and communication within teams, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
Potential Limitations and Considerations
While list maps offer numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge their potential limitations and consider specific scenarios where alternative methods might be more suitable. Some considerations include:
- Complexity: List maps can become complex and difficult to navigate when dealing with extremely large and intricate data sets. In such cases, alternative visualization techniques might be more appropriate.
- Static Representation: List maps typically represent information in a static manner, which may not be suitable for dynamic or rapidly changing data. In these situations, interactive visualizations or dashboards might be more effective.
- Limited Data Types: List maps are best suited for representing hierarchical relationships and structured data. They might not be as effective for visualizing unstructured data, such as text documents or social media content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about List Maps
Q: What are some common tools for creating list maps?
A: There are various software tools available for creating list maps. Some popular options include:
- Mind Mapping Software: Tools like MindManager, XMind, and FreeMind provide features for creating hierarchical structures and visual maps, which can be used for list map creation.
- Diagraming Software: Tools like Visio, Lucidchart, and Draw.io offer a wide range of diagram types, including hierarchical structures, suitable for creating list maps.
- Spreadsheets: Spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to create basic list maps by organizing data into columns and rows.
Q: What are some best practices for creating effective list maps?
A: Creating effective list maps requires a methodical approach, ensuring clarity, conciseness, and visual appeal. Some best practices include:
- Start with a clear purpose: Define the objective of the list map and the specific information you want to represent.
- Use a consistent structure: Maintain a consistent hierarchy and visual style throughout the map, ensuring clarity and ease of navigation.
- Limit the number of levels: Avoid creating overly complex maps with too many levels, as this can make them difficult to understand.
- Use visual cues: Employ color, size, and other visual elements to highlight important information and guide the viewer’s attention.
- Keep it concise: Avoid overloading the map with too much information. Focus on presenting key concepts and relationships in a clear and concise manner.
Q: How can list maps be used in collaboration and knowledge sharing?
A: List maps can be valuable tools for collaborative work and knowledge sharing. They provide a common framework for organizing information, facilitating discussion, and ensuring shared understanding.
- Shared Workspace: Collaborative tools like Google Docs or Miro can be used to create and edit list maps in real-time, allowing multiple individuals to contribute and collaborate on the structure.
- Knowledge Base: List maps can be incorporated into knowledge bases or wikis, providing a structured framework for organizing and accessing information.
- Training and Onboarding: List maps can be used to create training materials or onboarding guides, providing a clear and structured overview of information for new employees or team members.
Tips for Effective List Map Creation
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the list map and the specific information you want to represent.
- Use a consistent structure: Maintain a consistent hierarchy and visual style throughout the map, ensuring clarity and ease of navigation.
- Limit the number of levels: Avoid creating overly complex maps with too many levels, as this can make them difficult to understand.
- Use visual cues: Employ color, size, and other visual elements to highlight important information and guide the viewer’s attention.
- Keep it concise: Avoid overloading the map with too much information. Focus on presenting key concepts and relationships in a clear and concise manner.
- Test and refine: Regularly review and refine the list map, ensuring it effectively communicates the intended information.
Conclusion
List maps serve as a valuable tool for organizing, visualizing, and communicating hierarchical information. Their versatility across various domains, from knowledge management to data analysis, makes them a powerful instrument for enhancing clarity, improving efficiency, and facilitating decision-making. By understanding the principles of list map construction, exploring their diverse applications, and embracing best practices for effective creation, individuals and organizations can leverage this powerful tool to unlock the potential of complex data and navigate the ever-growing landscape of information.
