A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance
- 3.1 Mapping the Frozen World: A Journey Through Time and Space
- 3.2 The Evolution of Glacier Mapping: From Traditional Surveys to Modern Technology
- 3.3 Data Integration and Analysis: A Multidisciplinary Approach
- 3.4 Unveiling the Secrets of the Frozen World: FAQs on Glacier Maps
- 3.5 Navigating the Frozen Landscape: Tips for Using Glacier Maps
- 3.6 A World of Ice: Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance
Glaciers, vast rivers of ice sculpted by time and climate, are critical components of the Earth’s cryosphere, playing a vital role in regulating global climate and water cycles. These frozen landscapes hold a wealth of information about past environmental conditions and provide insights into future climate change scenarios. To understand the dynamics of glaciers and their impact on the planet, scientists rely on detailed and comprehensive glacier maps.
Mapping the Frozen World: A Journey Through Time and Space
Glacier maps are visual representations of the distribution, extent, and characteristics of glaciers across the globe. They serve as invaluable tools for researchers, policymakers, and resource managers, providing a critical foundation for understanding the following:
1. Glacier Inventory and Dynamics: Glacier maps offer a comprehensive inventory of glacier locations, size, and shape, providing a baseline for monitoring changes in glacier extent and volume over time. These maps reveal the intricate patterns of glacier retreat or advance, offering valuable insights into the interplay between climate change and glacial dynamics.
2. Water Resource Management: Glaciers are significant sources of freshwater, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Glacier maps help identify potential water sources, assess their availability, and guide sustainable water resource management strategies. This information is crucial for ensuring water security for communities reliant on glacial meltwater, especially in areas facing increasing water scarcity.
3. Hazard Assessment and Mitigation: Glaciers can pose significant hazards, including glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) and avalanches. Glacier maps help identify areas at risk from these hazards, facilitating the development of early warning systems and mitigation measures to protect human life and infrastructure.
4. Climate Change Research: Glacier maps provide a historical record of glacial changes, serving as a powerful tool for understanding the impacts of climate change on the cryosphere. By comparing maps from different time periods, scientists can quantify the rate of glacier retreat and assess the potential consequences of continued warming on global water resources and sea level rise.
The Evolution of Glacier Mapping: From Traditional Surveys to Modern Technology
The creation of glacier maps has evolved significantly over time, reflecting advancements in technology and data acquisition methods. Traditional glacier mapping relied on aerial photography, ground surveys, and manual interpretation. While providing valuable information, these methods were time-consuming, labor-intensive, and often limited by weather conditions.
The advent of remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), revolutionized glacier mapping. These technologies offer high-resolution, multi-spectral data, enabling the creation of detailed and accurate glacier maps over vast areas.
Satellite imagery provides a synoptic view of glaciers, capturing large-scale changes in glacier extent and morphology. LiDAR utilizes laser pulses to measure distances, generating 3D models of glacial terrain, revealing detailed information about glacier thickness, surface elevation, and ice flow patterns.
Data Integration and Analysis: A Multidisciplinary Approach
Glacier maps are not merely static representations of ice; they are dynamic tools that require ongoing analysis and integration with other datasets. Combining glacier maps with meteorological data, climate models, and hydrological information allows researchers to:
- Predict future glacier changes: By incorporating climate change projections into glacier models, scientists can simulate future glacier retreat scenarios, assessing the potential impacts on water resources, sea level rise, and ecosystem stability.
- Develop adaptation strategies: Understanding future glacier changes enables policymakers and resource managers to develop adaptation strategies for mitigating the negative impacts of glacier retreat, such as water scarcity and increased flood risk.
- Assess the vulnerability of communities: Glacier maps can be used to identify communities most vulnerable to the impacts of glacier changes, allowing for targeted interventions and support programs.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Frozen World: FAQs on Glacier Maps
1. What are the different types of glacier maps?
Glacier maps can be classified based on their scale, purpose, and the data used for their creation.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover large geographical areas, providing a general overview of glacier distribution and extent.
- Large-scale maps: These maps focus on specific glaciers or regions, providing detailed information about glacier morphology, ice thickness, and flow patterns.
