A Journey Across Canada’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the Weather Map
Related Articles: A Journey Across Canada’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the Weather Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across Canada’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the Weather Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across Canada’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the Weather Map
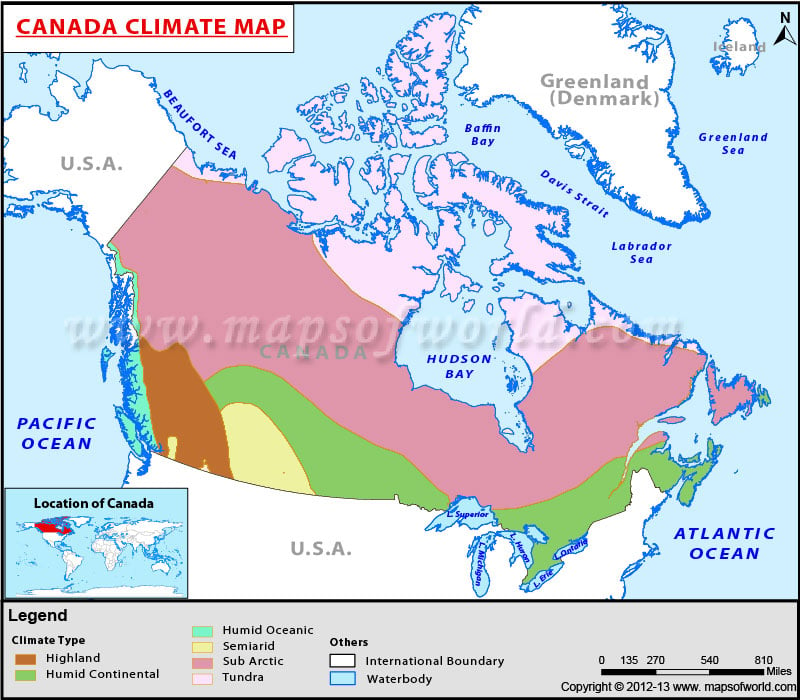
Canada, a vast expanse of land stretching from the Arctic to the Pacific, is renowned for its breathtaking landscapes and diverse ecosystems. This diversity is reflected in its weather patterns, which vary significantly across the country. Understanding the intricacies of Canada’s weather is crucial for planning travel, engaging in outdoor activities, and appreciating the delicate balance of its natural environment.
The Influence of Latitude and Geography
Canada’s vast size and geographic position play a pivotal role in shaping its weather. The country’s northern latitude exposes it to long periods of darkness and cold during winter, while the summer months see extended daylight hours and warmer temperatures. However, the influence of latitude is not uniform.
Coastal vs. Inland Climates
The presence of large bodies of water, like the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and Great Lakes, has a profound impact on regional weather patterns. Coastal areas experience milder temperatures compared to inland regions due to the moderating influence of the ocean. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced on the west coast, where the Pacific Ocean’s currents create a maritime climate characterized by cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers.
In contrast, inland regions, especially those far from large bodies of water, experience more extreme temperature fluctuations. These areas are prone to cold, snowy winters and hot, humid summers, as they are less influenced by the moderating effects of the ocean.
The Role of Mountain Ranges
Mountain ranges, like the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains, act as barriers, influencing the movement of air masses and precipitation patterns. The Rockies, for example, create a rain shadow effect, causing the western slopes to receive abundant rainfall, while the eastern slopes are relatively drier.
Key Weather Patterns
Canada’s weather is influenced by several key weather patterns:
- Jet Stream: This high-altitude wind current plays a crucial role in determining temperature and precipitation patterns. The jet stream’s position can shift, leading to variations in weather across the country.
- Arctic Outbreaks: Cold air masses originating from the Arctic region can plunge into Canada, bringing frigid temperatures, snowstorms, and strong winds.
- Pacific Storms: Storms originating in the Pacific Ocean can bring heavy rain and snow to western Canada, particularly during the winter months.
- Lake-Effect Snow: During the winter, cold air passing over the Great Lakes can pick up moisture, leading to heavy snowfall downwind.
Regional Weather Variations
Canada’s diverse weather patterns are reflected in its distinct regional climates:
- Atlantic Canada: This region experiences a humid continental climate, characterized by warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. The maritime influence results in frequent rain and fog.
- Quebec: The province of Quebec has a humid continental climate with cold, snowy winters and warm, humid summers. The St. Lawrence River moderates temperatures in some areas.
- Ontario: Ontario also has a humid continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. The Great Lakes have a significant impact on local weather patterns.
- Prairies: The Canadian Prairies are characterized by a semi-arid climate with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters.
- British Columbia: British Columbia experiences a variety of climates, ranging from the mild, wet climate of the coast to the dry, continental climate of the interior.
- Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut: These northern territories experience a polar climate with extremely cold winters and short, cool summers.
Understanding Canada’s Weather Map
To navigate Canada’s diverse weather patterns, it is essential to consult weather maps and forecasts. These maps provide valuable information on temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other weather conditions.
