A Tapestry of Indigenous Cultures: Exploring the Indian Tribes of California
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Indigenous Cultures: Exploring the Indian Tribes of California
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Indigenous Cultures: Exploring the Indian Tribes of California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Indigenous Cultures: Exploring the Indian Tribes of California

California, renowned for its diverse landscape and vibrant culture, is also home to a rich tapestry of indigenous peoples. The state’s history is deeply intertwined with the stories, traditions, and resilience of its Native American communities. Understanding the distribution and cultural diversity of these tribes is crucial for appreciating the state’s past, present, and future. This article delves into the intricate map of California’s Indian tribes, highlighting their significance and contributions to the state’s unique identity.
A Diverse Landscape of Tribes:
California boasts a remarkable diversity of Native American cultures, with over 100 distinct tribes recognized by the federal government. These tribes, representing numerous language families and cultural traditions, once inhabited every corner of the state, from the rugged Sierra Nevada mountains to the vast desert regions and the Pacific coastline. This intricate mosaic of indigenous groups reflects the varied geographical and ecological features of California, each tribe adapting to their unique environment and developing distinctive cultural practices.
Navigating the Map:
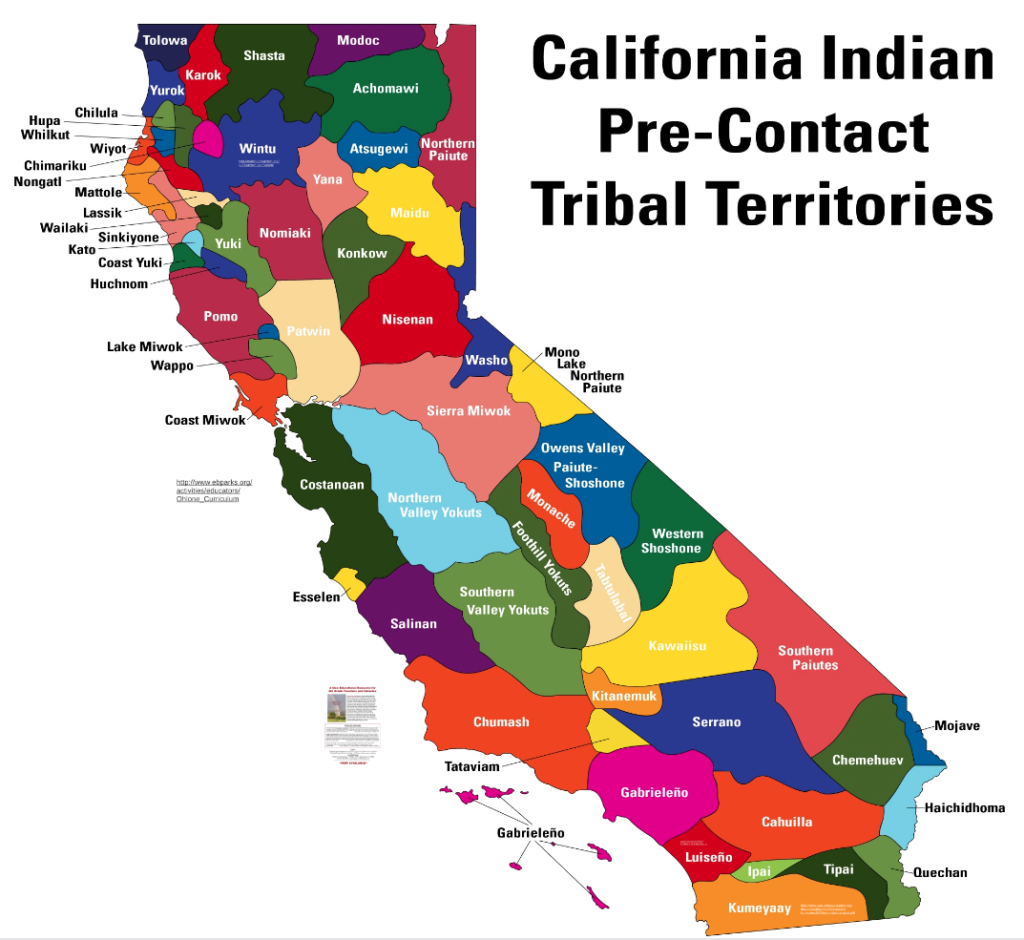
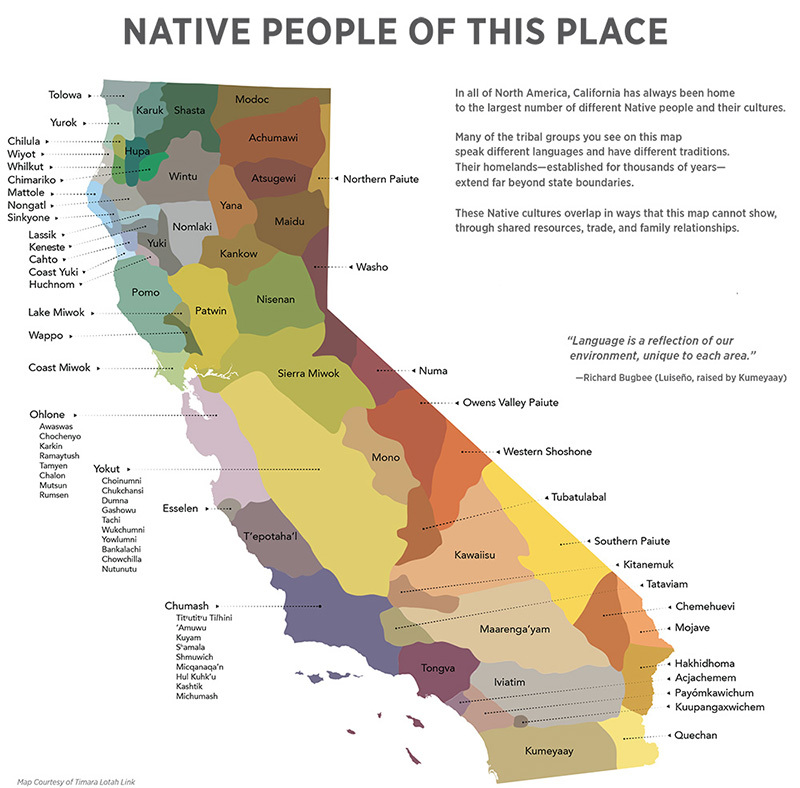
The "Indian Tribes of California" map serves as a visual guide to understanding the distribution of these communities across the state. It reveals the intricate web of tribal territories, highlighting their geographic proximity and potential historical interactions. While the map primarily showcases the locations of federally recognized tribes, it also serves as a reminder of the numerous unrecognized tribes who have endured historical injustices and continue to fight for recognition and self-determination.
Understanding the Map’s Importance:
The map’s significance lies in its ability to:
- Visualize the historical presence of indigenous communities: It offers a powerful reminder of the deep roots of Native American cultures in California, dispelling the misconception that the state was unpopulated before European arrival.
- Acknowledge the diversity of tribal cultures: The map illustrates the vast range of languages, customs, and traditions that existed within California’s indigenous population, highlighting the richness and complexity of Native American culture.
- Promote understanding and respect: By showcasing the geographic distribution of tribes, the map encourages a deeper appreciation for the unique history and contributions of each community.
- Foster a sense of place: The map connects specific locations with the cultural heritage of the indigenous peoples who lived there, enriching our understanding of the state’s landscape and its cultural significance.
- Inform policy and decision-making: The map serves as a valuable resource for policymakers, educators, and researchers, providing a foundational understanding of the historical and contemporary needs of California’s indigenous communities.
