Defining Canada’s Borders: A Tapestry of Geography, History, and Identity
Related Articles: Defining Canada’s Borders: A Tapestry of Geography, History, and Identity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Defining Canada’s Borders: A Tapestry of Geography, History, and Identity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining Canada’s Borders: A Tapestry of Geography, History, and Identity
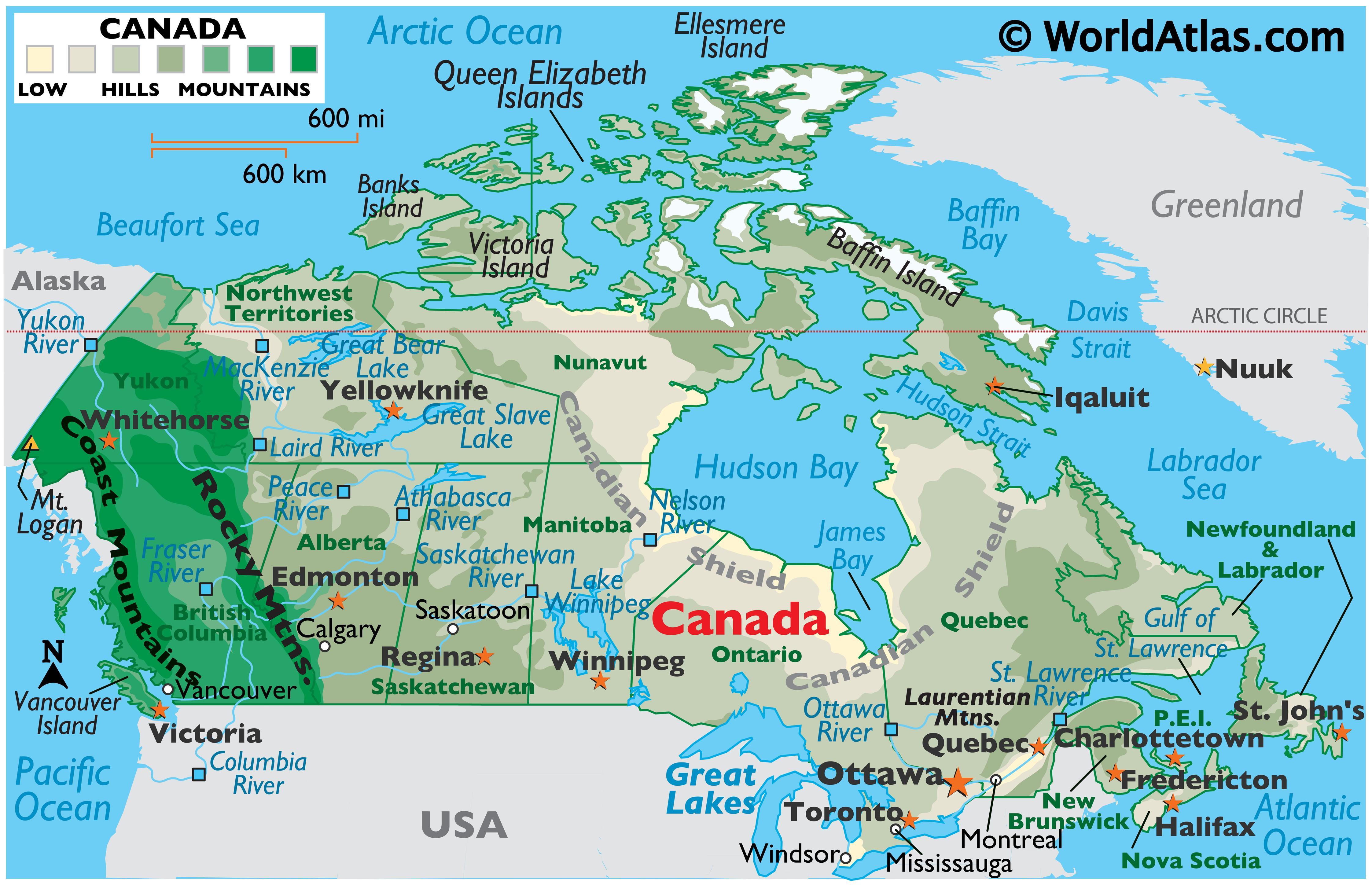
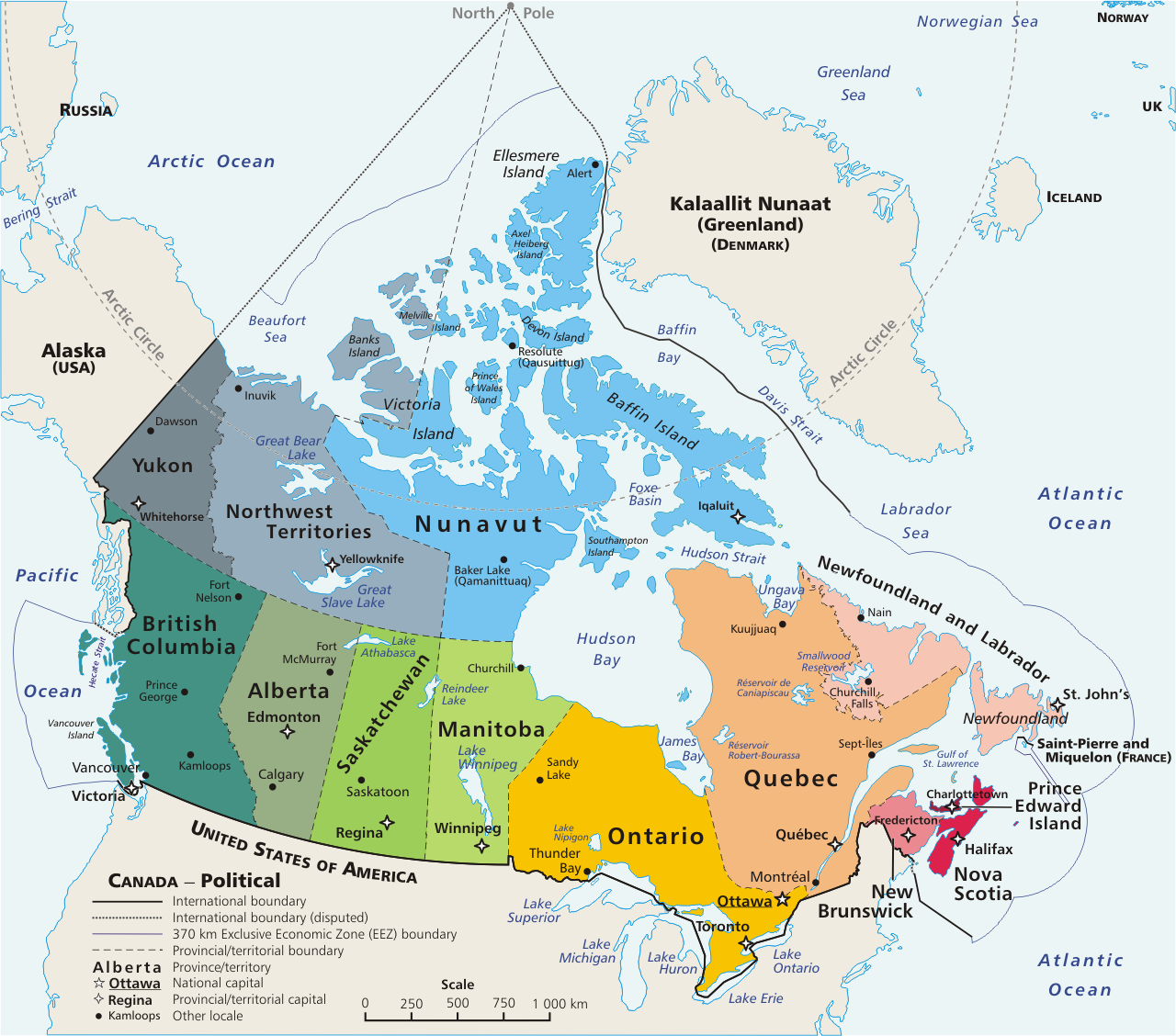
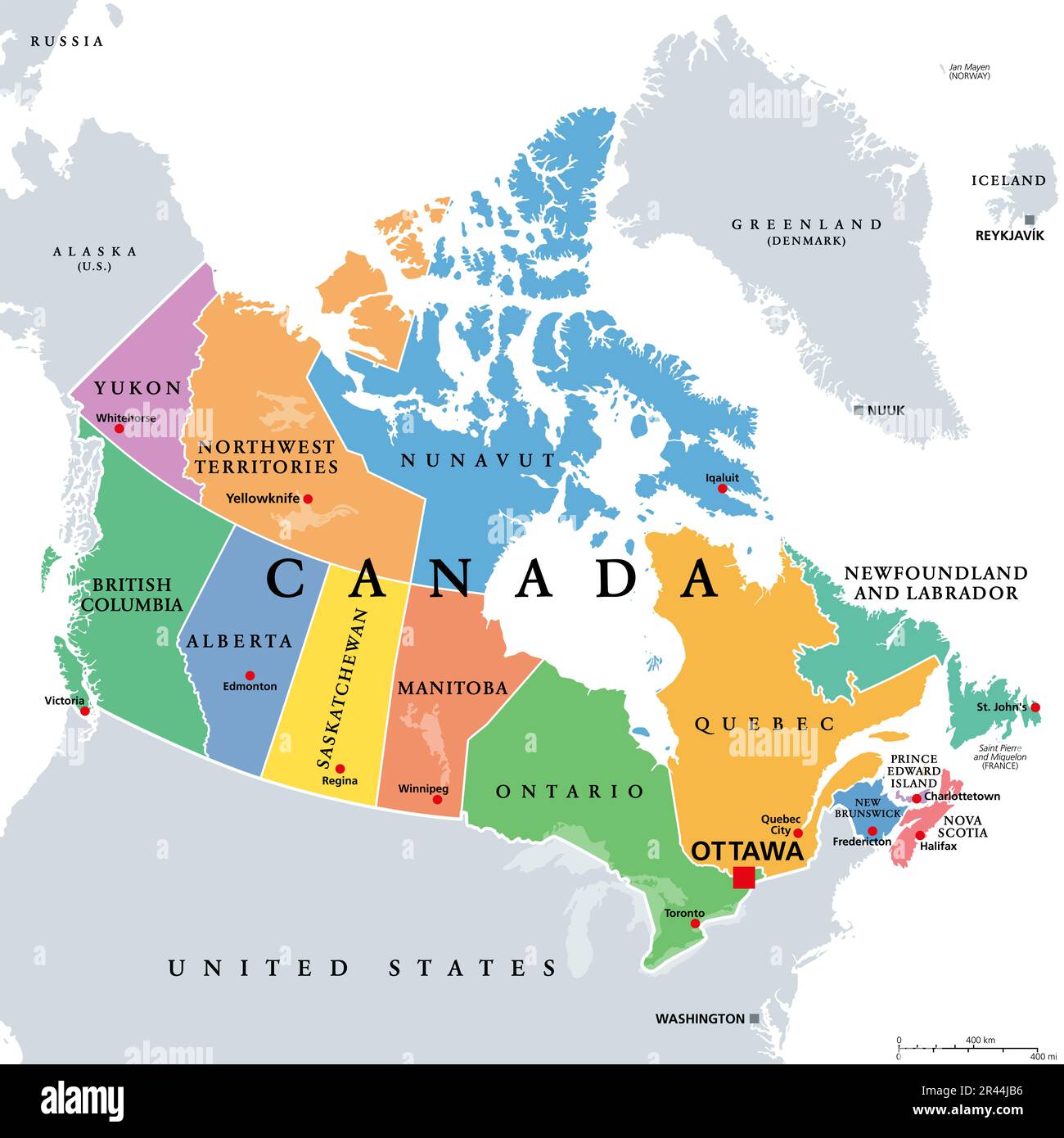
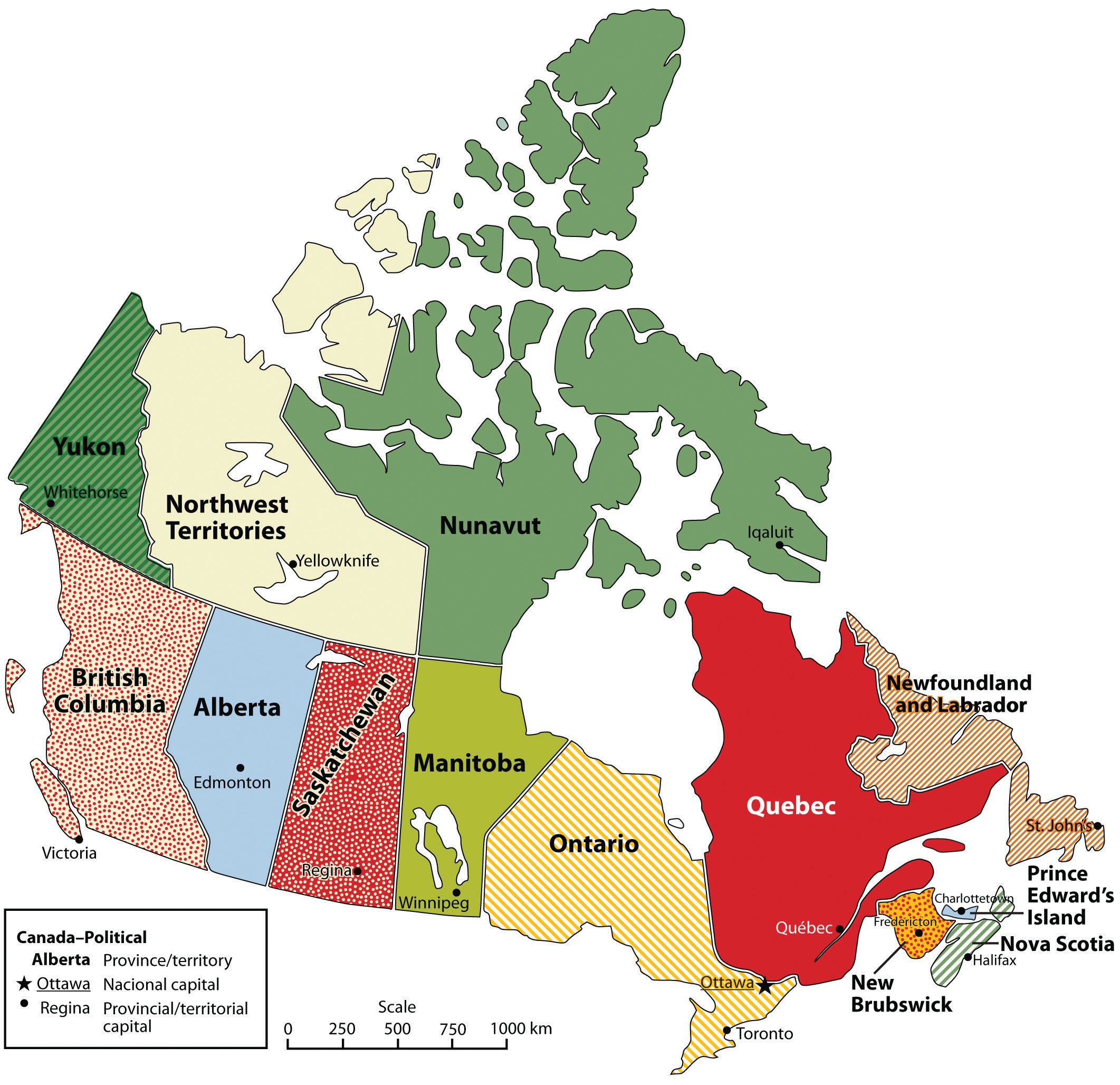
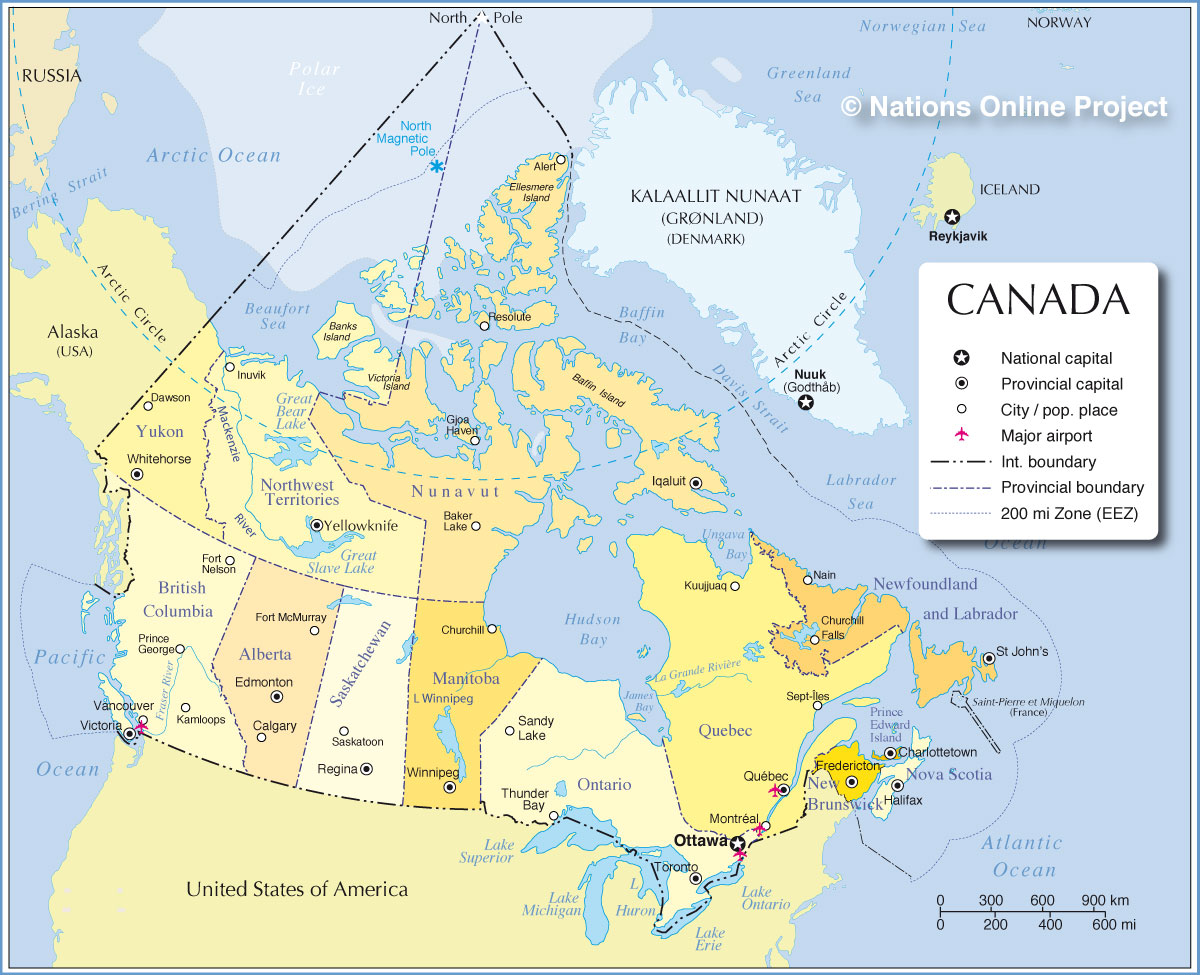
Canada, the second-largest country in the world, is geographically diverse, boasting vast stretches of wilderness, sprawling urban centers, and a coastline spanning three oceans. Its borders, both land and water, are not merely lines on a map but rather intricate threads woven into the fabric of Canadian history, culture, and identity.
A Land of Borders:
Canada shares land borders with the United States to the south and the United States territory of Alaska to the west. The Canada-United States border, the longest undefended border in the world, stretches for over 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles) and traverses a diverse array of landscapes, from the rugged mountains of the Rocky Mountains to the lush forests of the Great Lakes region. The Alaska-Canada border, though much shorter, is equally significant, tracing a path through the vast and remote wilderness of the Yukon and British Columbia.