Key Elements of a Canadian Weather Map:
- Temperature: The map typically displays temperature readings in Celsius or Fahrenheit, indicating the current or forecasted temperature across the country.
- Precipitation: Symbols or colors represent different types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, or freezing rain.
- Wind: Arrows indicate wind direction and speed.
- Weather Fronts: Lines on the map represent weather fronts, which are boundaries between different air masses.
- Warnings and Advisories: The map may also display warnings and advisories for severe weather events, such as thunderstorms, tornadoes, or blizzards.
Benefits of Understanding Canada’s Weather
Understanding Canada’s weather patterns offers numerous benefits:
- Travel Planning: Weather forecasts help travelers choose the best time to visit different regions and pack accordingly.
- Outdoor Activities: Knowledge of weather conditions is essential for outdoor enthusiasts, from hikers and skiers to campers and boaters.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather forecasts to make decisions about planting, harvesting, and protecting crops.
- Infrastructure: Understanding weather patterns helps engineers and planners design infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events.
- Public Safety: Weather forecasts are crucial for emergency preparedness and response, helping to minimize the impact of severe weather events.
FAQs about Canada’s Weather
Q: What is the best time to visit Canada?
A: The best time to visit Canada depends on your interests. For warm weather and outdoor activities, summer is ideal. For skiing and winter sports, winter is the best time to visit.
Q: What are the most common weather hazards in Canada?
A: Canada experiences a variety of weather hazards, including blizzards, tornadoes, floods, and heat waves.
Q: How does climate change affect Canada’s weather?
A: Climate change is leading to more extreme weather events in Canada, including more frequent and intense heat waves, droughts, and floods.
Q: What are some tips for staying safe during extreme weather events in Canada?
A: Stay informed about weather forecasts and warnings. Have an emergency kit prepared. Be aware of the risks associated with extreme weather events and take necessary precautions.
Conclusion
Canada’s vast geography and diverse climates create a complex and fascinating weather system. Understanding the factors that influence weather patterns across the country is essential for travel planning, outdoor activities, and appreciating the delicate balance of Canada’s natural environment. By consulting weather maps and forecasts, staying informed about weather hazards, and taking necessary precautions, individuals can navigate Canada’s diverse weather landscape and enjoy all that this beautiful country has to offer.


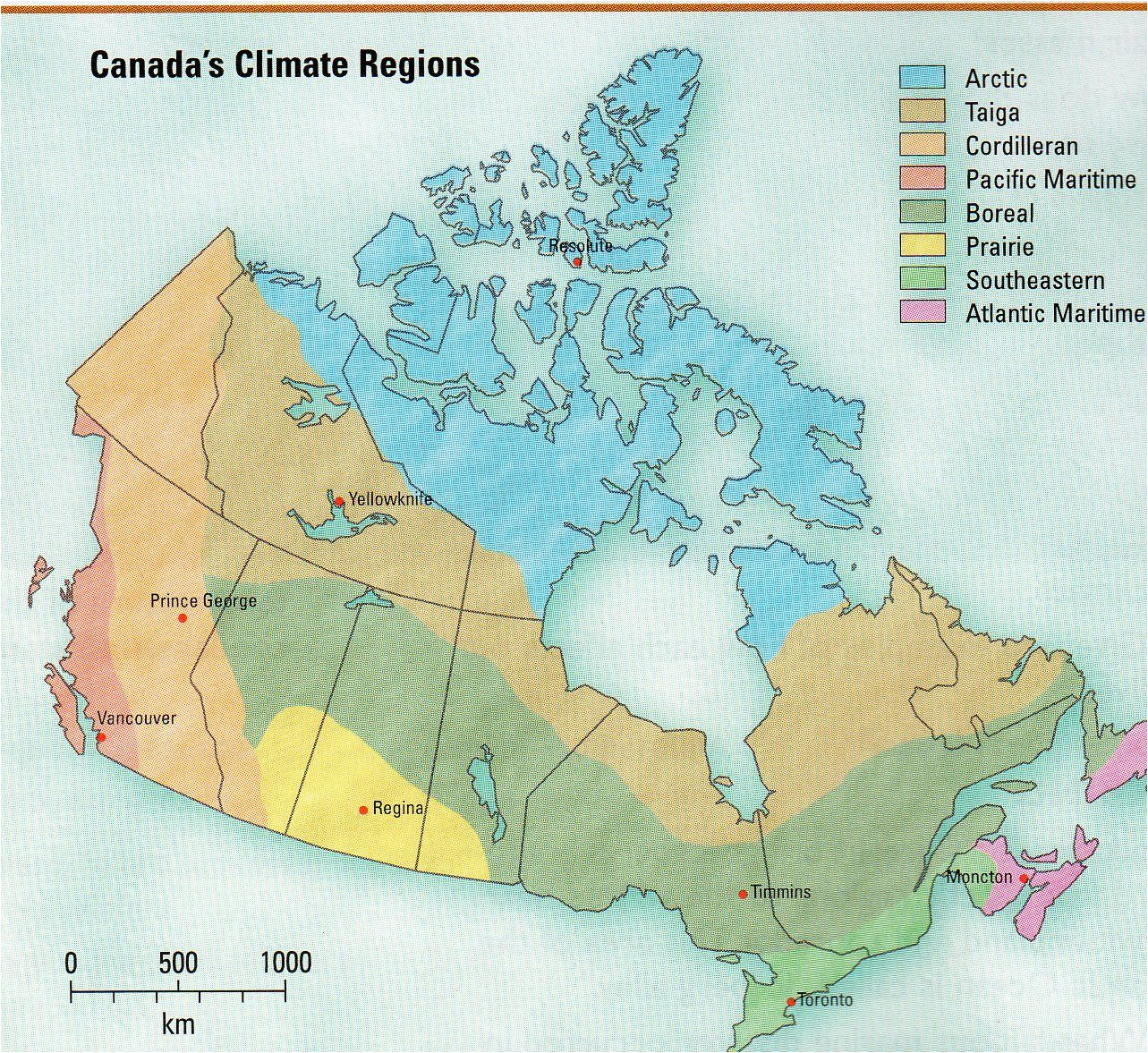

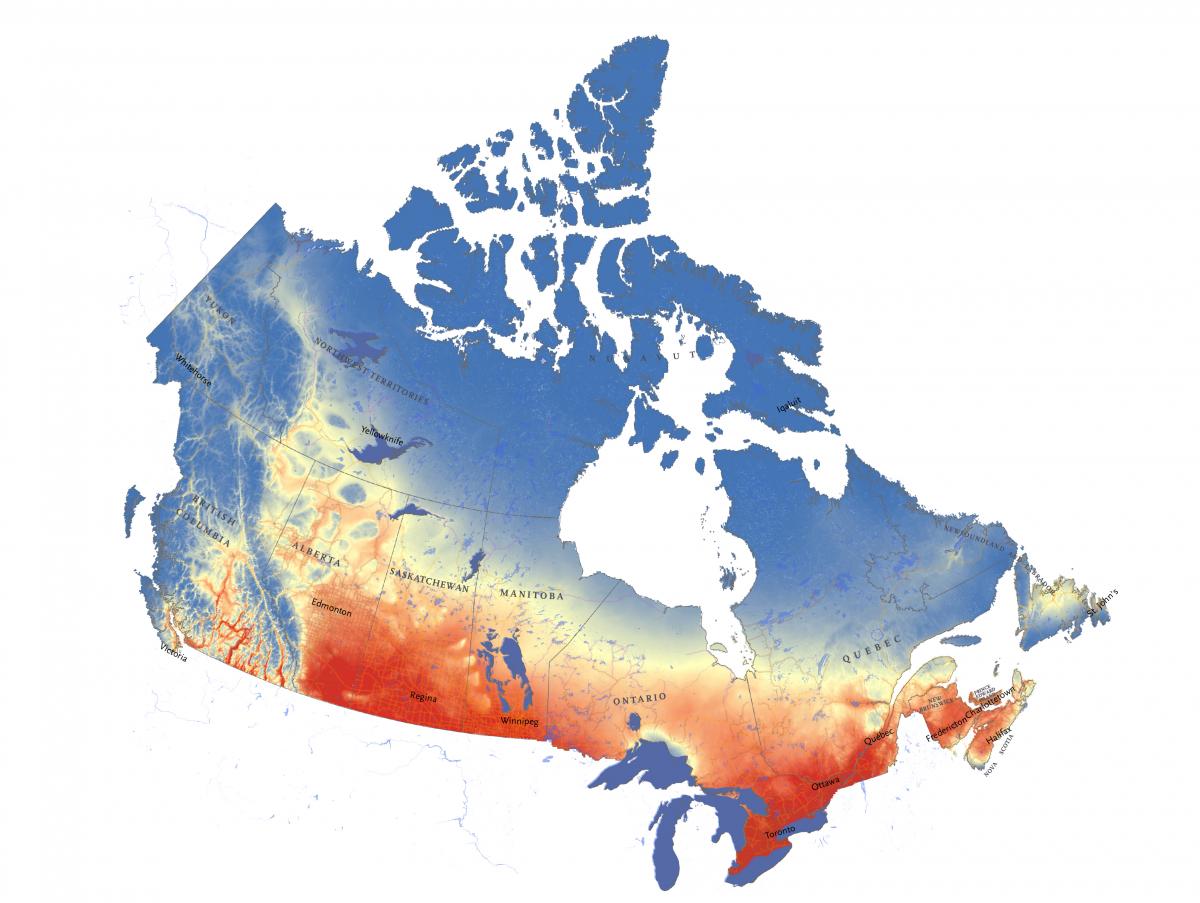



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across Canada’s Diverse Climates: Understanding the Weather Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!