Deciphering the Grid: A Guide to Understanding Longitude and Latitude Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Grid: A Guide to Understanding Longitude and Latitude Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Grid: A Guide to Understanding Longitude and Latitude Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Grid: A Guide to Understanding Longitude and Latitude Maps

Longitude and latitude, often referred to as "geographic coordinates," form the backbone of our understanding of the Earth’s surface. These invisible lines, drawn across the globe, provide a precise system for locating any point on the planet. Mastering the art of reading longitude and latitude maps unlocks a world of possibilities, enabling navigation, geographic analysis, and a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between locations.
The Fundamentals: Lines of Longitude and Latitude
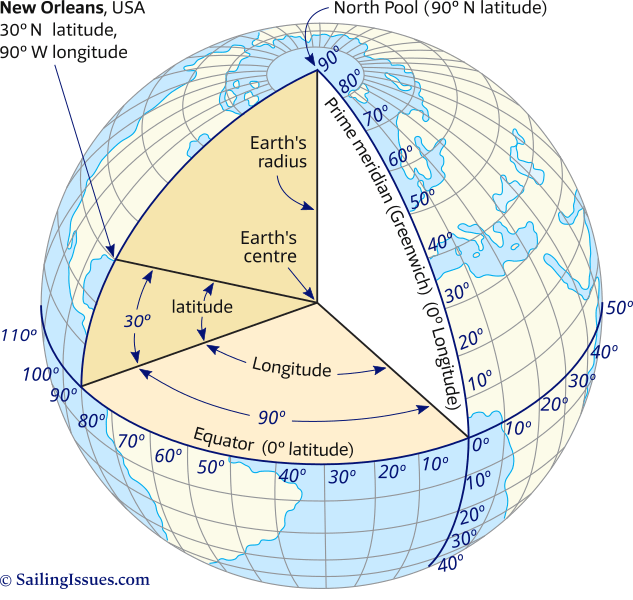
Imagine the Earth as a perfect sphere. Longitude lines, also known as meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, resembling slices of an orange. Each meridian represents a specific angular distance east or west of the prime meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England. The prime meridian serves as the zero-degree longitude, and lines to its east are assigned positive values, while lines to its west are assigned negative values.
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the Earth, like circles drawn on a globe. They are defined by their angular distance north or south of the equator, which is the imaginary line that circles the Earth at zero degrees latitude. Latitude lines are numbered from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
Reading the Grid: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
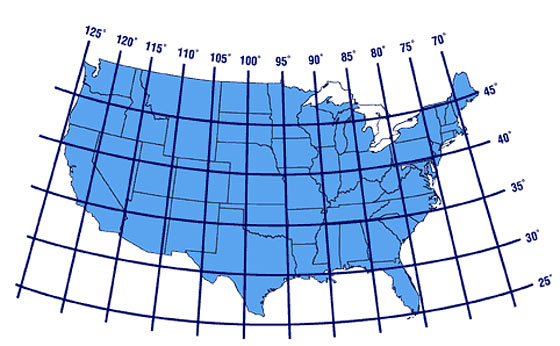
Identify the Grid: Longitude and latitude maps feature a grid system consisting of horizontal and vertical lines. The horizontal lines represent latitude, while the vertical lines represent longitude.
-
Locate the Prime Meridian and Equator: The prime meridian is usually marked as a thick vertical line, often with the label "0°" or "Greenwich Meridian." The equator is represented by a thick horizontal line, labeled "0°".