Maritime Boundaries:
Canada’s maritime boundaries extend far beyond its land borders, defining its jurisdiction over the surrounding waters and resources. These boundaries are established through international agreements and encompass the Arctic Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific Ocean. The Arctic Ocean, in particular, is a region of increasing geopolitical importance, with Canada asserting its sovereignty over a significant portion of the Arctic waters and seabed.
The Historical Context:
Canada’s borders are not static, but rather have evolved over time, shaped by historical events, treaties, and negotiations. The border with the United States, for instance, was established through a series of treaties and agreements, beginning with the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The Alaska-Canada border was defined by the Treaty of Alaska in 1867, which transferred Alaska from Russia to the United States. The demarcation of maritime boundaries, particularly in the Arctic, continues to be a subject of ongoing discussion and negotiations.
The Importance of Borders:
Canada’s borders are crucial for a variety of reasons:
- National Security: Borders play a vital role in protecting national security by controlling the flow of people, goods, and information across international boundaries.
- Economic Prosperity: Borders facilitate trade and investment, fostering economic growth and prosperity. Canada’s strong economic ties with the United States, facilitated by their shared border, are a testament to the importance of border management for economic success.
- Environmental Stewardship: Borders help to manage and protect shared ecosystems and natural resources. Canada’s commitment to environmental conservation is evident in its efforts to collaborate with its neighbors on issues such as transboundary pollution and resource management.
- Cultural Identity: Borders define national identity and help to preserve cultural heritage. Canada’s diverse cultural landscape is shaped by the interaction of different cultures along its borders.
Benefits of a Well-Managed Border:
A well-managed border system offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: Effective border control measures help to prevent the entry of illegal goods, individuals, and threats to national security.
- Increased Trade and Investment: Streamlined border processes facilitate the movement of goods and people, boosting trade and investment opportunities.
- Improved Environmental Protection: Collaborative border management helps to protect shared natural resources and mitigate environmental risks.
- Stronger Regional Integration: Well-managed borders contribute to closer regional integration, fostering cooperation and collaboration among neighboring countries.
FAQs:
-
What are the main challenges facing Canada’s border management?
Canada faces a number of challenges in managing its borders, including:
- Transnational Organized Crime: Criminal organizations operate across borders, posing challenges to law enforcement and security agencies.
- Illegal Immigration: The flow of illegal immigrants seeking refuge in Canada poses challenges to border security and immigration management.
- Terrorism: The threat of terrorism requires heightened security measures at border crossings.
- Environmental Degradation: Transboundary pollution and resource depletion require collaborative efforts to protect shared ecosystems.
-
What are the key initiatives being undertaken by Canada to improve border management?
Canada is taking a number of steps to enhance its border management capabilities, including:
- Investing in Border Security Technologies: Canada is investing in advanced technologies such as facial recognition, biometrics, and intelligence analysis to improve border security.
- Strengthening Partnerships with International Organizations: Canada is collaborating with international organizations such as INTERPOL and the United Nations to combat transnational crime and enhance border security.
- Promoting Regional Cooperation: Canada is working with its neighbors to improve border management practices and address shared challenges.
- Developing a Comprehensive Border Strategy: Canada is developing a comprehensive border strategy that outlines its long-term goals and objectives for border management.
Tips:
- Travelers should be aware of border regulations and requirements before crossing the border. This includes obtaining necessary travel documents, such as passports and visas, and understanding customs and immigration procedures.
- Businesses should be familiar with trade regulations and procedures. This includes understanding import and export requirements, customs regulations, and trade agreements.
- Border communities should be engaged in border management issues. This includes providing input on border policies and procedures, and participating in community outreach programs.
Conclusion:
Canada’s borders are a complex and dynamic entity, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse geography, and interconnectedness with its neighbors. Their management is essential for national security, economic prosperity, environmental protection, and cultural identity. As Canada continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its borders will remain a critical element of its national strategy and global engagement.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining Canada’s Borders: A Tapestry of Geography, History, and Identity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!