- Thematic maps: These maps highlight specific aspects of glaciers, such as glacier elevation, ice volume, or the presence of glacial lakes.
2. How are glacier maps used in climate change research?
Glacier maps are essential for monitoring and understanding the impacts of climate change on the cryosphere. By comparing glacier maps from different time periods, scientists can quantify the rate of glacier retreat, assess the contribution of glaciers to sea level rise, and evaluate the effectiveness of climate change mitigation strategies.
3. How are glacier maps used in water resource management?
Glaciers are a significant source of freshwater, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Glacier maps help identify potential water sources, estimate their availability, and guide sustainable water management practices. This information is crucial for ensuring water security for communities reliant on glacial meltwater.
4. What are the challenges associated with glacier mapping?
Glacier mapping presents several challenges, including:
- Remote and inaccessible locations: Many glaciers are located in remote and mountainous regions, making access difficult and posing safety risks for field surveys.
- Rapidly changing conditions: Glaciers are constantly changing, making it challenging to maintain accurate and up-to-date maps.
- Data availability and processing: Access to high-quality data, such as satellite imagery and LiDAR scans, is crucial for creating detailed and accurate glacier maps.
Navigating the Frozen Landscape: Tips for Using Glacier Maps
1. Understanding the Map Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map legend, which explains the symbols and colors used to represent different glacier features, such as ice thickness, elevation, and flow direction.
2. Cross-referencing with Other Data: Combine glacier maps with other relevant data sources, such as meteorological data, climate models, and hydrological information, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of glacier dynamics and their impacts.
3. Recognizing Map Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of glacier maps, such as their scale, data resolution, and potential inaccuracies due to changing glacier conditions.