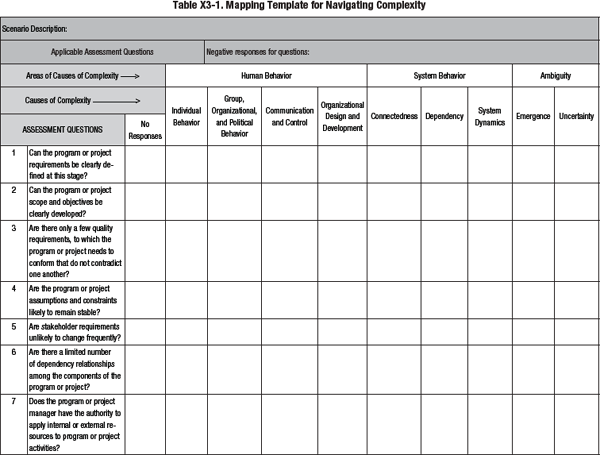
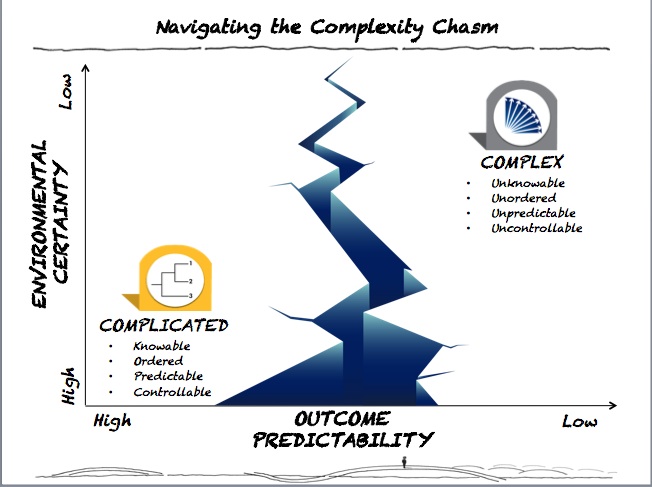
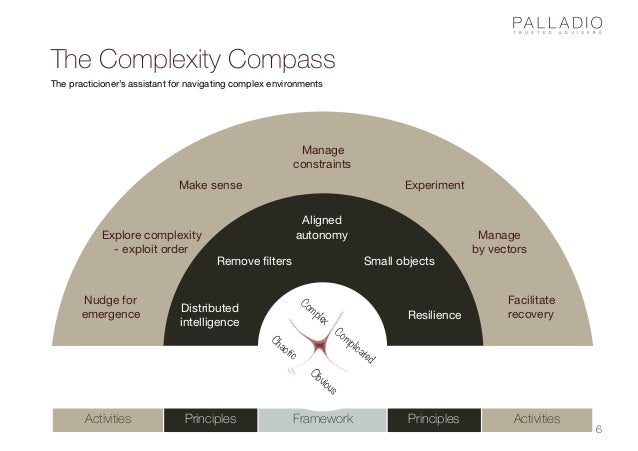
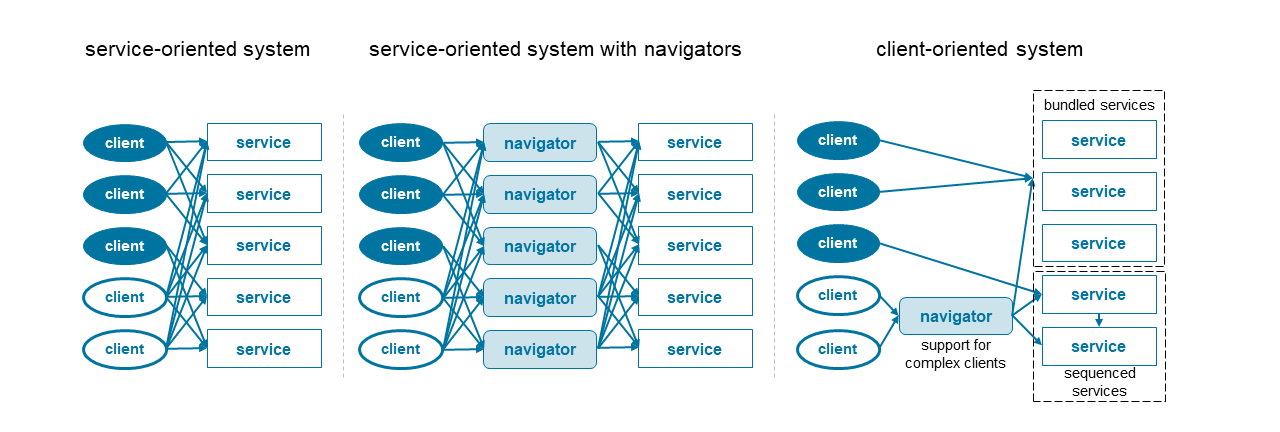

![EBOOK [P.D.F] Navigating Complexity: A Practice Guide [Full]](https://www.yumpu.com/en/image/facebook/64064146.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to List Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!