-
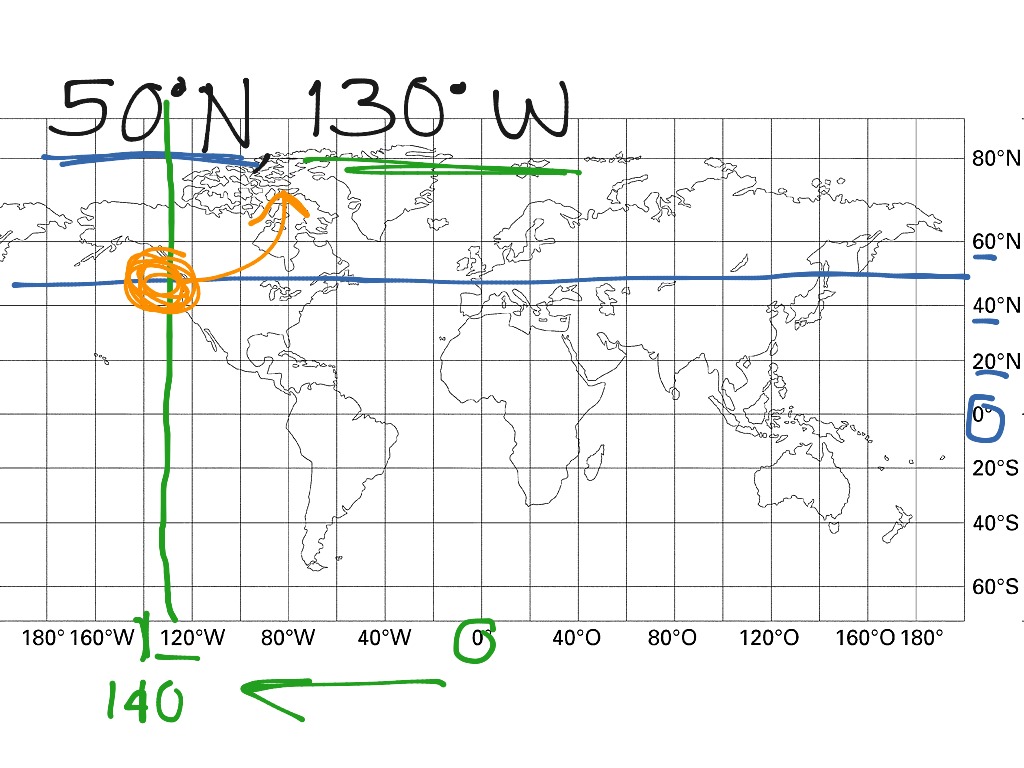
Read Latitude: Begin by locating the horizontal line that corresponds to the latitude you are seeking. Latitude values increase as you move north or south from the equator. For instance, 30° North is located above the equator, while 30° South is located below the equator.
-
Read Longitude: Next, find the vertical line representing the desired longitude. Longitude values increase as you move east from the prime meridian. For example, 10° East is located east of the prime meridian, while 10° West is located west of the prime meridian.
-
The Intersection Point: The intersection point of the latitude and longitude lines indicates the exact location on the map.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Map Scales and Projections
While the grid system provides a fundamental framework, it is crucial to understand the map’s scale and projection. The scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the Earth’s surface. A larger scale map represents a smaller area in greater detail, while a smaller scale map covers a larger area with less detail.
Map projections are mathematical methods used to represent the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map. Each projection distorts the Earth’s shape in different ways, affecting distances, shapes, and areas. Understanding the specific projection used for a particular map is essential for accurate interpretation.
Applications of Longitude and Latitude: A World of Possibilities
The ability to read longitude and latitude maps has far-reaching applications:
-
Navigation: Navigational systems, including GPS devices and maritime charts, rely heavily on longitude and latitude coordinates.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software uses geographic coordinates to analyze and visualize spatial data, enabling applications in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
-
Scientific Research: Longitude and latitude are crucial for mapping and analyzing data in fields like meteorology, geology, and oceanography.
-
Travel and Exploration: Understanding geographic coordinates allows travelers to pinpoint locations, plan routes, and explore new destinations.
FAQs: Clarifying the Concepts
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth, measuring distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically from pole to pole, measuring distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Q: How can I convert decimal degrees to degrees, minutes, and seconds?
A: Decimal degrees can be converted to degrees, minutes, and seconds using a simple formula:
- Degrees: The whole number part of the decimal degree represents the degrees.
- Minutes: Multiply the decimal portion of the degree by 60 to get the minutes.
- Seconds: Multiply the decimal portion of the minutes by 60 to get the seconds.
Q: Are there any online tools that can help me understand longitude and latitude?
A: Numerous online resources, including Google Maps, Google Earth, and interactive map applications, provide tools for visualizing and exploring longitude and latitude coordinates.
Tips for Mastering Longitude and Latitude Maps
-
Practice: Practice reading longitude and latitude maps using various online resources or physical maps.
-
Explore Different Projections: Become familiar with different map projections and their unique distortions.
-
Utilize Online Tools: Explore interactive map tools that allow you to zoom in and out, measure distances, and identify specific coordinates.
-
Connect with Real-World Applications: Relate your understanding of longitude and latitude to real-world situations, such as planning a trip or interpreting weather maps.
Conclusion
The ability to read longitude and latitude maps empowers us to navigate the world with precision, analyze geographic data with sophistication, and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between locations. By mastering the fundamental concepts and practicing with various resources, we can unlock the vast potential of geographic coordinates and explore the world with newfound understanding and confidence.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Grid: A Guide to Understanding Longitude and Latitude Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!