4. Consulting Expert Resources: For in-depth analysis and interpretation of glacier maps, consult with experts in glaciology, remote sensing, and climate change research.
A World of Ice: Conclusion
Glacier maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding the distribution, dynamics, and significance of glaciers in the Earth’s cryosphere. They provide a critical foundation for monitoring glacial changes, assessing their impacts on water resources and climate, and developing adaptation strategies for mitigating the consequences of glacier retreat. By leveraging advancements in remote sensing technologies and data analysis techniques, glacier maps continue to evolve, providing a more comprehensive and insightful view of the frozen world and its vital role in the global climate system.

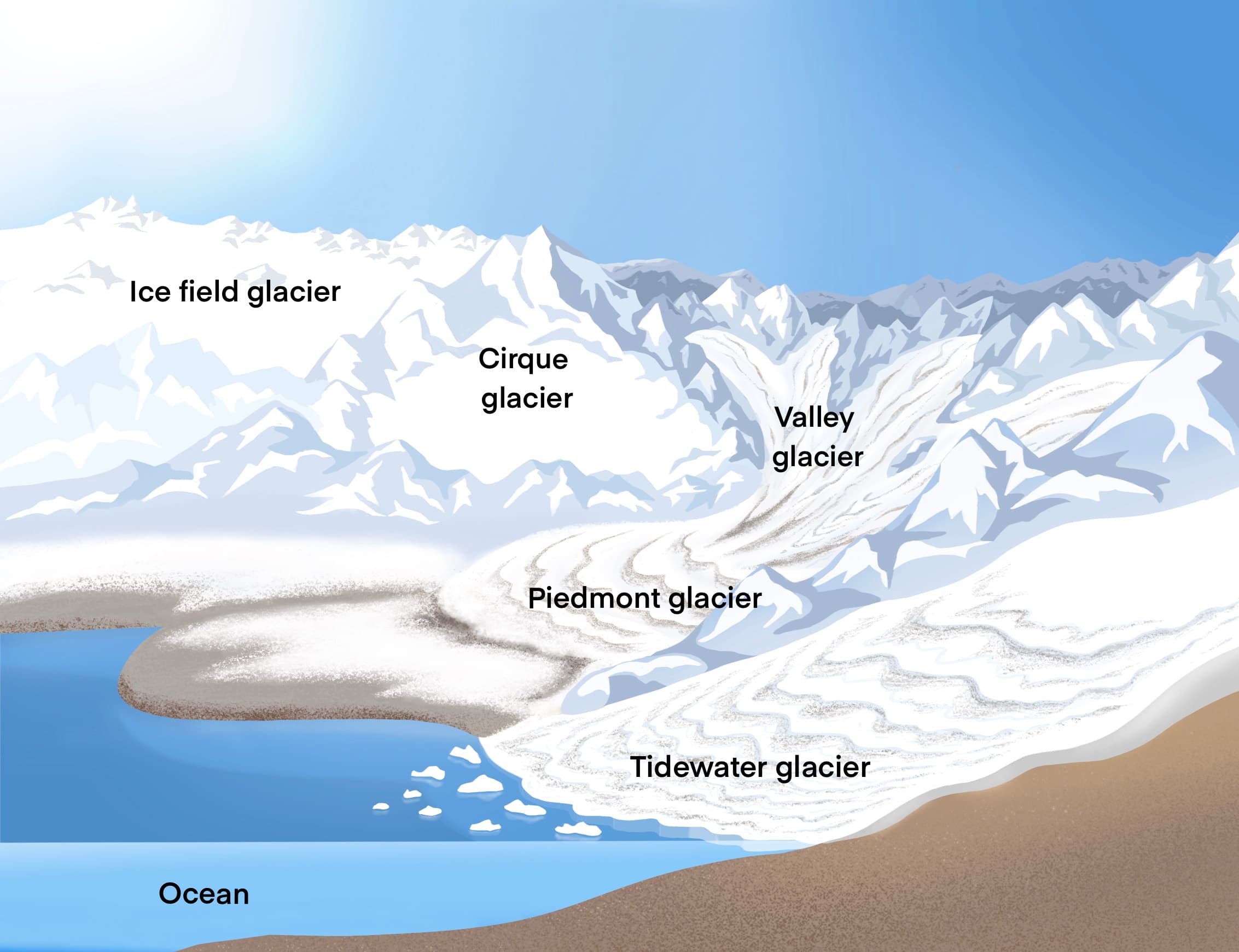

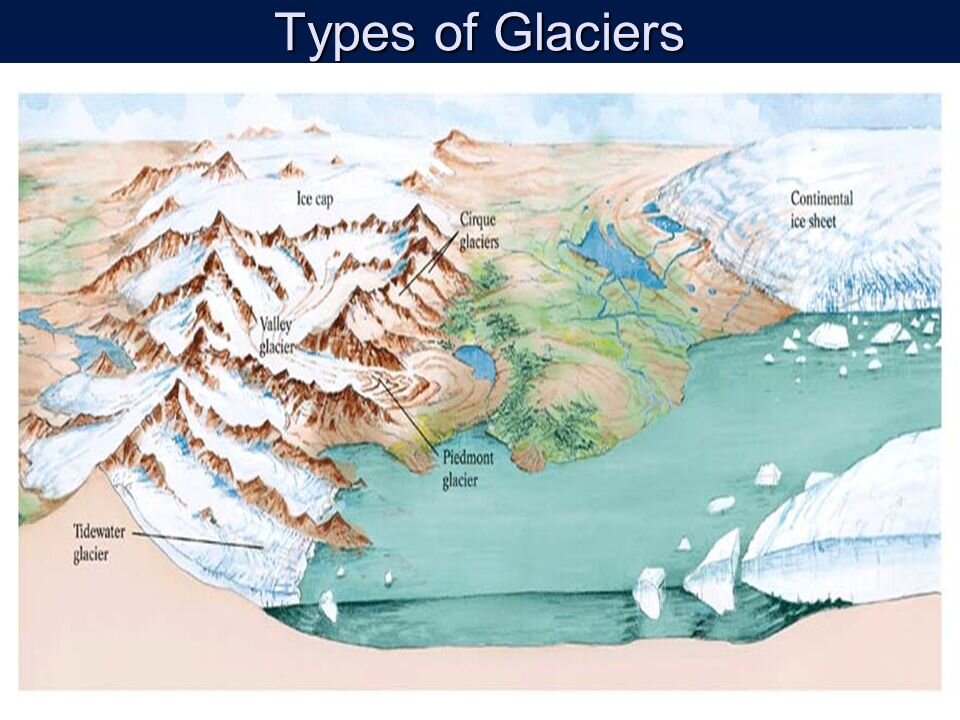
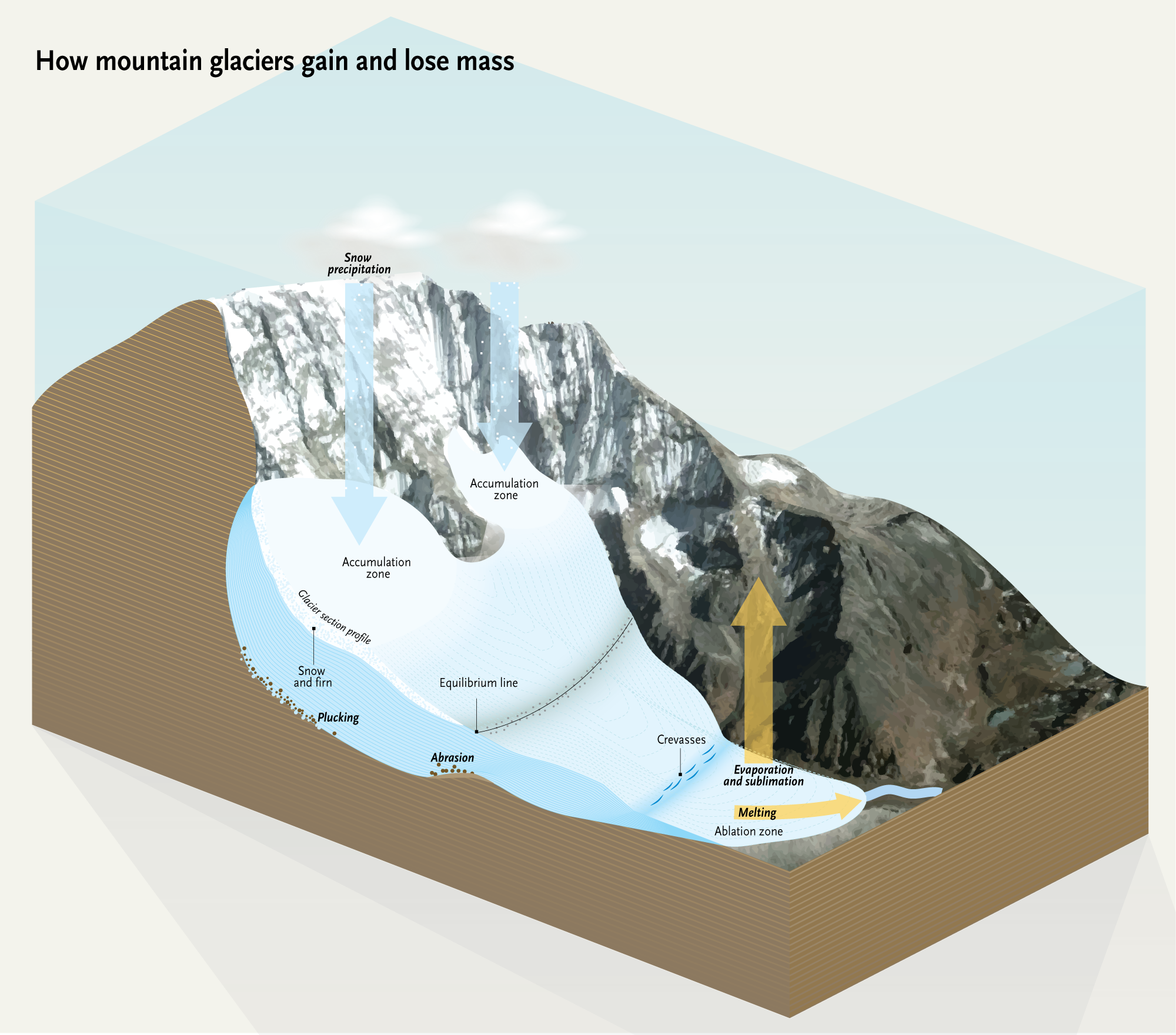


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World of Ice: Understanding Glacier Maps and Their Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!