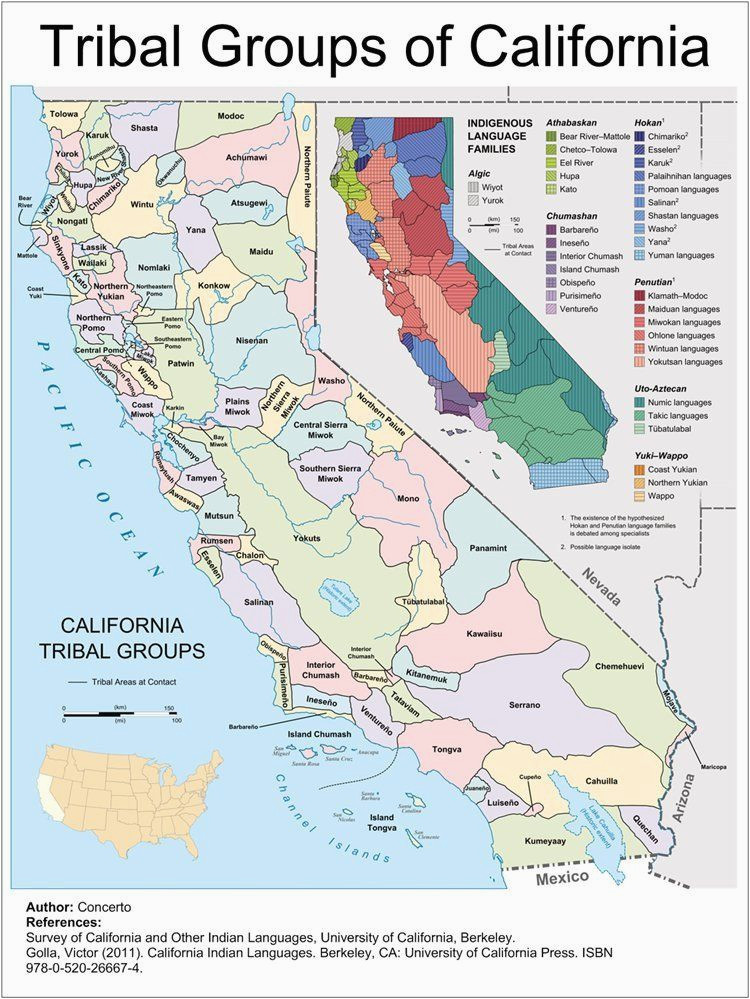
Cultural Diversity on the Map:
The map reflects the diverse linguistic and cultural landscape of California’s indigenous population. Some of the prominent language families represented include:
- Penutian: Tribes belonging to this family, including the Miwok, Maidu, and Wintun, were primarily located in the central and northern parts of the state.
- Hokan: Tribes like the Chumash, Yuman, and Pomo, belonging to the Hokan language family, inhabited coastal regions and inland valleys.
- Uto-Aztecan: The Uto-Aztecan language family encompassed tribes like the Shoshone, Mono, and Paiute, primarily residing in the eastern Sierra Nevada and the Mojave Desert.
Each of these language families represents a distinct cultural tradition, with unique beliefs, rituals, art forms, and social structures. The map serves as a reminder of the rich tapestry of cultures that once flourished in California, each contributing to the state’s cultural heritage.
Challenges and Resilience:
The map also reflects the historical challenges faced by California’s indigenous communities. European colonization, disease, and forced assimilation policies resulted in significant population decline and cultural disruption. Many tribes lost their traditional lands, languages, and cultural practices. Despite these hardships, Native American communities in California have demonstrated remarkable resilience, actively working to preserve their cultures and traditions while advocating for self-determination and sovereignty.
FAQs about Indian Tribes of California Map:
1. What is the purpose of the Indian Tribes of California map?
The map provides a visual representation of the distribution of federally recognized tribes across California, showcasing their geographic locations and highlighting the diversity of indigenous cultures within the state.
2. How many tribes are represented on the map?
The map currently features over 100 federally recognized tribes in California, though it is important to note that there are numerous unrecognized tribes who are actively pursuing recognition.
3. What information can I find on the map?
The map typically includes tribal names, locations, and sometimes additional information such as language family, historical territory, and current reservation status.
4. How can I access the map?
The map can be found online through various resources, including websites of state and federal agencies, tribal websites, and academic databases.
5. What are some of the limitations of the map?
While the map offers valuable information, it should be noted that it does not fully encompass the complex history and cultural diversity of California’s indigenous communities. It may not reflect the presence of unrecognized tribes, the historical changes in tribal territories, or the ongoing efforts of tribes to reclaim their sovereignty.
Tips for Using the Map:
- Combine the map with other resources: Utilize online databases, historical accounts, and tribal websites to gain a deeper understanding of the cultures and histories represented on the map.
- Focus on specific regions: Explore the map to identify tribes located within particular geographic areas of interest, such as the Sierra Nevada or the coastal regions.
- Consider the historical context: Understand that tribal territories and boundaries have shifted over time due to colonization and other historical events.
- Engage with tribal communities: Reach out to tribal governments or organizations for information and perspectives on their cultures, histories, and current issues.
Conclusion:
The "Indian Tribes of California" map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the rich cultural heritage of the state’s indigenous communities. It provides a visual representation of their historical presence and ongoing resilience, highlighting the diversity of languages, traditions, and perspectives that have shaped California’s identity. By engaging with the map and its accompanying resources, we can deepen our appreciation for the contributions of Native Americans to the state’s history, culture, and future. The map serves as a reminder of the importance of acknowledging and respecting the rights and sovereignty of indigenous peoples, ensuring that their voices and perspectives are heard and valued in the ongoing narrative of California.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Indigenous Cultures: Exploring the Indian Tribes of California. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!